A route through which electric current flows is known as an electric circuit. An electric circuit can also be a loop if it is a closed path (both ends are connected). Because of the closed circuit, electric current can flow freely. An open circuit is one in which the flow of electrons is interrupted because the circuit is broken. An open circuit does not allow electric current to flow.
In 1800, Alessandro Volta created the first electric circuit. Volta discovered that he could create a continuous flow of electricity by attaching bowls of salt solution with metal strips. Later, he constructed his voltaic pile out of alternating copper, zinc, and cardboard discs soaked in a salt solution (an early battery). He was capable of making the electric current flow across the circuit by connecting a wire from top to bottom. The first practical implementation of electric current was electrolysis.
A collection of conducting components built to transport electric current for a specific purpose is known as an electric circuit. This route is powered by a battery and built with electrical cables. The point at which electrons start to flow is called the source, and the point at which electrons leave the electrical circuit is called the return.
Basic components of an electric circuit
- Cell: The term “cell” refers to a device that is used to supply electric current.
- Load: It’s a resistor as a load. It’s essentially a light bulb that glows when the circuit is activated.
- Conductors: Copper wires with no insulation are used as conductors. The wire carries current from the power source to the load and from the load to the power source on one end and from the power source on the other.
- Switch: A switch is a component of a circuit that regulates the flow of current through it. Its purpose is to open or close a circuit.
Types of electric circuit
Electric circuits are divided into two categories.
- Series circuit: There will be only one path for electrons to flow in a series circuit. At a particular time, the entire circuit is either closed or open. The major disadvantage of a series circuit is that there is no current flow in the circuit in the event of a circuit break because the entire circuit is open. If several light bulbs are attached in a series circuit, for example, if one light bulb fails, the others will also fail.
- Parallel circuit: Various parts of the circuit are connected across different branches in a parallel type of electric circuit. As a result, electron flow occurs in multiple stages. If a circuit break occurs in one path, electric current continues to flow in other paths. Parallel circuits are used in household appliance wiring, so if one light bulb goes out, the other will continue to work.
Common symbols used in electric circuit diagrams
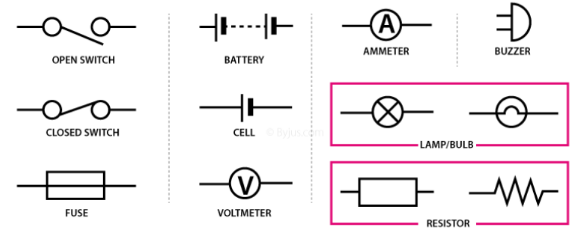
Parts of an electric circuit
- Active circuit parts: Parts that can generate energy on their own are grouped together as active parts. Diodes, amplifiers, batteries, and generators are just a few examples. The associated electrical device’s supply parts are the most important active component. Sources of voltage or current are divided into two categories: freelance sources and reliant sources. An electric battery is a self-contained power source that provides a constant voltage to the circuit, regardless of the current flowing through the terminals. A semiconductor unit can be a supply that supplies current to a circuit; however, the semiconductor unit is dependent on the facility used.
- Passive circuit parts: Passive parts are elements that are capable of controlling the flow of electrons through them. They have the ability to increase or decrease the voltage. Some examples of passive parts are shown below.
- Resistor: An electrical component opposes the flow of current through a linear circuit. Ohm’s law states that the voltage across an electrical device is directly proportional to the current passing through it, with the resistance serving as the proportional constant.
- Inductor: The associated electrical device aids in the storage of energy within the magnetic force field’s variety so that the voltage across the associated electrical device can maintain a constant current flow.
- Capacitor: An electrical condenser aids in the storage of energy in a variety of electric fields, and the voltage across an electrical condenser can charge.
Conclusion:
An electric circuit is a collection of electrical components that work together to create a closed path for current to flow. A source of electric power (electric cell or battery), a load that uses up electric power, connecting wires manufactured of good electric conductors, and a switch or key make up an electric circuit.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




