Energy is defined as the capacity to work. It exists in various forms like potential energy, kinetic energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy, electrical energy, etc. It can also be converted from one form to another.
For example, in solar cells, the light energy is converted into heat energy, which gets converted into electrical energy. Joule is the unit for energy, and the value of 1 joule is 1kg.m²/s².
Kinetic energy: Explained
The term ‘kinetic’ was first used by William Thomson, which means “to move” in the Greek language. It is derived from the word Kinesis. A moving object possesses kinetic energy.
Thus, Kinetic energy is a form of energy possessed by an object due to its motion. It applies to all the objects which are in motion. If we want to explain kinetic energy in terms of work, then it can be stated as the work done to accelerate the object to move at a certain velocity.
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the body’s mass and the square of the velocity with which the body is moving. Kinetic energy examples include energy possessed by a moving bus, a ball thrown in the air, and a swing doing to and fro motion.
Since Kinetic energy is a form of energy possessed by an object due to its motion, it tends to be zero when the object is in rest position. Radiant energy, Thermal energy, Sound energy, and Mechanical energy as some forms of kinetic energy. The formula for kinetic energy is 1/2mv², where v is velocity and m is mass.
Potential Energy: Explained
William Rankine introduced the term Potential Energy. Potential energy is defined as the stored form of energy. When the object starts moving, potential energy gets converted into kinetic energy. Thus, for an object to move, it must have potential energy. It is energy present in the object by virtue of its position with respect to other bodies.
Energy in the electrical charges is an example of potential energy. Gravitational energy also comes under potential energy. Potential energy depends on the mass of the object. Another potential energy example is the restoring energy in the stretched string, which helps it return to its original position.
Potential energy depends on the mass of an object, its height relative to another object, and the strength of the gravitational field.
To get the concept of potential energy clear, let’s take an example. Imagine an object is thrown upward with a certain force. When the object moves upward with a particular velocity, it possesses kinetic energy. Still, when it reaches a maximum height, the kinetic energy gets converted into potential energy since the velocity becomes zero at maximum height.
Thus, the formula for potential energy comes to be PE = mgh. Where m is the mass of an object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the maximum height.
Difference between Kinetic energy and Potential energy
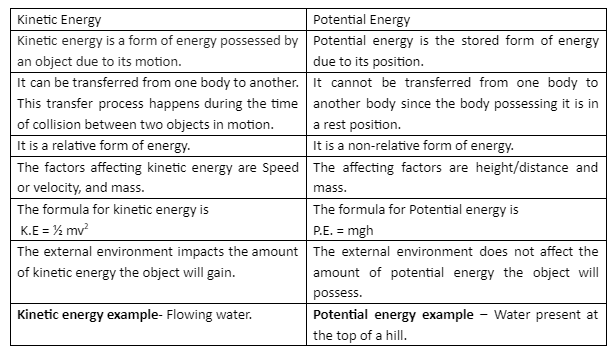
Conclusion.
Thus we can conclude, Kinetic energy is a form of energy possessed by an object due to its motion. In contrast, Potential energy is defined as the stored form of energy due to its position. Kinetic energy can be transferred from one body to another, whereas potential energy is non-transferable. Kinetic energy is affected by environmental conditions, while potential energy does not affect environmental conditions. The object’s velocity and mass are the factors on which kinetic energy is dependent. In the case of potential energy mass, acceleration due to gravity and height are the factors.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




