What is a Black Body?
A black body is an ideal surface or body that completely absorbs and re-emits all the radiation that falls on it without reflection. Absorption of radiation is independent of the direction of incidence, frequency and wavelength of radiation.
Properties of a perfect black body
To be able to call a body a perfect black body, it needs to possess the following properties:
- It absorbs all the incident radiation irrespective of wavelength and frequency range.
- There would be no radiation reflected or transmitted.
- An object which is a good absorber will always be a good emitter. Therefore, a perfect black body will also be a very good emitter.
In reality, there is no perfect black body in nature.
Black Body Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation emitted by any heated object is called black body radiation. It is also called cavity radiation.
- Depending on their temperature, all objects generate electromagnetic radiation.
- Colder objects emit low-frequency waves such as radio or microwaves.
- Heated objects emit high-frequency waves such as visible light and ultraviolet rays.
Black Body Spectrum
One of the characteristic features of black body radiation is a continuous frequency spectrum called the Black body spectrum. It is completely dependent on temperature.
Experimental Facts about Black Body Radiation
- The black body spectrum depends only on the temperature.
- The black body spectrum does not depend on the material of the body or object.
- As the temperature of an object increases, Black body radiation will also increase.
- The peak wavelength of the blackbody spectrum becomes shorter as an object’s temperature rises (i.e. bluer).
Example: Blue stars are hotter than red stars.
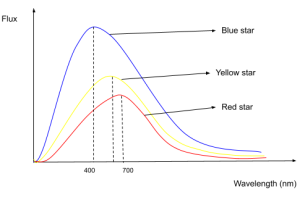
Above is the graphical representation of Black body radiation at different temperatures. As we can see:
- A blue star has the highest peak at 400 nm.
- A red star has the lowest peak at 700 nm.
Examples of Black Body Radiation
A few examples of Black body radiation are as follows:
- The filament of a light bulb.
- The heating element in a toaster.
- Solar radiations.
- Cooling of the earth at night.
Factors affecting Black Body Radiation
- Temperature: As the temperature increases, black body radiation increases.
- Emissivity: As the emissivity increases, black body radiation increases.
Types of Black Body Radiation
We can classify black body radiation based on temperature range as follows.
Type of Radiation | Temperature range |
Low temperature extended area black body | -40°C to 150°C |
High temperature extended area black body | Ambient temperature to 160°C |
High-temperature cavity black body | Ambient temperature to 1200°C |
Applications of Black Body Radiation
Black bodies are used in the following:
- Thermal imaging.
- Calibrating and testing the radiation thermometers.
- Lighting, heating and security.
- Optical sensors.
Radiation Laws
There are three major laws governing black body radiation, and they are as mentioned below:
- Planck’s law: It is the fundamental law that governs black body radiation. We can calculate the spectral energy density of emission at each wavelength using this law.
Eλ=8πℎcλ5eℎcλkT– 1
Here, E is the spectral energy density
ℎ is Planck’s constant
λ is the wavelength of radiation
k is Boltzmann constant
T is the absolute temperature
c is the velocity of light
- Wien’s displacement law: It is derived from Planck’s law. It states that the maximum frequency of the peak of emissionfmax is related to absolute temperatureT, i.e.fmax∝ T
- Stefan Boltzmann law: This law is also derived from Planck’s law. It states that the total energy emittedE is related to the fourth power of absolute temperatureT, i.e., E ∝ T4
Conclusion
A black body is an ideal surface or body that completely absorbs and re-emits all of the radiation that falls on it without reflection. Electromagnetic radiation emitted by any heated object is called black body radiation or cavity radiation. One of the characteristic features of black body radiation is a continuous frequency spectrum that is only dependent on body temperature, and it is called the black body spectrum.
We also studied the classification of black body radiation based on temperature variation. Planck’s law, Wien’s displacement law, and Stefan Boltzmann’s law are the three laws of radiation that regulate Black body radiation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




