Iron oxides are iron and oxygen-containing chemical compounds. Rust, a type of iron(III) oxide, is the most well-known of the sixteen known iron oxides and oxyhydroxides.
Iron oxides are common compounds found in nature that can be easily synthesised in the laboratory. Magnetic iron oxides have been used by humans for centuries; for example, small iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) have been used as a contrast agent for in vitro diagnostics for nearly half a century.
The synthesis of magnetic IONPs has been intensively developed over the last decade, not only for its fundamental scientific interest, but also for its numerous technological applications, including targeted drug delivery, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic hyperthermia and thermoablation, bioseparation, and biosensing. Bioapplications based on magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) in particular have received a lot of attention because NPs have distinct advantages over other materials.Magnetic IONPs, for example, are the inexpensive to manufacture, the physically and the chemically stable, the biocompatible, and the environmentally safe.
What is Iron oxide?
Iron oxides are common naturally occurring compounds that can also be easily synthesised in the laboratory. There are 16 different types of iron oxides, which include oxides, hydroxides, and oxide-hydroxides. These minerals form as a result of aqueous reactions at various redox and pH levels. They all have the same basic composition of Fe, O, and/or OH, but the valency of iron and overall crystal structure differ. Goethite, akaganeite, lepidocrocite, magnetite, and hematite are all important iron oxides.
Iron oxide (IO) nanoparticles are made up of maghemite (α-Fe2O3) and/or magnetite (Fe3O4) particles with diameters ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers and are used in magnetic data storage, biosensing, drug delivery, and other applications. The surface area to volume ratio of nanoparticles (NPs) increases significantly. This results in significantly increased binding capacity and excellent dispersibility of NPs in solutions. Magnetic nanoparticles (NPs) with sizes ranging from 2 to 20 nm exhibit superparamagnetism, which means that their magnetization is zero in the absence of an external magnetic field and that they can be magnetised by an external magnetic source. This property increases the stability of magnetic nanoparticles in solutions.
Iron oxide structure-Fe2O3
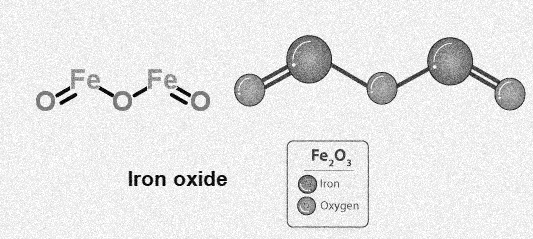
Uses of Iron oxide
- In both copperplate and die stamping inks, ordinary black iron oxide has been used.
- Iron oxides are the most common component of products used in the pharmaceutical, paint, plastic, ink, and cosmetic industries.
- Titanium dioxide is a natural pigment that is used as a pigment.
- Its salt is used as a flocculant in wastewater treatment, textile dyeing, and fertiliser and feed additive production.
- In the jewellery industry, it is used as a polishing material.
Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Synthesis
A new version of the solution combustion synthesis was used to create the magnetite and maghemite nanoparticles used in the preparation of colloidal suspensions. In a round bottom flask, an aqueous solution containing Fe(NO3)39H2O and C6H8O7H2O (fuel for the synthesis of magnetite) and D-(+)-C6H12O6 (fuel for the synthesis of maghemite) was heated to 400°C in the absence of air. A smouldering combustion reaction occurred as the water evaporated, resulting in the formation of a black powder. The black powder that resulted was hand crushed, washed with warm distilled water, and dried at 80°C. The black powder produced by using glucose as fuel was then treated with H2O2 to remove the residual carbon on the surface of the particles following the combustion reaction.
Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Characterization
XRD phase composition (Rigaku Ultima IV, CuK, Tokyo, Japan), specific surface area (nitrogen adsorption-desorption, Micromeritics ASAP 2020, Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, USA), and magnetic properties (VSM 880 ADE/DMS magnetometer DMS/ADE Technologies, Massachusetts, USA) were used to characterise iron oxide nanoparticles.
Oxidation number
The oxidation number represents the number of electrons gained or lost by an atom in a molecule. The oxidation state of an element is zero, and atoms in ionic compounds are usually assigned a positive or negative oxidation state.
In other words, an atom’s oxidation state is equal to the number of electrons removed from an element (resulting in a positive oxidation state) or added to an element (resulting in a negative oxidation state) (producing a negative oxidation state).
Conclusion
Iron oxides are iron and oxygen-containing chemical compounds. Rust, a type of iron oxide, is the most well-known of the sixteen known iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. Iron oxides are common compounds found in nature that can be easily synthesised in the laboratory. In both copperplate and die stamping inks, ordinary black iron oxide has been used. Iron oxides are the most common component of products used in the pharmaceutical, paint, plastic, ink, and cosmetic industries. A new version of the solution combustion synthesis was used to create the magnetite and maghemite nanoparticles used in the preparation of colloidal suspensions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




