What is an Oxidation and Oxidizing Agent?
There are several definitions of oxidation and oxidizing agent based on the chemical reactions occurring in the substrate. These definitions are categorized on the following basis:
Oxidation can be described as the loss of electrons in an atom or compound based on the oxygen transfer. The substance that adds oxygen to the other is known as an oxidizing agent.
An example of oxidation by oxygen transfer is the extraction of iron from its ores.
- Based on the hydrogen transfer: Oxidation is referred to as the addition of oxygen from a compound. The substance that removes the hydrogen from a compound or adds oxygen is known as the oxidizing agent.
Conversion of ethanol to ethanal takes place by the process of hydrogen transfer oxidation.
- Based on the electron transfer: The process of a loss of electrons is known as oxidation. The substance that removes electrons from the ion or compound is the oxidizing agent.
For example, the conversion of magnesium into magnesium ions is an oxidation process taking place by the electron transfer method.
Some Common Examples of Oxidizing Agents:
- Oxygen
- Ozone
- Hydrogen Peroxide and other inorganic peroxides
- All halogens like fluorine, chlorine
- Nitric acid and nitrate compounds
- Sulfuric acid
- Hypochlorite, Chlorite, Chlorate, and Perchlorate
- Permanganate
- Sodium borate
- Nitrous oxide and nitrogen dioxide
- Potassium nitrate
- Lead oxide
- Sodium dichromate
- Chromic and Dichromic acids
What is a Redox Reaction?
A reaction in which oxidation and reduction reactions co-occur is known as a redox reaction.
Oxidation is just the reverse of reduction. Reduction is the gain of electrons, whereas oxidation is the loss of electrons from an atom or compound.
For example, when calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide, the gain and loss of electrons take place simultaneously. Hence, the process of oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously.
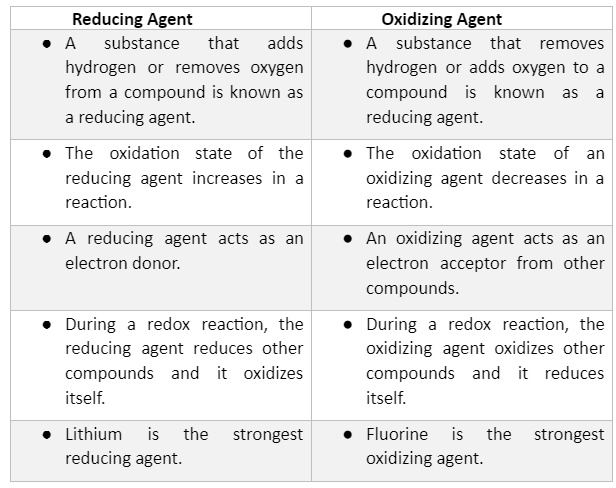
Difference Between Oxidizing Agent and Reducing Agent
What is an oxidation number of a compound?
Oxidation number and oxidizing state are often used interchangeably. Oxidation number refers to the total number of electrons lost or gained to form a chemical bond. The oxidation number shows the ability of an atom to lose, gain, or share electrons during the bonding with another atom.
For example, the Cu²+ ion has an oxidation number of +2, which denotes that copper can lose 2 electrons to form a bond with another atom.
The SO4²– ion has an oxidation number of -2 which means that it can gain 2 electrons to form a chemical bond with another atom.

reaction; this statement means that an oxidizing agent is known as an electron accepting species which is readily reduced in an oxidation-reduction reaction. The oxidation number in these species decreases in redox reactions.
Conclusion
This article explains the process of oxidation and the oxidizing agents in detail. Several examples of oxidizing agents are listed to make the concept clear. The key differences between the oxidizing and reducing agents have been listed in the tabular form to avoid confusion.
By going through this article, one can easily understand the topic of oxidizing agents easily. We hope this article proved to be helpful.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






