Matrices
A matrix is a rectangular or square arrangement of numbers, alphabets, or any kind of element in specific columns and rows. This arrangement of elements in rows and columns is enclosed by a box bracket on either side, left and right.
The denotation of a matrix is done usually by an alphabet in upper case. For example, a capital ‘A’, ‘M’, ‘I’, etc.
Types of Matrices
There are various types of Matrices in the mathematical world, the name of some are-
- Square Matrix
- Rectangular Matrix
- Row Matrix
- Column Matrix
- Diagonal Matrix
- Scalar Matrix
- Null Matrix
- Triangular Matrix
- Unit Matrix or Identity Matrix
- Upper and lower triangular Matrix
As we know, a matrix consists of rows and columns. The count of rows and columns in a matrix is called ‘the order of a matrix’, it is also sometimes mentioned as ‘the dimensions of a matrix’.
Following the rules of matrices, while finding the order of a matrix, the number of rows is written first followed by the columns.
For example-
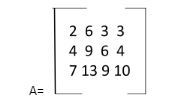
We now have a matrix above, named ‘A’. If we want to find out the order/dimensions of matrix ‘A’ we need to count the number of rows in the matrix ‘A’ first and then the number of columns in it.
The number of rows in matrix ‘A’ is 3 and the number of columns in the above- given matrix is 4.
Thus, the required order of matrix ‘A’ is written by – 3 x 4.
Determinant
Every square matrix has an association with a scalar, this is called a determinant.
A determinant is denoted by writing det(A) or I A I.
Note: The determinant value of a matrix with order 1 is its scalar value. But, the determinant of a matrix with order 2 x 2 is the difference of its cross products.
For example-

Some Important Properties Of Determinants-
- If the columns and rows of a given determinant are interchanged, then the value of the determinant remains unchanged.
- In case, 2 rows in a determinant are interchanged then the value of the determinant becomes negative (-ve).
- If all the elements of a specific row or column are multiplied by a number (a non-zero number) then the value of the given determinant automatically changes to the multiplied number multiplied by the old determinant value.
For an instant, if every element in row 1 of a given determinant is multiplied by 2 then the new value of the determinant becomes 2 multiplied by the original value
- If any two columns or rows of a given determinant are similar then the value of the determinant is supposed to be zero.
- If all the elements in a specific row or column are zeros then the determinant value is 0.
Equality of Matrices
If the order or dimensions of two given matrices and also the corresponding elements are equal then the two matrices are said to be equal.
For an instance if matrix ‘A’ has order 2 x 4 and matrix ‘B’ also has order 2 x 4
Then, matrix ‘A’ and matrix ‘B’ is said to be equal and we write them as-
A = B.
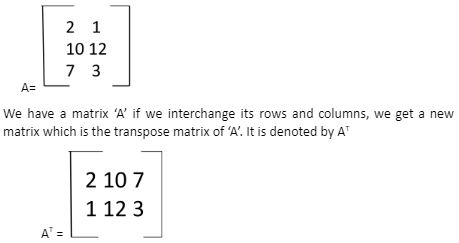
Transpose of Matrix
If the corresponding rows of a given matrix are flipped and converted into its columns then the newly formed matrix is called the transpose of the earlier matrix.
Conclusion
Matrices provide us with a lot of help and shows us an extremely linear and easy path for solving hectic equations in day to day life, especially in algebra.
The laws and solutions of matrices as well as determinants are used for plotting graphs, statistical studies and also to do research and scientific studies in different fields. Matrices can also be used to generate and show us data of the world in real life like the population of people, infant mortality rate, population per square meter, deaths per year, etc. They are the best representation methods for plotting and performing surveys.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






