
Be a part of Last Mile Program for JEE 2024
The Van’t Hoff factor is the ratio of final moles after dissociation or association to the initial moles before dissociation or association of an electrolyte in a solution.The solute’s property is the number of particles, which is independent of the solution’s concentration. The Van’t Hoff factor for a solution may be lower than the calculated value of the actual solution at a higher concentration where the solute ions are associated with one another.
The Van’t Hoff factor is always a positive integer value; it can never be negative.
Characteristics of the Van’t Hoff Factor
The Van’t Hoff factor showcases how solutes influence the solution’s colligative characteristics. The concentration ratio of the particles gets generated when the material gets mixed with the substance’s concentration by mass, known as the Van’t Hoff factor.
When a specific non-electrolytic chemical dissolves in water, the Van’t Hoff constant value is generally 1. And the value of ‘i’ equals the total ions available in the single formula unit of an ionic molecule when the solution gets formed.
We can take CaC2 as an example. It contains an optimum Van’t Hoff factor of about 3 as it gets dissociated into two different Cl– ions and one Ca²+ ion. However, a few such ions inside the solution form associations among themselves. It results in an overall reduction in the solution of the particles.
The Degree of Association and Dissociation
The degree of dissociation is defined as the fraction of total molecules that dissociates into cation and anion. It is the fraction of the total molecules that associates into forming larger molecules.
Calculation of Van’t Hoff Factor
Several formulas can be used to calculate the value of the Van’t Hoff factor. The formulas are based on molar mass and colligative properties.
- i = observed colligative property / normal or theoretical colligative property.
- i = normal molar mass / observed molar mass.
- i = actual number of particles / observed number of particles.
In the first formula, we calculate the Van’t Hoff factor by using the colligative property.
In the second formula, we know that particles with colligative properties have an abnormal molar mass. So, the Van’t Hoff factor can be calculated by taking the values of the calculated molar mass and the experimentally observed molar mass.
In the third formula, we use the principle of colligative property as we know that colligative property is directly proportional to the number of particles present in the solution.
One of the most common formulas used to calculate the value of the Van’t Hoff factor is
i = moles of particles in solution/moles solute dissolved.
Van’t Hoff Factor for the Association Solute
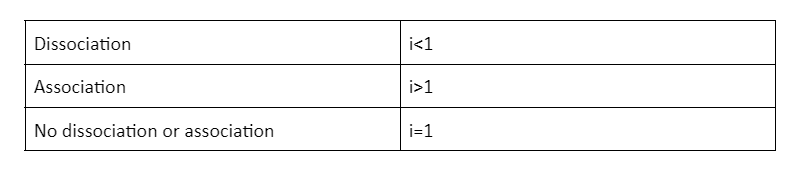
When the ions of solute associate in the solution, they give values lesser than 1. Let us look at the example of dimerisation of acetic acid in the presence of benzene. In this reaction, the acetic acid is dimerised into two molecules where the association of the ions takes place. Therefore, the Van’t Hoff factor is less than 1.
Van’t Hoff Factor for the Dissociation Solute
When the solute particles associate together in the solution, they give values of more than 1. For example, when NaCl dissolves in water, it breaks down into Na+ ions and Cl- ions.
Non-electrolyte
For non-electrolytes, the Van’t Hoff factor is 1. Glucose and sucrose, for example, are non-electrolytes and their Van’t Hoff factor is 1. In other words, they get completely dissolved in the solution.
Strong Electrolyte
The strong electrolyte has a Van’t Hoff factor greater than 1, and is equal to the number of ions formed in an aqueous solution when solutes dissociate. Examples of these are strong acid bases and salts.
Weak Electrolytes
A weak electrolyte doesn’t completely dissociate into the solution to find the Van’t Hoff factor. In this case, the Van’t Hoff factor is not directly proportional to the number of ions formed.
Significance of the Van’t Hoff Factor
The significant characteristic of the Van’t Hoff factor is that it is used in denoting the colligative properties. The formulas of colligative properties are included in the Van’t Hoff factor.


Related Links:
Conclusion
The Van’t Hoff factor is the ratio between the number of particles of the solute and the number of particles of the solvent. The Van’t Hoff factor presents the influence of the solute in determining the solution’s colligative characteristics.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





