Time to Read :🕑 3 Mins
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar 2024 announced.
Time to Read :🕑 3 Mins

Time to Read :🕑 3 Mins
Recently, a Japanese spacecraft landed on the lunar surface, becoming the 5th country to reach the moon.

Time to Read :🕑 3 Mins
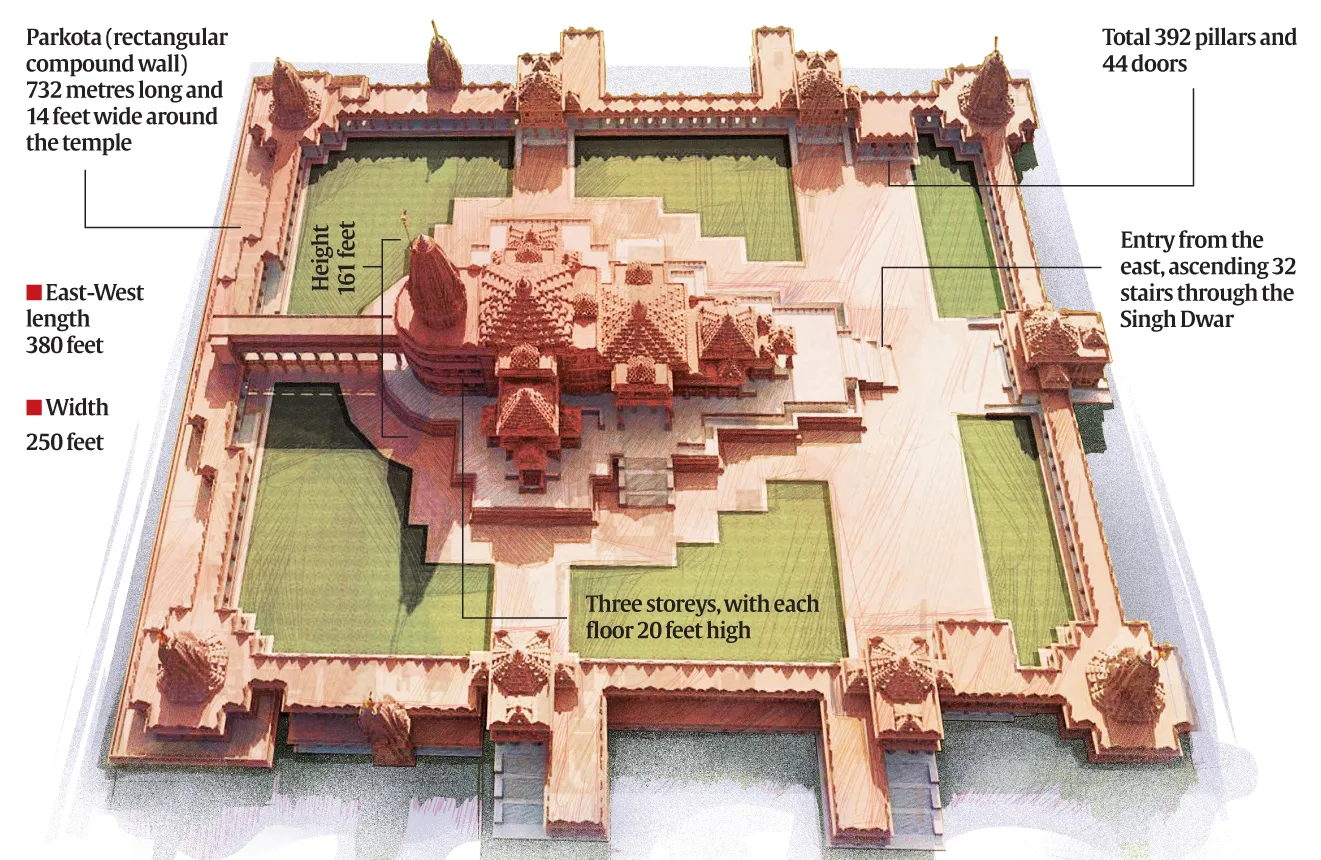
The Ram temple in Ayodhya will be inaugurated on January 22.


The Civil Services Exam is conducted every year by the UPSC to select suitable candidates for the Indian Administrative Service (IAS), IFS (Indian Foreign Service), IPS (Indian Police Service), IRS (Indian Revenue Service) and other Central Services like the Audits and Accounts, Railway Technical Services etc.
These services are vital for the administration of the Nation as they form the underlying basis of the policy formulation, implementation and execution in almost all the domains of the Governance. Sardar Patel had called the Civil Service the “Steel Frame of India“, the backbone of India’s Administration.
Being part of the Services is associated with prestige, power and a sense of responsibility toward the Society and the Nation. No doubt, the Services attract the best among the vast talent pool of the country.
And it is no surprise that the competition for the CSE is becoming fiercer every year. Over the last 3-4 years the number of applicants has hovered around 1,000,000 out of which approximately 500,000 appear for the Preliminary Exam. On an average 10,000 candidates qualify for the Mains Examination and less than 2,500 are called for the interview. Finally, only about 1,000 or fewer candidates qualify to be part of the Services. Thus the conversion ratio from appearing in the Preliminary Examination to the final selection in the Services is less than 0.2% (considering only the
Thus only sincere hard work may not be enough to be part of the Services. The aspirants need suitable guidance and study material to get selected and fulfil their dream of serving the Nation. Unacademy strives to provide quality content to the learners in order to supplement the guidance they receive from top Educators on the Unacademy Platform and aid their preparation.