Doppler’s effect is an important discovery for various fields in sciences, including planetary sciences. The Doppler effect or Doppler shift is a moving object related to the wave when there is a change in frequency of a wave about the observer. This phenomenon was discovered by an Australian physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler in 1842.
What do you mean by Doppler’s Effect?
Doppler’s effect in the field of physics is defined as the alteration in the frequency of a wave from the side of an observer that moves relatively towards its source.
The observer thus observes a shift in the upward direction in the wave’s frequency when the wave source moves towards them and a downward shift in the frequency when the wave source is retreating is observed in this effect.
Doppler’s effect is applied to all the waves in physics, namely sound waves, water waves and light waves.
Doppler’s Effect Formula
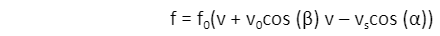
Here, α is the angle between the line joining the source and the observer and the velocity of the source.
β is the angle between the line joining the source and the observer and the velocity of the observer.
Some Basic Concepts required to know the Doppler’s Effect are-
Wavelength
The distance between 2 successive occurring crests in a sound or electromagnetic wave is the wavelength of that wave.
The symbol for wavelength is ‘λ’.

Where ‘v’ is the speed of the wave and ‘f’ is the wave’s frequency.
Frequency
The frequency of a wave is defined as the number of occurrences that happen per unit of time. The wave’s frequency is defined as the number of times the wave passes through one point in a unit of time. It is measured in Hertz and represented by ‘f’.
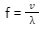
Velocity
The velocity of a wave is defined as the multiplication of the frequency and wavelength of the given wave. It is represented by ‘v’.
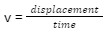
Explanation of the Doppler’s Effect
Doppler Effect is related to both sounds as well as light objects. For example, when an object producing sound (source of sound) moves closer to you, the frequency of the sound waves increases and gives us a much high-level pitch. On the other hand, if the sound source moves away from the observer, the sound waves’ frequency decreases and the pitch level becomes low.
The reduction in the pitch of ambulance sirens as they approach and move away from an observer and the shift in red light on top of the ambulance that faded with distance is a perfect and common example of the Doppler Effect.
Applications of Doppler’s Effect
A common use of the Doppler Effect is that it is used in hunting. Bats use this phenomenon for hunting prey. Bats select their flying paths with the help of echoes by sending their screams, commonly called whistles. While they are hunting and chasing behind prey, they emit a certain whistle and thus, detect a change in the pitch and can easily chase and catch the prey. This helps the chasing bat know how fast its prey is fleeing away from it.
The Doppler’s Effect is used in certain types of radars to measure and know the speed of certain objects.
Police officers use their radar guns to examine and fine over-speeding vehicles.
Doppler Radar is a new and commonly used technology used by official government officials as well as meteorologists. They use this technology to determine the direction of the velocity of falling drops of rain, the direction of the wind and various other weather events.
Doppler’s Effect is also used to predict weather patterns like storms.
Physicians, as well as medical personnel, use Doppler’s effect to measure the direction and rate of flow of blood in a patient’s body with ultrasound techniques.
Doppler effect has found its use in several other fields, including:
Vibration measurement
To sense gestures (in computers)
Astronomy
Velocity profile measurement
Audio
Conclusion
From the above-given module, we understand the basics of Doppler’s Effect. We know that the Doppler effect, commonly called the Doppler shift, is a moving object that is related to the wave when there is a change in the frequency of a wave concerning the observer.
Doppler’s effect has a lot of applications in our day-to-day life. For example- A star that produces electromagnetic waves can be that source in stargazing.
This topic is of utmost importance in the field of Physics. Any individual who wishes to pursue a bachelor’s or master’s degree in the field of Physics must know about the basics of this topic as well as the various other concepts related to this topic. This module is of great use and has an aim to help students appearing for entrance as well as college examinations.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




