Modulation is the technique of encoding data from a message source to make it more suitable for transmission. The encoding of information in a carrier wave by modifying the wave’s instantaneous frequency is known as frequency modulation (FM). FM technology is frequently employed in computing, telecommunications, and signal processing.
The maximum deviation fmax in FM is a variation (or) deviation in frequency.

The maximum frequency deviation is KAm.
In general, frequency deviation measures the change in carrier frequency caused by the input modulating signal’s amplitude.
Frequency modulation
Frequency modulation is a type of modulation where the carrier wave’s frequency changes in response to the modulating signal’s instantaneous amplitude while maintaining the phase and amplitude constant. The objective of changing the carrier wave frequency is to transfer data or information over short distances.
The frequency modulation index is consistently greater than one, requiring a wide bandwidth of 200 kHz, operating in a very high-frequency range of 88 to 108 Megahertz, a complex circuit with an endless number of sidebands, and receives a high-quality signal with good sound quality. Angle modulation is a type of carrier frequency modulation commonly employed in telecommunications transmission systems. Frequency and phase modulation complement basic types of angle modulation.
Frequency Modulation equation
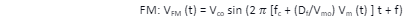
Types of frequencies in frequency modulation
There are two types of frequency deviation:
Narrow-band FM
The form of frequency modulation in which the modulation index value is too low is known as narrow-band FM. When the modulation index is less than 0.3, there is only one carrier and corresponding sidebands with double the modulating signal’s bandwidth. As a result, 0.3 is referred to as narrow-band frequency modulation. The maximum modulating frequency range is 3 kHz. 75 kHz is the most significant frequency deviation value.
Wide-band FM
The form of frequency modulation in which the modulation index value is significant is known as wide-band FM. More than two sidebands will have double the modulating signal’s bandwidth when the modulation index is more than 0.3. As the modulation index value rises, so do the number of sidebands. Narrow-band frequency modulation is defined as >0.3. Between 30 Hz and 15 kHz is the maximum range of modulating frequencies.
75 kHz is the most significant frequency deviation value.
This frequency modulation requires a broader bandwidth range than narrow-band frequency modulation, nearly 15 times larger.
The Bandwidth of Frequency Modulation Signal
One of the most critical aspects of an FM signal is its bandwidth. The sidebands will extend to infinity on either side; however, their strength will diminish. It can limit the BW of an FM signal without affecting its value considerably.
Remember that the bandwidth of a complex signal like FM is measured in Hertz and is defined as the difference between its highest and lowest frequency components (Hz). Bandwidth is only concerned with frequencies. The bandwidth of AM was discovered to be 2 FM, with only two sidebands (USB and LSB).
It is not that easy in FM, and its signal spectrum is highly complex and has many sidebands. The spectrum extends as the modulation index rises.
Frequency deviation
The difference between a frequency modulated signal’s minimum or maximum extent and the nominal centre or carrier frequency is called frequency deviation in FM radio. Frequency drift is an accidental offset of an oscillator’s nominal frequency that is commonly confused with frequency drift.
A radio’s frequency deviation is significant in terms of bandwidth because minor deviation means that more channels can fit into the same amount of frequency spectrum. A standard channel spacing of 100 or 200 kHz is used in the FM broadcasting range between 87.5 and 108 MHz, with a maximum frequency variance of +/-75 kHz, with a buffer above and below the highest and lowest frequencies in some situations to reduce interference with other channels.
Importance of frequencies in frequency modulation
Frequency modulation (FM) is most widely utilised for radio and television broadcasts. The FM band is used for several different things. Channels 0 to 72 on analogue television use bandwidths ranging from 54 to 825 MHz. FM radio, which broadcasts between 88 and 108 MHz, is also part of the FM spectrum. Each radio station uses a frequency band of 38 kHz to broadcast audio.
Conclusion
Modulation is the technique of encoding data from a message source to make it more suitable for transmission. The maximum frequency deviation is KAm. There are two types of frequency deviation – Narrow-band FM and wide-band FM. One of the most critical aspects of an FM signal is its bandwidth. The sidebands will extend to infinity on either side; however, their strength will diminish. The difference between a frequency modulated signal’s minimum or maximum extent and the nominal centre or carrier frequency is called frequency deviation in FM radio.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






