Triangle is a form of a polygon with three sides and three vertices. The Sum of all three internal angles is 180 degrees. These two-dimensional shapes can be classified based on their side length and angles such as isosceles (with any two sides equal), scalene (with no sides equal), equilateral(with all equal sides), obtuse-angled (with any one angle measuring more than 90 degrees, acute-angled (with any one angle measuring less than 90 degrees and lastly right-angled triangle with one 90 degrees angle.
Here, C denotes the complex plane.
We have to take the modulus of w: IwI
For triangle inequality,
Iw1 + w2I ≥ Iw1I –Iw2I … (i)
Further disintegrating into real and imaginary components:
w1 = m1 + im2
w2 = n1 + in2
By implementing the definition of modulus, the equation(i) can be written as:
((m1 + n1)2 + (m2 + n2)2)½ ≤ (m12 + m22)½ + (n12 + n22) ½
The equation is Minkowski’s Inequality, with n = 2.
For our reference, RM = w1 MN = w2 RN = w1 + w2
As RMNO is a parallelogram, we are sure that RO = MN.
The lengths of RM, MN, and RN are Iw1I, Iw2I, and Iw,1 + w2I respectively.
But as we can notice, the sides RM, RO, and RN are the sides of the triangle.
Therefore, we can conclude that the sum of the two sides of the triangle is greater than the third side.
Mathematical representation is: I IIxII – IIyII I ≤ IIx-yII
Inequality for the reverse triangle can be proven using the regular triangle inequality.
IIy-xII = 1 –II (x-y)II = I-1I IIx-yII = IIx-yII
The first and second triangle inequality shows that:
IIxII = II(x-y) + yII ≤ IIx-yII + IIyII => IIxII – IIyII ≤ IIx-yII
IIyII = II(y-x) + xII ≤ IIy-xII + IIxII => IIyII – IIxII ≤ IIy-xII
In the last step, we can prove the reverse triangle inequality by combining the above two statements.
-IIx-yII ≤ IIxII – IIyII ≤ IIx-yII => I IIxII – IIyII I ≤ IIx-yII.
Triangle Inequality
The term “inequality” applies to any triangle. In a mathematical context, a triangle is a form of a polygon with three sides and three angles that share a mutual relationship between them. Let p, q and r denote three sides of a triangle where r is the greatest of all sides. Triangle inequality arises when: r ≤ p + q. This is the symbolic representation of the triangle inequality theorem.Triangle Inequality in Vectors
This concept is simply a continuation of the theorem as per plane geometry. To understand the idea let us consider ←u, ←v, and ←u+←v as the three sides of the triangle ABC. Here, AB = I←uI, BC = I←vI and CA = I←u + ←vI. Then, as per the triangle inequality theorem, we can say: I←u + ←vI < I←uI + I←vI. …(i) Simultaneously, we know that the difference between the two sides of a triangle is less than the third side. For triangle ABC, the difference between side AB and BC is less than CA. I AB – BC I < I CA I Here, a modulus sign is induced to eliminate the negative result as we don’t know which side is larger in length. The above equation (ii) in vector form: II←uI – I←vII < II←u + ←vII …(ii) If we combine equation (i) and (ii), we get the triangle inequality for vectors. II←uI – I←vII < I←u + ←vI < I←u + ←vI Though the final equation might seem to be complicated it merely states that any side of triangle ABC is bound to be less than the sum of the other two sides and greater than their difference value.What are Complex Numbers?
The sum of a real number and an imaginary number is said to be a complex number. For instance, 5 + 2i is a complex number having both real and imaginary elements. The question may arise as to why we need to distinguish between real and imaginary numbers. This is because a squared imaginary number produces a negative real number. An imaginary number is denoted by i. The value of i2 is -1. The implementation of complex numbers is to represent periodic motions like water waves, alternating current, light waves, etc.Triangle Inequality and Complex Numbers
Let w1, w2, … , wn ∈ C.Here, C denotes the complex plane.
We have to take the modulus of w: IwI
For triangle inequality,
Iw1 + w2I ≥ Iw1I –Iw2I … (i)
Further disintegrating into real and imaginary components:
w1 = m1 + im2
w2 = n1 + in2
By implementing the definition of modulus, the equation(i) can be written as:
((m1 + n1)2 + (m2 + n2)2)½ ≤ (m12 + m22)½ + (n12 + n22) ½
The equation is Minkowski’s Inequality, with n = 2.
Proof of Triangle Inequality Complex Numbers
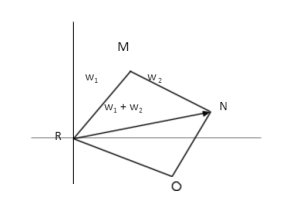
For our reference, RM = w1 MN = w2 RN = w1 + w2
As RMNO is a parallelogram, we are sure that RO = MN.
The lengths of RM, MN, and RN are Iw1I, Iw2I, and Iw,1 + w2I respectively.
But as we can notice, the sides RM, RO, and RN are the sides of the triangle.
Therefore, we can conclude that the sum of the two sides of the triangle is greater than the third side.
Reverse Triangle Inequality
The reverse triangle inequality follows the norm of a triangle inequality except it gives a lower bound instead of an upper bound. Thus, it is an elementary consequence of the triangle inequality.Mathematical representation is: I IIxII – IIyII I ≤ IIx-yII
Inequality for the reverse triangle can be proven using the regular triangle inequality.
IIy-xII = 1 –II (x-y)II = I-1I IIx-yII = IIx-yII
The first and second triangle inequality shows that:
IIxII = II(x-y) + yII ≤ IIx-yII + IIyII => IIxII – IIyII ≤ IIx-yII
IIyII = II(y-x) + xII ≤ IIy-xII + IIxII => IIyII – IIxII ≤ IIy-xII
In the last step, we can prove the reverse triangle inequality by combining the above two statements.
-IIx-yII ≤ IIxII – IIyII ≤ IIx-yII => I IIxII – IIyII I ≤ IIx-yII.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




