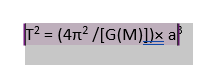Kepler’s law of planetary motion seems to be a common physics course during class 11th exams, and it is necessary to practice to ace the school exam and other competitive exams too. Here, in this tutorial, we will learn Kepler’s law and other important subjects linked to this. Let us learn how it was discovered and how it is significant to learn.
Johannes Kepler suggested three principles of planetary movement during the early 1600s between 1609 and 1619. Kepler was able to compress his mentor Tyco Brahe’s observations into three fundamental laws that changed the course of study of planetary motion substantially. Kepler’s attempts to describe the underlying causes of such movements are no longer accepted; however, the rules are completely in accordance with the theory we have developed till date.
The following are Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion:
- Kepler’s first law:The journey of every planet around the sun appears elliptical, having the sun’s centre placed at one point (The focus of the Ellipse ).
- Kepler’s second law:An imaginary line from the sun’s centre to that planet’s centre will sweep equal areas at equal period intervals (The Equivalent Areas Law).
- Kepler’s third law:The square of time period of revolution of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of semi-major axis of the ellipse.
The Elliptic Curve:
The first principle of Kepler, commonly known as the law of elliptical motion , describes that planets revolve the sun in an elliptical path.
This ellipse denotes a conic section under which the total sum of actual distances between two points known as foci is always fixed. The nearer these spots seem to be together, the more nearly the ellipse matches the form of a circle. In reality, a circle is a particular example of an ellipse with two focuses in the same place. Kepler’s first principle is straightforward: all planets revolve around the sun on the elliptical path, with the sun at one of the foci.
The Equal Areas Law:
Kepler’s second law or law of areas states that a planet during its revolution sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time by the imaginary line joining it and the sun. This gives us the idea that the planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun and moves slower when it is away from the sun.The special points are known as Apogee(farthest from sun) and Perigee(closest to the sun). The planet has highest speed at Perigee and movesic the slowest at Apogee.
The PeriodLaw:
The square of any planet’s time frame of rotation all-around the sun within an elliptical path is precisely equal to the square of one’s semi-major pole, based on Kepler’s rule of periods.
The narrower the planet’s rotation around this sun, the shorter its duration to finish one rotation. Kepler’s third rule gets a more broad version when utilising the formulas of Newton’s principles of gravity and movemen
Here M is the mass of the sun.
Interpretation of Kepler’s Third Law:
We may establish Kepler’s third principle by beginning with Newton’s principles of movement and the fundamental law of gravity. As a result, we can show that gravitation is the source of Kepler’s rules.
Imagine a spherical orbital of a tiny mass m orbiting a massive mass M. Also suppose it is revolving in radius R. Even though Kepler’s original law was supposed to prove for elliptical paths, we are only proving for a certain special case of ellipse i.e circle. Gravitation provides the centripetal pressure on mass m. To establish this we use Newton’s laws and our equation of circular motion:
F=GMm/R2
Thus this provides the required centripetal force.

Conclusion
Kepler’s laws were a breakthrough in the field of planetary motion and helped shape further studies. These were purely empirical laws and Kepler’s attempts to prove them were later rendered incorrect. However the laws were found to be correct and it helped debunk many myths about planetary motion. Also they provide easy ways to compare planetary motion and insightful information about angular momentum of the planets in their motion.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out