Introduction
Because of the Earth’s massive magnetic field, a free-floating bar magnet points north-south. The electric currents circulating from the earth’s core to space are thought to be responsible for the earth’s magnetic field. The earth’s magnetic field is supposed to protect the planet from solar wind, which could cause the ozone layer to deplete. The SI unit for the earth’s magnetic field is tesla.
Theory of Earth’s magnetism
There is no valid reason for the cause of the earth’s magnetism or why the earth has a giant magnetic field, but there are some theories about the earth’s magnetic field that help us understand why the earth behaves as a giant magnet.
- The magnetic field of the Earth is thought to be caused by the dynamo effect. The dynamo effect is caused by the movement of metallic fluids in the earth’s outer core, which results in electric current. The earth has its own magnetic field lines because of this electric current.
- Another theory proposes that the rotation of the earth around its own axis generates a strong electric current because the earth’s outer layers are ionised. As a result of the earth’s rotation, there is a movement of charged ions, which produces electric current.
Distinctive aspect of Earth’s magnetism
A fictitious giant magnetic dipole is thought to be located at the centre of the Earth. It does not coincide with the earth’s axis. As shown in the diagram below, the dipole is tilted by 11.3° with respect to the earth’s axis:
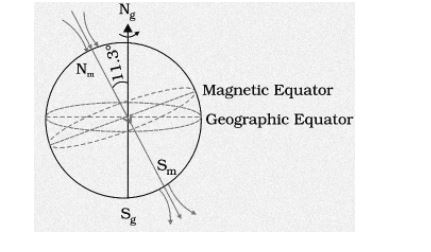
The above diagram shows that the earth’s poles have two north (magnetic north and geographic north) poles and two south (magnetic south and geographic south) poles.
The dipole produces the magnetic north and magnetic south poles. The magnetic north pole is at 79.74° N (latitude) and 71.8° W (longitude) (longitude). Similarly, the magnetic south pole is located at 79.74° South (latitude) and 108.22° East (longitude) (longitude)
If we carefully observe the magnetic field lines of the earth, we can see that they enter the north pole and leave the south pole, in contrast to the Bar magnet, where the magnetic field lines enter the south pole and leave the north pole. This is due to the fact that the magnetic north pole behaves similarly to the south pole of a bar magnet and vice versa. Magnetic north was named after the magnetic needle (North Pole) of a bar magnet that pointed in this direction.
Components of Earth’s magnetic field
The magnetic field of the planet can be resolved in different directions near the planet’s surface. These are the components that determine the magnitude and direction of the earth’s magnetic field at a given location:
- Declination of Magnetic Field
- The Earth’s Magnetic Field’s Horizontal Component
- Dip angle or Magnetic Inclination
When a magnetic needle is suspended in the air, it always points north-south, independent of all other attracting forces. This is referred to as the Magnetic Meridian.
Magnetic declination is the angle formed by the magnetic meridian and the geographic meridian. The plane passing through the earth’s north and south poles is defined as a geographic meridian.
As shown in the diagram below, suspend a magnetic needle freely so that it can rotate about a horizontal axis:
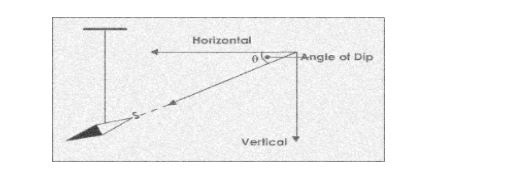
The magnetic inclination or angle of dip
The Angle of Dip or Magnetic Inclination is the angle formed by the north pole of the needle with the horizontal axis.
Variations in Earth’s magnetic field
Secular Variation: The magnetic axis changes on a regular basis due to its spin around its own axis from east to west. This variation has a time cycle of 960 years.
Eleven-year Sunspot Cycle: The earth faces the sunspot, which is a region of strong magnetic field, once every eleven years. As a result, this variation has a significant impact on the earth’s magnetic activity.
Variation on a daily and annual basis: The sun’s ultraviolet rays ionise the earth’s atmosphere. As a result, current is generated, which causes the magnetic field to form. This is due to daily and yearly variations.
Lunar Variations: In addition to the sun, the moon has an impact on the earth’s magnetic activity. During a lunar eclipse, the earth’s magnetic field varies due to the tidal motions of the ionised layer. This is known as the Lunar Variation.
Irregular and aperiodic variation: During a specific period of time when the sun’s solar activity is more active, the sun’s radiations ionise the earth’s atmosphere. When the earth revolves around its own axis, current flows, resulting in the magnetic field.
Conclusion
The electric currents circulating from the earth’s core to space are thought to be responsible for the earth’s magnetic field. The earth’s magnetic field is supposed to protect the planet from solar wind, which could cause the ozone layer to deplete. The SI unit for the earth’s magnetic field is tesla. There is no valid reason for the cause of the earth’s magnetism or why the earth has a giant magnetic field, but there are some theories about the earth’s magnetic field that help us understand why the earth behaves as a giant magnet. The magnetic field of the Earth is thought to be caused by the dynamo effect. The magnetic field of the planet can be resolved in different directions near the planet’s surface. The plane passing through the earth’s north and south poles is defined as a geographic meridian. In addition to the sun, the moon has an impact on the earth’s magnetic activity. During a lunar eclipse, the earth’s magnetic field varies due to the tidal motions of the ionised layer.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






