In physics, the distance-time graph is crucial in calculating various values associated with motion. This graph can also be used in mechanics. It is very simple to compare two journeys that are taking place at the same time using this graph.
In general, it is nothing more than a line graph from which we can derive various concepts such as velocity, speed, and acceleration, among others. These are not just random physics concepts; they also serve as a foundation for applied physics, which is extremely useful when solving real-world problems.
Distance vs Time Graph Definition
Time, speed, and distance are the three most important elements to discuss when learning about the distance-time graph. In a graphical representation, time is shown on the bottom X-axis, while distance is shown on the top Y-axis. Once the axes have been determined, the values can be easily plotted in the graph.
This distance vs. time graph teaches us about the various variations of a body’s movement. For example, a straight line on the graph indicates that the body moves at a fixed (or constant) speed. The following graph depicts the same –
What Is a Velocity Time Graph?
The Velocity-time graph is the graph that explains velocity in relation to time. This explains how velocity changes over time.
Acceleration is controlled by the slope of a Distance time graph uniform velocity. Consider three objects in a distance-time graph, A, B, and C, all of which are in a horizontal position.
Object A is represented by a flat horizontal line of uniform velocity on the distance-time graph, indicating that the body is always moving. If the straight line has a slope, it indicates that the body’s velocity is changing at a constant rate or that the body has a constant acceleration
Zero acceleration Velocity Time graph.
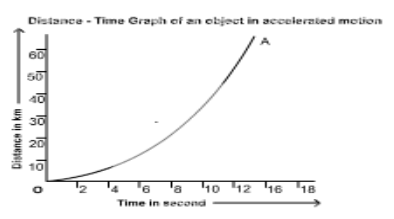
Distance – Time Graph of an Accelerated Motion Body:
When a graph of distance versus time for an object moving with accelerated motion, i.e. with increasing non-uniform speed, the slope of the graph will not be a straight line. The rising trend of the slope corresponds to the rising trend of the velocity.
Here’s a time-distance graph with uniform speed:
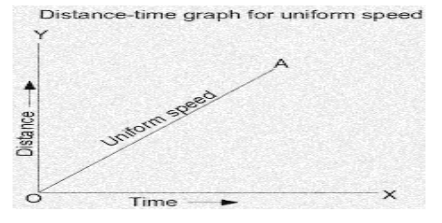
The concept of uniform speed is straightforward. I’m sure you’ve heard of speed; it’s the distance travelled per unit of time. Uniform speed is defined as covering equal distances in equal time intervals, i.e. if your speed is 10 km/h, that must be your speed throughout the journey, i.e. you cover 10 km again in the next hour, 20 km in the next 2 hours, or 30 km in the next 3 hours.
That was simple, but if you covered 20 km in the next two hours, you must have covered 10 km in one hour, 5 km in 30 minutes, or 2.5 km in 15 minutes… so on until zero, which you will clearly understand as you use calculus in physics in higher classes.
As a result, if you plot the distance-time graph of a body moving at uniform speed using the example I provided, or one of your own, you will always end up with a straight line, but the angle will vary depending on whether the body is moving at high or low speed.
This relates to your last question, and uniform speed and constant speed are the same thing because the speed remains constant throughout the journey.
Uses of Distance time graph:
- The distance-time graph is used to determine the position of an object at any point during the given time interval.
- To calculate the speed of an object at any point in time within a given time interval.
- The distance-time graph can be used to study the graph of uniform and non-uniform motion of an object.
What does a velocity time graph show?
We get an increasing graph, or to put it another way, a straight line that is not parallel to the x-axis. It is angled to the x-axis. The velocity time graph of uniform acceleration shows that the velocity increases uniformly with time, resulting in a positive acceleration graph.
The graph for uniform acceleration or uniform acceleration graph or uniform motion graphs or uniformly accelerated motion graph concludes that the body is moving with uniformly increasing velocity and that a particle’s acceleration increases linearly. When a particle begins at rest, its acceleration versus time graph gives the particle’s maximum velocity.
A force time graph for a body’s motion shows the change in linear momentum of the body.
Conclusion
The distance-time graph is crucial in calculating various values associated with motion. Time, speed, and distance are the three most important elements to discuss when learning about the distance-time graph. The Velocity-time graph is the graph that explains velocity in relation to time. Acceleration is controlled by the slope of a Distance time graph uniform velocity. When a graph of distance versus time for an object moving with accelerated motion, i.e. with increasing non-uniform speed, the slope of the graph will not be a straight line. The distance-time graph is used to determine the position of an object at any point during the given time interval. The distance-time graph can be used to study the graph of uniform and non-uniform motion of an object. The velocity time graph of uniform acceleration shows that the velocity increases uniformly with time, resulting in a positive acceleration graph.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






