As an alternative to element groups, Charles Janet proposed the concept of element blocks (along with helix and left-step periodic tables).
s, p, d, and f are the element blocks. The valence electron orbital determines them. The periodic table divides the elements into blocks depending on their valence electron orbitals.
The four periodic table blocks are used to create the main group (s- and p-blocks), transition metal (d-block), and inner transition metal (f-block) elements. The main group, transition metal, and inner transition metal elements are determined by element blocks.
Block
A periodic table block is a group of elements linked by the atomic orbitals in which their valence electrons or vacancies reside. Charles Janet is thought to have coined the word. The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block are all named for the orbitals they represent. The block designations (s, p, d, and f) come from the spectroscopic nomenclature for an electron’s azimuthal quantum number value: sharp, principal, diffuse, or fundamental. Following notations are in alphabetical order, as g, h, and so on, despite the fact that elements that would belong in such blocks have yet to be discovered.
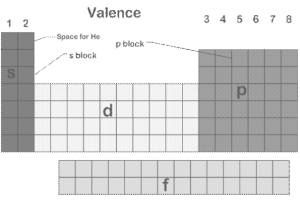
Figure:1 Periodic table blocks
d – block Elements
Transition metals are referred to as d-block elements (groups 3-12). d-block elements have qualities that are similar to both highly reactive electropositive s-block elements and more electronegative p-block elements. It is for this reason that they are referred to as “transition” metals.
They’re called “d-block elements, because their valence electrons are in one or more d-orbitals, they are referred to as “d-block elements” (but not in any p-orbitals)
Characteristics of d – block Elements
- Metals with high melting and boiling points make up the d-block components.
- The d-block elements have transitional properties that fall between highly reactive electropositive alkali metals and covalent compound-forming elements. The d-block elements are hence referred to as transition elements.
- Valence electrons can be found in both the outermost and second outermost (penultimate) shells of certain elements. Chemical reactions can involve valence electrons from the outermost, or both the outermost and penultimate shells. As a result, the oxidation states of d-block elements vary.
- They’re tough and feature a high density.
- They exhibit a wide range of oxidation states.
- They produce a variety of coloured ions and compounds.
- The atomic radii decrease as the atomic number increases.
s – block Elements
The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, often known as groups 1 and 2, are part of the s-block in the periodic table of elements. The s block also includes helium. The s orbital is filled with the primary quantum number “n.” The s orbital can only hold a maximum of two electrons at any given moment.
s-subshell contains only one s-orbital, according to Pauli’s principle, an s-block element can only host two electrons with opposite spins. Group I (or IA) and group 2 are the two groups (or IIA).
Characteristics of s – block Elements
- The spherical s orbital is the outermost orbital of s block components.
- These s electrons can be easily lost to create unipositive ions (one electron in the outermost orbital) or dipositive ions (two electrons in the outermost orbital).
- Their electronegativities and ionisation potentials are both low.
- Except for H2 and He, they are good heat and electrical conductors.
- They’re metallic substances that are silvery and gleaming (with the exception of hydrogen and helium which are gaseous nonmetals).
- They are malleable and ductile, which means they may be made into sheets and wires (exception: H2, He)
- Most nonmetals readily create ionic salts with them.
- Their oxides are alkaline in aqueous solutions.
- With the exception of He, who is at the right end of the Periodic Table, they are listed in two columns at the left end.
- The elements in the first column are known as alkali metals, whereas those in the second column are known as alkaline-earth metals.
- There are many more that aren’t included in this list.
p – block Elements
The p-block is the part of the periodic table that contains columns IIIA through VIIIA but not helium. The p-block consists of 35 elements that all have valence electrons in the p orbital. The p-block elements are a group of elements with a variety of properties.
The valence electrons in the s-block and p-block elements are in an orbital s or p, respectively. To highlight them from the transformation sequence and internal transformation, these are often referred to as Standard Components.
Characteristics of p – block Elements
- ns2np1-6 is the general electrical configuration of p-block components (except He). The electronic configuration of the inner core, on the other hand, may alter. The physical and chemical properties of the elements alter as a result of this difference in the inner core.
- When the total number of valence electrons, i.e. the sum of s and p electrons, equals the total number of valence electrons, the oxidation state of elements in the p – block is maximal. The fact that the p-block elements comprise both nonmetals and metalloids is one of the most intriguing aspects about them.
In two important ways, the initial member of the p block elements differs from other elements:
- The first is the size, as well as all of the properties that are dependent on it.
- The second difference exclusively affects the p-block element and is caused by d-orbitals in the valence shell of heavier elements.
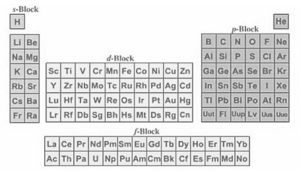
Figure:2 s,p,d,f Elements blocks
Conclusion
The periodic table, often known as the periodic table of (chemical) elements is a representation of the chemical elements in a table format. It’s a chemistry icon that’s often used in chemistry, physics, and other sciences. It’s a visual illustration of the periodic law, which states that chemical elements’ properties are correlated with their atomic numbers in a predictable way. The table is divided into four sections, each about rectangular in shape. The table’s rows are referred to as periods, while the columns are referred to as groups. Chemical characteristics of elements in the same column of the periodic table are comparable. A periodic table block is a collection of elements linked by their atomic orbitals, which contain their valence electrons or vacancies. Charles Janet is thought to have coined the phrase. The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block are all named for the orbitals they represent.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






