Introduction:
In the presence of water, chlorophyll, sunlight, and carbon dioxide, photosynthesis is the process by which plants prepare their own food for consumption. The majority of this process occurs in the leaves of the plants. In some other plants, photosynthesis is also carried out by the stems. The chloroplast cells of the leaves are where photosynthesis takes place. There are a variety of factors that influence photosynthesis, including its rate and efficiency.
Examine these factors that have an impact on photosynthesis and try to figure out what they are :-
Light
It is one of the most significant factors influencing photosynthesis. Photosynthesis cannot take place in the absence of light, and the only source of light for plants is sunlight. Photosynthesis depends on three characteristics of light: intensity, colour, and wavelength.
Intensity: Photosynthesis begins at low light intensities and gradually increases in intensity until it reaches its maximum at the time of day when the sun is shining the brightest. Depending on the plant, a different amount of light may be required. Photosynthesis uses up to 1.5 percent of the available light in the process, and as a result, light is generally not a limiting factor when the light is of high intensity. However, when the light is of low intensity, it becomes a limiting factor because, no matter how much water or CO2 is present, photosynthesis cannot occur without the presence of light. When the intensity of the light is high, the temperature of the plant rises, which causes the plant to produce more transpiration. As a result, the stomata close, resulting in a reduction in CO2 absorption and consumption. As a result, photosynthesis is reduced, and eventually ceases to exist. As a result, excessive light is detrimental to photosynthesis.Qualitatively, experiments conducted by Engelmann demonstrate that chlorophyll is capable of absorbing the most red and blue wavelengths across the entire spectrum of light. Quantity: As a result, when the plant is exposed to light with these wavelengths, it produces the most amount of photosynthesis.
The length of time that a plant is exposed to light determines how long the photosynthesis process will continue to operate. When the temperature of the plant is maintained at a stable level, photosynthesis will take place.
The Concentration of Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide makes up 0.03 percent of the atmosphere’s total gaseous content, which includes other gases. Carbon dioxide is taken up by plants from the atmosphere. The fact that CO2 is present in such small amounts in the atmosphere means that it serves as a limiting factor for photosynthesis. In order to determine the effect of increasing CO2 concentration in the atmosphere on the rate of photosynthesis, experiments have been carried out in the laboratory.
Increased CO2 concentration leads to an increase in the rate of photosynthesis when light and temperature are not the limiting factors, as demonstrated by the experiments conducted. However, once a certain limit is reached, CO2 begins to accumulate in the plant, causing the process to slow down. Consequently.
Temperature:
It is commonly observed in all biological and biochemical processes that they perform best when the temperature is within a specific optimum range. This holds true for both photosynthesis and respiration. We have observed that, in the absence of limiting factors such as CO2 and light, the rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing temperature until it reaches the optimum level for that particular plant type. After reaching optimum levels on both sides of the normal range, enzymes are deactivated or destroyed, and photosynthesis comes to a complete standstill.
Water:
In the field of photosynthesis, water is considered to be one of the most important factors to consider. Because of a decrease in water intake or availability, the stomata begin to close in order to prevent any water from being lost during transpiration. With the closure of the stomata, the intake of CO2 is reduced, which has an impact on photosynthesis. As a result, water has a more indirect rather than direct effect on photosynthesis in plants.
Oxygen:
Photosynthesis is most successful when oxygen levels are at their highest. Photorespiration in C3 plants requires the presence of oxygen, and the by-product of photorespiration is CO2, which is required for photosynthesis to occur. In addition, the energy generated during oxygen respiration is required for the process of photosynthesis to take place in the plant. However, an increase in oxygen levels above what is considered to be optimal for the plant results in photosynthesis being inhibited.
This is due to the fact that oxygen has a tendency to degrade the intermediaries that are formed during photosynthesis. RUBISCO, which is a component of the dark reaction of photosynthesis and photorespiration, is completed by oxygen in conjunction with CO2. Due to the fact that O2 concentrations are increasing, it is expected that RUBISCO will combine with O2 to initiate photorespiration, resulting in photosynthesis slowing down.
Blackman’s Principle of Limiting Factors:
This principle states that when a process is governed by more than one factor, the rate of the process is governed by the factor that is closest to the process’s minimum value, according to the data.
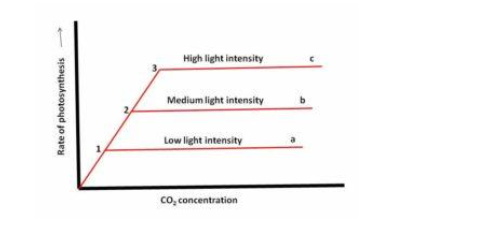
Consider the following scenario: If a leaf is exposed to a specific amount of light intensity at a constant temperature, but the amount of CO2 available is less, the rate of photosynthesis will not increase with an increase in the amount of light intensity. As a result, in this instance, CO2 is the limiting factor to growth.
Conclusion:
From the follo0wing article we can conclude that Light, temperature, water, and carbon dioxide all have an impact on photosynthesis. Stomata are involved in the process of transpiration but are not involved in photosynthesis.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






