Direct proportion meaning
Direct proportion in mathematics is the comparison between two numbers or variables in which the ratio of that numbers is equal or constant. When the ratio of these two numbers are equivalent, then there is a proportion. Proportions are denoted with ‘∝’ symbol. In a definitive form, the direct proportion is a situation where the relationship between two variables is in such a way that if either of the variables will increase, then another one will also increase the same. Suppose, A is the number of toys and B is the price for each toy. So here if we want more toys we have to spend more money or in simple words, more toys mean more money outflow and vice versa. So in this situation, we can conclude that the A is directly proportional to B.
Direct Proportion Formula
According to the direct proportion formula, if a variable A is directly proportional to another variable B, then it can be stated as A=cB, where c is the constant.
So the direct proportion formula I’m for the variable A and B will be:
A∝B, then A=cB
where,
c is the constant and A increases with the increase in B. Similarly A decreases with the decrease in A and vice versa.
So direct proportion is a concept that shows the relation between two measurable quantities or variables. The two quantities in this concept are said to be proportional if they are interlinked mathematically. Along with this, the proportional relationship is defined when the given two-variable have a constant ratio. If the two numbers have a constant ratio, then they are directly proportional to each other.
Another term used in proportionality is inverse proportion. If the two variables which we discussed above react exactly opposite of each other, then they are inversely proportional to each other. For example, If A is the price of a pen and B is the sales analysis of it. If the price of the pen that is A will increase, the sales which are B will automatically come down. Similarly, if the price of the pen decreases, then the sales will be increased. In this situation we can conclude that A is inversely proportional to B or the price of the pen is inversely proportional to the sale or demand of the pen.
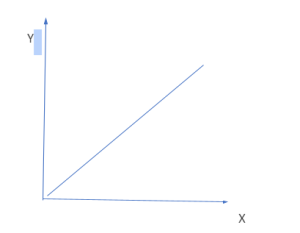
Direct Proportion Graph
The direct proportional graph means a strange line that slipped in an upward direction.
In the given graph above, there are two axes which are the x-axis and the y axis. The line between them which is started from the origin shows that there is a direct relationship between two variables which us in the x and y-axis.
Difference between Inverse and direct proportion
There is two proportionality as we have discussed a bit, above. These are direct proportion and inverse proportion. When any increase or decrease in any one of the variables will result in the same to another, then it can be concluded that both these variables are directly proportional to each other. While in the case of inverse proportion, if any decrease or increase in any one variable is affecting the exact opposite to another, then it can be concluded that both these variables are inversely proportional to each other. Like inverse proportion is the exact opposite of direct proportion, their graphs are also opposite.
Conclusion
Direct proportion can be a really simple topic if you have understood the concept behind it. Here we have covered every detail about direct proportion meaning, graph, and formula.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out