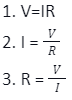Ohm’s law displays a straightforward relationship between three electrical terms known as voltage, current as well as resistance.
Ohm’s law is used to state that the current running with the help of a conductor between two points is known to be directly proportional to the voltage between the two points. Resistance is known as the constant of proportionality. The SI unit of resistance is known as ohms. Ohms is denoted by a symbol that is Ω. This helps in decoding an equation:
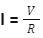
I = Current running through the conductor in terms of amperes
V = Voltage calculated between the conductor in terms of volts unit
R = Resistance of the conductor calculated in ohms unit
According to ohm’s law, the R in the given equation is always constant. In case the resistance is variable, the equation can’t be called ohm’s law. Ohm’s law was given this name after the German physicist, whose name is George Ohm.
Applications of ohm’s law
Given below are some major applications of ohm’s law:
- Ohm’s law helps in simplifying calculations involving power.
- Ohm’s law is utilised to maintain the required voltage drop between the components of electricity.
- Ohm’s law is used to give redirection to current in DC ammeters as well as other DC shunts.
5 examples of ohm’s law in everyday life
The usage of ohm’s law in daily life is quite high. Given below are applications of ohm’s law in regular life:
Electric heater
Electric heaters are used in winters to get protection from cold temperatures. The heaters consist of a metal coil. The metal coil contains high resistance that tends to allow a specific amount of current to run through the coil. This leads to the production of required heat. Along with this, the power which is supplied to the heaters is measured with the help of ohm’s law.
Fuse
Fuses are known to be the components of protection. Fuses limit the amount of current running through the circuit. This is done to establish a specific voltage amount. The requirement of resistors is determined through ohm’s law.
Mobile/Laptop charger
Mobile, as well as laptop chargers, utilise a DC power supply and are functioning. A variable output voltage is used to supply power. The overall functioning of the mobile/laptop charger is controlled with the help of ohm’s law.
Electric kettle
The electric kettle consists of multiple resistors inside them. The resistors help in putting a boundary line to the amount of current that runs through the resistors so that the needed amount of heat can be provided. Ohm’s law helps in measuring the size of resistors.
Domestic fans
A regulator helps in controlling the speed of a domestic fan. The regulator helps in controlling the current running through the fan by regulating resistance. Ohm’s law help in measuring the resistance current
Conclusion
Ohm’s law is used to state that the current running with the help of a conductor between two points is known to be directly proportional to the voltage between the two points. Ohm’s law was given this name after the German physicist, whose name is George Ohm. Some main applications of ohm’s law include simplifying calculations involving power, utilised to maintain the required voltage drop between the components of electricity, and to give redirection to current in DC ammeters as well as other DC shunts.
Ohm’s law is significant in describing electric circuits. The main reason behind this is that it relates to the voltage along with the resistance value that is controlling their relationship. 1 ohm is known as the resistance of a conductor. Ohm’s law can be applied in numerous ways in our daily life, including electric heaters, electric kettles, domestic fans, mobile chargers, and fuses.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out