INTRODUCTION:
The Tundra ecosystem is one with an absence of trees and is covered with snow for the majority of the year. This type of ecosystem can mostly be found in cold climates and places with little rainfall. This climate is found in places with lower altitudes and is very similar to deserts, because of their severe climate. They can be found in regions extending across North America, Europe, and Siberia moving towards Asia. The majority of Alaska and Canada cover the Tundra ecosystem. They have extremely long, dark, and cold winters and rarely have summer seasons throughout the year. Plantations and flowers can rarely be found in these places because they are always covered with snow. There are two major ecosystems in the Tundra, which are the Arctic and Alpines. The Arctic tundra is much colder when compared to the Alpine tundra.
TYPES OF TUNDRA REGIONS
There are three types of Tundra regions that can be seen in the world which are Arctic Tundra, Alpine Tundra, and Antarctic Tundra:
- Arctic Tundra: This type is most prominently found in the Northern Hemisphere and contains a stark landscape that is usually frozen for most of the year. In these regions, there are only two major seasons which are the winters and summers. Due to there being such a harsh climate in this type of Tundra region, there is very little human activity that can be seen, despite there being a good amount of natural resources like; Natural gas, petrol, etc. Places like Alaska and Russia have this type of Tundra ecosystem
- Antarctic Tundra: This can be seen in Antarctica and the islands around the Antarctic region. Most of this region is too cold to support any type of vegetation and most of the region is filled with ice fields. When compared to the Arctic region, this region lacks fauna which is mostly because of physical isolation from the other continents. There are a few seals and penguins that can be noticed in this region along with human occupation in the sub-Antarctic islands. One interesting fact is that the flora and fauna in this region are protected by the Antarctic Treaty
- Alpine Tundra: This region does not have any trees because the climate does not support the soil to grow any sort of vegetation. The climate here is very similar to the polar climate. This type of ecosystem can be seen in mountainous regions worldwide. The most common flora grown here includes mosses, cushion plants, lichens, etc. The vegetation is nicely adapted to the harsh climatic conditions of this region like low temperatures, radiation, global warming, and a very short growing season for the vegetation
ABOUT THE CLIMATE IN THE ECOSYSTEM
The climate that is found in this ecosystem is extremely low in annual temperature. In winters, the temperatures go as low as 40 degrees Celsius below the freezing point. However, the summers are warmer compared to the winters experienced there. There are also days and weeks of darkness experienced. There is a lot of frost and blizzards that can be experienced during any time and rainfall is generally not predictable.
TUNDRA VEGETATION
It can be seen that there are no trees in this ecosystem. This ecosystem is home to the lowest forms of vegetation like lichens, fungi, mosses, etc. While it can be seen that there are a few flowers that bloom during the summer season. The coastal lowlands give homage to hardy grasses and this moss is the only food for the reindeers in the ecosystem. The other plants that are seen in this region are cotton grass, birches, rushes, shrubs, etc.
ANIMALS IN THE TUNDRA ECOSYSTEM
Even though the tundra climate is extremely cold, there are many animal species that can be seen in the ecosystem while there are a few that migrate to avoid the cold climate. One interesting feature about the animals in this region, like the Arctic fox, hare, and caterpillars that change their colour to camouflage themselves. The reindeer is the most common species found here, they usually travel in large numbers and breed in the early summer. The grey wolves are also born during the warmer times and appear in the tundra and hunt after the herbivores.
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
There have been new minerals found in the Tundra region like gold, petrol, and copper. There have also been new ports on the Arctic seaboard that have been able to export goods like timber and fur. The reason these frozen seas are navigable is because of the modern ice-breakers.
Conclusion:
Out of all the biological ecosystems, the tundra region is the coldest of all as it is located in the mountainous regions and has very little wildlife and human habitat. There are three major types within this ecosystem, the Antarctic, Alpine, and Arctic ecosystems. They all have various different characteristics but are all located in the colder regions of the world. Rarely are any flora and fauna found in these regions. While this region was considered to be useless to mankind, there have been new developments in this ecosystem as well. There have been new ports established along with the discovery and exports of new minerals and settlements. There have also been railway lines constructed in the region to develop the industrial regions.
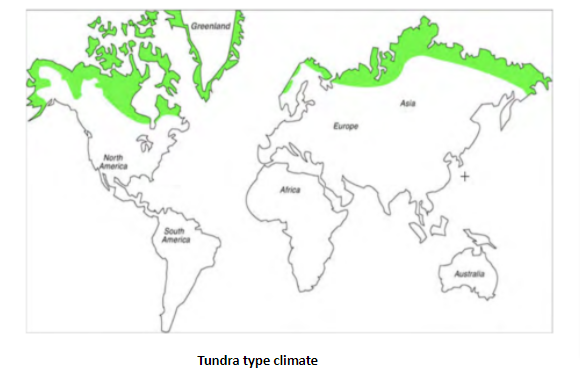
Climatic Conditions
Temperature:
- Featured by a very low mean annual temperature and its warmest month in June seldom goes to more than 10°C
- During mid-winter (January) temperature is as low as -35°C and much colder in the hinterland
- Winters are extreme, long, and very severe; summers are cool and short period
- The temperatures are so cold in this region that there is a layer of permanently frozen ground below the surface, called permafrost
Precipitation:
- Mainly falls in the form of snow, falling in winter and being drifted about during blizzards. Snowfall differs with locality; it may come down either as ice crystals or large, amalgamated snowflakes
- Convectional rainfall is generally absent due to the low rate of evaporation process and insufficient moisture in the cold polar air
Natural vegetation
- In such an adverse and extreme atmosphere as the tundra, only few plants survive
- Insufficient heat is the greatest inhibiting factor in this region
- With a growing season of only less than three months and the warmest month not exceeding 10 °C (the tree-survival line), there are no trees in the tundra region
- Such an environment can support only the lowest form of vegetation like mosses, lichens, and sedges
- Poor drainage due to sub soil which is permanently frozen
- Ponds and marshes and waterlogged areas are seen in hollows
Economy:
- Human activities of the tundra are mostly restricted to the coast. Where plateaus and mountains (permanently snow-covered) increase the altitude, it is uninhabitable
- The few people of this region live a semi-nomadic life and have to adapt themselves to a severe environment
- Once it was regarded as completely useless but now it is considered of some economic significance
- Apart from the efforts of the different governments of the world in assisting the advancement of the Arctic inhabitants the Eskimos, Lapps, Samoyeds etc., new settlements have sprung up due to the finding of minerals

 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out













