The comparison for pure substance vs mixture is done on the basis of their composition. A mixture is formed by two or more elements or compounds with different chemical properties. All the components are of the exact chemical nature in a pure substance. The types of matter are given below.
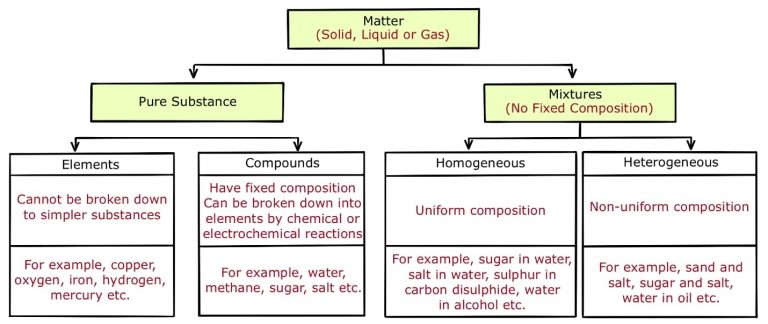
Fig.: Types of Matter
Pure substance
Pure substances are those substances that consist of a kind of element. A pure substance will always have the same properties regardless of the source.
Types of Pure Substances
Substances can be classified as elements or compounds based on chemical composition.
Elements
- An element is a basic form of matter and it cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions.
- The number of elements known at present is more than 100, out of which 92 elements are naturally occurring, and the rest are artificial.
- The majority of the elements are solid. Eleven components are vaporous at room temperature.
- Two components are liquid at room temperature – Mercury and Bromine.
- Gallium and caesium are the only elements that are liquids at temperatures slightly higher than room temperature.
Types of Elements
It can be divided into metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Metals: Metals usually show some or all the following properties:
- They have a lustre (shine), silvery-grey or golden-yellow colour.
- They have a property that they are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They exist in a solid state at room temperature except for Mercury which exists as a liquid.
- They are soft (can be pulled into the wires).
- They are weak (can be hammered into thin sheets).
- They are snug (ringing when killed).
- Few Examples: Gold, iron, sodium, etc.
Non-metals: Non-metals usually show some or all the following properties:
- They display a variety of colours.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are not lustrous, sonorous, or malleable.
- Few examples: Oxygen, iodine, carbon (like coal, coke), chlorine, etc.
Metalloids
- They have intermediate properties between those of metals and non-metals.
- For example, boron, silicon, germanium, etc.
Compounds
- It is a substance comprising at least two components, which are artificially blended to a decent extent.
- Intense heating of the two elements results in a mixture with very different properties compared to the mixed elements.
- The structure, surface, and shade of a compound are very similar all through.
- Examples of compounds include water, baking soda, and salt.
Mixture
- Compounds are made up of more than one type of substance, such as seawater, minerals, soil, etc.
- Constituents of a Mixture cannot be separated by physical process.
- Mixtures are classified into homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
- The components of a heterogeneous mixture are easy to separate through simple techniques such as handpicking and filtration. We require advanced techniques to separate the components of a homogeneous mixture.
Types of Mixtures
- Homogeneous mixture: It has a uniform composition throughout. However, the composition of the constituents could be variable. For example, sugar in water.
- Heterogeneous mixture: It has a non-uniform composition and contains physically distinct parts. For example, water in oil.
Methods of Separation of Mixtures
- Evaporation can be used to separate the volatile component (solvent) from its non-volatile solute.
- When there are microscopic solid particles in a liquid mixture, they move through filter paper. As a result, we use centrifugation. The denser particles are driven to the bottom while the lighter particles remain at the top when centrifugation is applied.
- Distillation is used to separate components of a mixture that contains two miscible liquids that boil sans decomposition and have a considerable enough variation in boiling points.
- The crystallisation process is followed to purify solids. Crystallisation is the separation of a pure solid in the shape of crystals from a solution.
- These methods have many practical applications. One such application is the purification of water from the source to homes.
- The water purification process involves sedimentation, removal of suspended particles, filtration, and chlorination.
Conclusion
The comparison of Pure Substance vs Mixture is based on their composition. Pure matter means that all the components of this substance are of the exact chemical nature. Compounds are made up of more than one type of substance, such as seawater, minerals, soil, etc. A mixture is a combination of more than one ingredient in any proportion. Constituents of a Mixture cannot be separated by physical process. So there are various types of methods of separation of mixtures. A solution is a homogeneous combination of two or more components. A suspension is a heterogeneous mixture when the mixture’s components do not mix thoroughly. Elements are classified as metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
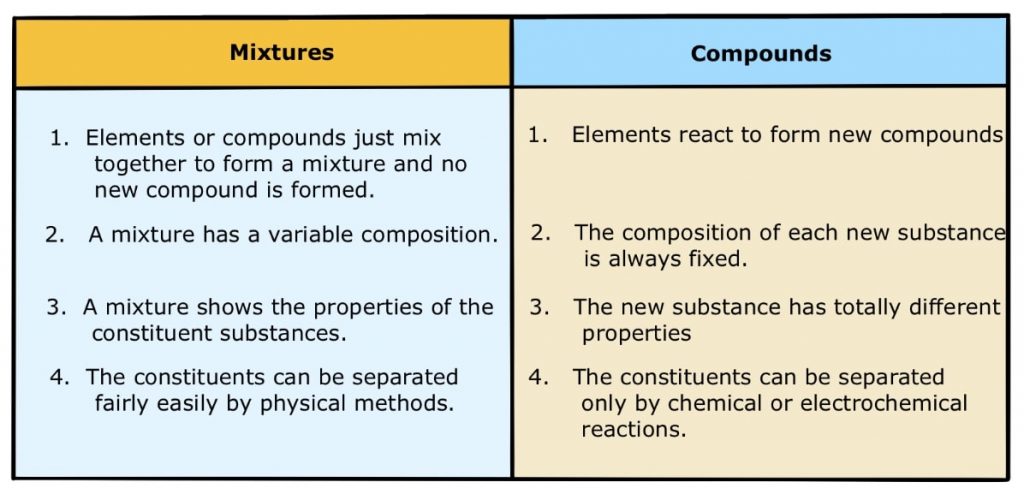
Table: Difference between Mixtures and Compounds
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











