Chemical Communication in Plants and Human Beings
- Chemical coordination is seen both in plants and animals through the use of Hormones
- Hormones are chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands and have specific functions
Hormones in Plants
- Rather than producing an electrical impulse, invigorated cells discharge a substance compound
- This compound would diffuse all around the original cells and other cells around can detect this compound, recognize information, as well as transmit it
- They are incorporated at places from where they act and essentially diffuse to the space of activity from where it may later branch out to all the cells of the body
- Different plant hormones help in different activities such as coordinated growth, development and responses to the environment, such as:
- Auxin: Auxins are blended at the tip of roots and shoots, it assists the cells with longer development. They play a cardinal role in coordinating various growth and behavioural processes in the life cycles of plants.
- Gibberellins: Gibberellins also help in regulating various developmental processes in plants. Like auxins, they help in the growth of the stem. They also play an important role in dormancy, flowering and flower development. Dwarf plants have low levels of gibberellins. It also functions to stop seed and bud dormancy.
- Cytokinin: Promote cell division and are present in greater concentration in areas of rapid cell division, such as in fruits and seeds. They also play an important role in promoting cell division in the roots and shoots of plants.
- Abscisic acid: Abscisic acid regulates various aspects of plant development and growth. It results in wilting of leaves. It inhibits growth and also helps the plants manage stress responses.
- Ethylene: Ethylene mainly performs two functions- it helps in the ripening of fruits and it plays an important role in the dropping of leaves, fruits and flowers (abscission). It is a very unusual plant hormone as it occurs in the gaseous form.
Hormones in Animals
Hormones play an essential role in coordinated growth in animals (humans) such as:
- Thyroxine: It directs sugar, protein, and fat digestion in the body to give the best equilibrium to development. Iodine is important for the thyroid organ to make thyroxine chemicals.
- Insulin: This is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels.
- Growth hormone: It is secreted by the pituitary gland. It manages the development and advancement of the body. Its lack of youth prompts dwarfism.
- Testosterone in males and Oestrogen in females: These are responsible for dramatic changes in appearance associated with puberty.
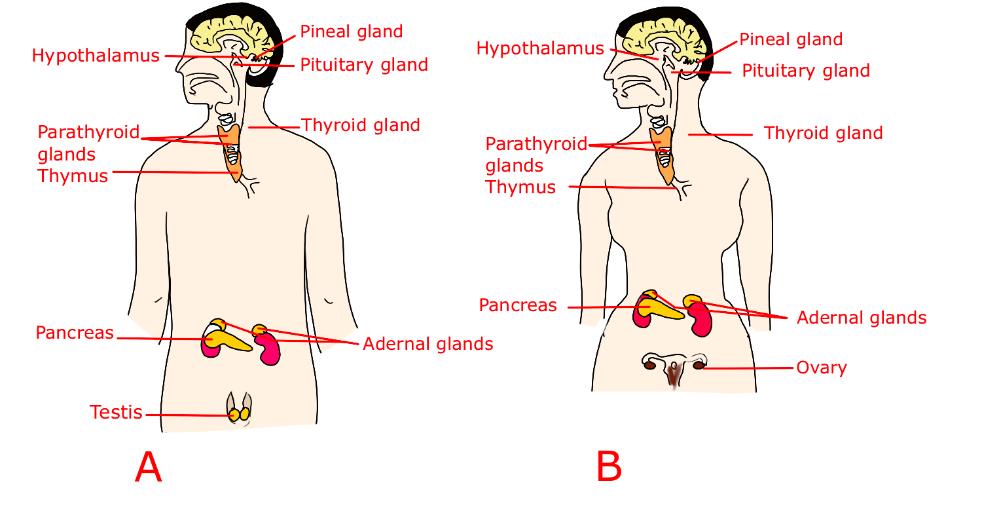
Endocrine Glands in Human Beings
- Adrenaline is secreted from the adrenal glands and is part of the endocrine system, which helps control and coordinate our body
- Secretion of the adrenaline hormone maintains the salt balance in the blood
- Adrenaline is produced by the adrenal gland that helps the body adjust to a stressful situation like anger
- The thyroid gland produces thyroxine hormone and an imbalance in the level of thyroxine causes Goitre disease
- The parathyroid gland is also located in the neck region and it helps in controlling the calcium levels in our bones and blood
- The pineal gland is located in the middle of the brain
- It regulates the sleep-wake cycle
- Insulin hormone is produced by the pancreatic gland and its deficiency causes Diabetes disease
- Glands such as sweat, oil, and salivary glands release their secretions through ducts
- Hormones are directly released into the bloodstream, and so they are called ductless glands or endocrine glands
The amount of each hormone released is controlled by the endocrine system. This can be influenced by the quantities of hormones already present in the blood, as well as the levels of other chemicals present in the blood, such as calcium. Hormone levels are affected by a variety of factors, including stress, illness, and changes in blood fluid and mineral balance.
Conclusion
In plants and animals, chemical communication takes place through chemical messengers like hormones. Different plant hormones help in different activities such as coordinated growth, development and responses to the environment, such as auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins and abscisic acid. Auxins are chemicals that aid in the development of plants. The true function of abscisic acid is to preserve dormancy by closing the stomata, the microscopic holes in leaves that enable things to arrive and depart. Hormones called cytokinins encourage plant cells to proliferate. Gibberellins are chemicals that encourage the production of plants. Hormones are transmitters in animals that assist regulate physiological activities like temperature, appetite, development, maturation, and reproduction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











