A prism is a clear, smooth flat optical object that reflects light. Because objects with both parallel surfaces polished cannot be considered as prisms, one of their surfaces must be tilted in a prism. Prisms are formed from materials that are permeable to the wavelengths for which they were created. Glass, plastic, and fluorite are among the most common materials used to construct prisms. A prism has a triangular form in the classical sense.
Prism is really a unique optical object on its own. Do you guys know a prism can disperse white light into seven colours? If not then don’t worry we are going to cover this unique property of prism in this article.
An optical prism’s conventional geometrical shape is a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular side.
Atmospheric refraction
Because of the difference in air density as a function of height, atmospheric refraction causes light or other electromagnetic waves to deviate from a straight path as they move through the atmosphere. When measuring the location of celestial and earthly objects, atmospheric refraction is taken into account. The bending of light beams as they move through the layers of the earth’s atmosphere with various optical densities causes atmospheric refraction.
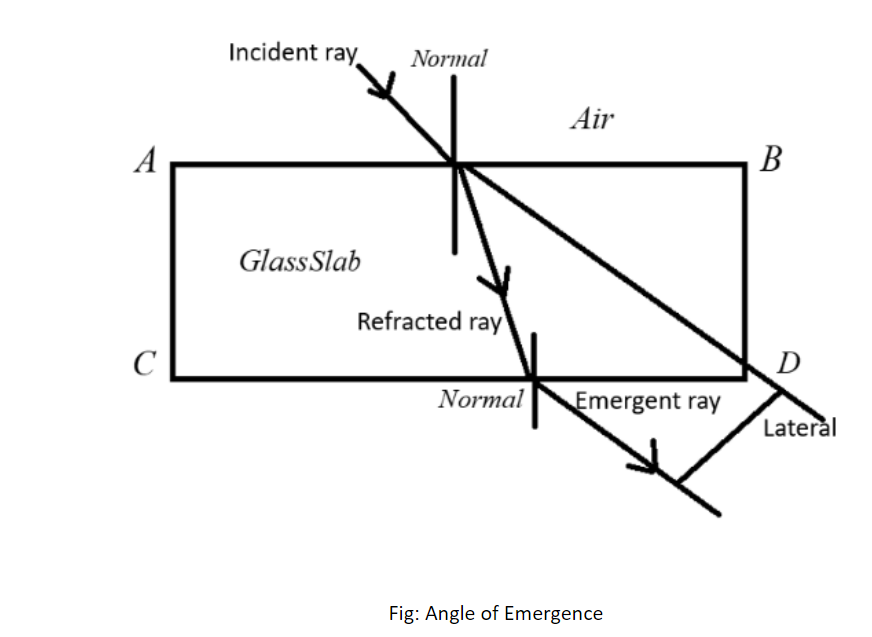
Glass Prism:
A beam of light is diverted twice as it enters the glass prism. The first time it enters the glass prism, and the second time it exits the prism.
Prism and Phenomenon of Rainbow
- The incident white light is divided into a band of colours by the prism.
- The first person to utilise a glass prism to get the spectrum of sunlight was Isaac Newton.
- The spectrum of a light beam is the band of its coloured components.
- Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red are the different colours of the spectrum. The abbreviation VIBGYOR can be used to recall these.
- Dispersion is the breaking of light into its component colours.
- As light passes through a prism, it bends at various angles in relation to the incident ray. The violet light bends the least, whereas the red light bends the most.
- White light is a term used to describe any light that has a spectrum comparable to that of sunshine.

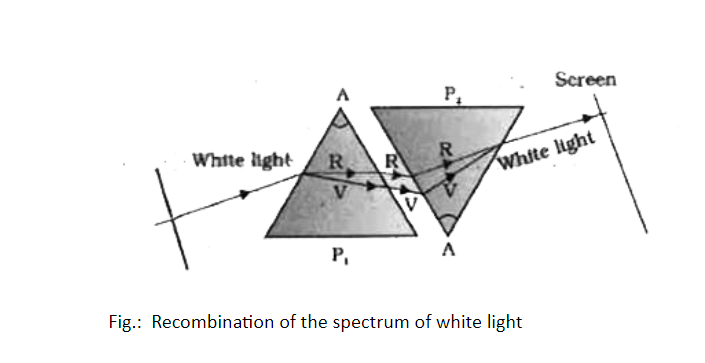
- If a second identical prism (in an inverted position with respect to the first prism) is placed and all the colours of the spectrum are allowed to pass through the second prism:
- Then a beam of white light emerges from the other side of the second prism.
- This is referred to as the Recombination of the spectrum of white light.
Deviation of light by prism
The deviation of light in prism happens because the light of different colours has different wavelengths that are refracted to different extents. Let’s have a look to understand the cause of dispersion in detail.
The seven different colours of the visible light spectrum have different wavelengths and frequencies. The band of prism colour in the visible spectrum is given by the VIBGYOR (V for Violet, I for Indigo, B for Blue, G for Green, Y for Yellow, O for Orange and R for Red). Among these colours, violet light has the lower wavelength, and red light has the higher wavelength. Also, violet light has more frequency, whereas red light has less frequency. When white light like Sunlight travels through air or vacuum, all the seven colours of light travel at the same speed. But when the same colours of light enter a dispersive medium like a Prism, their speed changes.
Dispersion of light by prism
The phenomenon of splitting the light when passing through the prism in 7 different colours is called dispersion of light by prism. The different colours seen are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red. The sequence of colours is by default taken as VIBGYOR. Where the V indicates Violet, I indicates Indigo, B indicates Blue, G indicates Green, Y indicates Yellow, O indicates Orange and R indicates Red.The band of seven colours is called visible light spectrum. The different colour of light bends at a different angle with respect to the incident angle. The violet light is bending the least while the Red light is bending the most. The recombination of light was first observed by Newton.
The phenomenon of Rainbow:
A rainbow is a natural spectrum that appears in the sky after the rain stops.
- The dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets in the atmosphere produces it.
- It always forms in the opposite direction of the Sun.
- Small prisms are formed by the water droplets. It refracts and disperses incident sunlight, then reflects it inside before refracting it as it leaves the raindrop.
Conclusion
Prism is a unique optical instrument that has certainly shown us some great optical phenomena. From breaking the white light into seven colours to the unrealistic bending of the incident ray, it has done nothing but amazed us.
In this article, we have tried our level best to help you in understanding such phenomenon of the prism with the help of angle of incidence, angle of deviation, dispersion of light, etc. So, we hope that you found this article useful and it would have added some insight to your knowledge base regarding this topic.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











