Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition refers to how an organism consumes food and how the body processes it. Nutrients are food components that include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals. Plants make their food using the Sun’s energy. Nutrition in plants is received through the process of photosynthesis. In this process, the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is converted into oxygen by the chlorophyll in plants. The plants that create their food are called autotrophs. The plants that receive nutrition through autotrophs are called heterotrophs.
Different Modes of Nutrition in Plants
Here are the different modes of nutrition in plants:
Autotrophs: They are green plants that can produce food for themselves through photosynthesis. Some examples of autotrophs are grass, wheat, and so forth.
Heterotrophs: Heterotrophs are plants that rely on other plants (autotrophs) for their food supply, similar to humans and animals. Cuscuta, for example, eats ready-made nourishment from the plant it climbs. The host plant is the one on which it climbs. Cuscuta is a parasite because it deprives the host of essential nutrients.
Saprotrophs: Many fungi get their food from decaying and dead materials. Mushrooms, for example, are saprotrophs.
Insectivorous: Just a few plants are capable of trapping and digesting insects. Insectivorous plants are those that consume insects. The pitcher-like or jug-like structure is a transformed portion of the leaf in such plants. They could be green or in any other colour.
Symbiosis: Symbiosis is a relationship in which two or more organisms live together and share shelter and nourishment. Symbiosis is the term for this type of association. Lichen, for example, is a symbiotic relationship between algae (a partner that contains chlorophyll) and fungus. The fungus provides the algae with shelter, water, and minerals. In return, algae prepare and provide food to the fungus.
Photosynthesis:
Green plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
- The roots take water and minerals from the soil and transmit them to the leaves
- Carbon dioxide from the air is absorbed through tiny pores on the leaf’s surface. A ring of ‘Guard Cells surrounds these openings.’ Such pores are known as stomata
- Chlorophyll, a green pigment found in the leaves, contributes to capturing solar energy. The process of food synthesis that occurs in the presence of sunlight is known as photosynthesis
- It’s the only process of its kind on the planet. Solar energy is captured by the leaves and stored in the form of food by the plant
- When chlorophyll-containing cells in leaves use carbon dioxide and water to make carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight, this is known as photosynthesis. Oxygen is also emitted throughout the process
- Apart from the leaves, photosynthesis occurs in other green parts of the plant. Desert plants, for example, have spine-like leaves and photosynthesising green stems
- Chlorophyll can also be found in non-green plants. The green colour of such plants is hidden by a large amount of red, brown, and other colours
- Algae can also do photosynthesis to prepare their food
Synthesis of Plant Food Other than Carbohydrates:
- Proteins are nitrogenous substances and another major nutrient
- Plants are unable to absorb Nitrogen in their gaseous state. Some soil bacteria that live in the roots of the plants transform gaseous Nitrogen into a usable form, which the plants take along with water
- Farmers’ fertiliser also supplies Nitrogen straight to the soil in a helpful form
- The plants can meet their nitrogen requirements and the requirements of the other elements in this manner. Plants can then synthesise proteins and vitamins
Nutrient Replenishment in Soil:
- To enhance the soil, fertilisers and manures are employed. Nutrients including Nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus are found in these
- Rhizobium is a bacteria that can transform ambient Nitrogen into a helpful form. Rhizobium is a nitrogen-fixing bacteria that resides in the roots of legumes like gram, peas, moong, beans, and other legumes. In exchange, the bacteria receive food and shelter from the plants. They have a symbiotic interaction as a result. This can help to reduce the amount of nitrogen fertiliser used
Conclusion
Food contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These food components are known as nutrients, and our bodies require them. All living beings need nourishment. Creating food and receiving nutrition in plants is through the process of photosynthesis. Plants can make their food, but animals, including humans, cannot. It is obtained from plants or animals that consume plants. As a result, humans and animals are directly and indirectly dependent on nature. Nutrition is the process through which an organism consumes food and uses it. Autotrophic nutrition refers to how organisms produce their sustenance from essential ingredients. Plants prepare food for animals and most other creatures. They are known as heterotrophs. Saprophytes are organisms that get nourishment from dead and decaying substances.
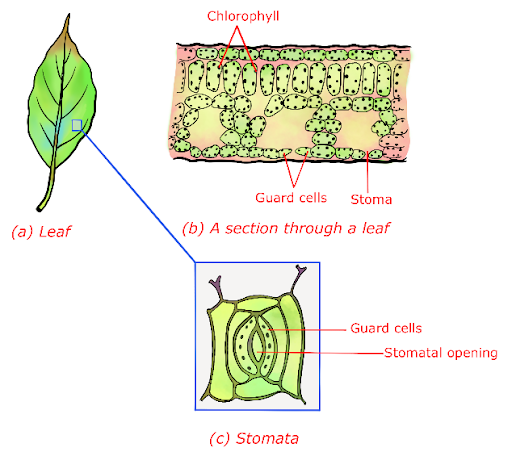
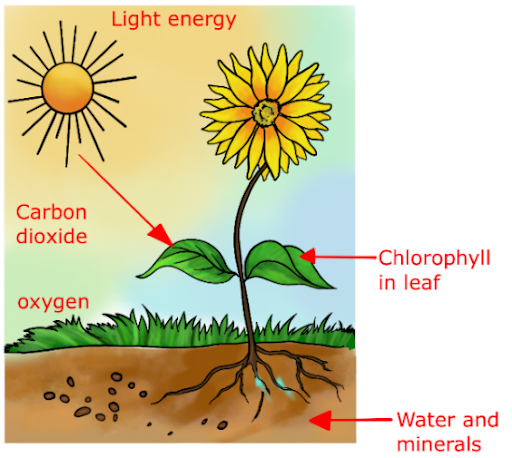
Fig.: Leaf Details
Fig.: Diagram showing Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
- Apart from the leaves, photosynthesis occurs in other green parts of the plant as well. Desert plants, for example, have spine-like leaves and photosynthesizing green stems
- Chlorophyll can also be found in non-green plants. The green colour of such plants is hidden by a large amount of red, brown, and other colours
- Photosynthesis can also be done by algae to prepare their food
Synthesis of Plant Food Other than Carbohydrates:
- Proteins are nitrogenous substances and another major nutrient
- Plants are unable to absorb nitrogen in their gaseous state. Some soil bacteria that live in the roots of the plants transform gaseous nitrogen into a usable form, which is taken by the plants along with water
- Farmers’ fertilizer also supplies Nitrogen straight to the soil in a useful form
- The plants can meet their nitrogen requirements as well as the requirements of the other elements in this manner. Proteins and vitamins can then be synthesized by plants
Nutrient Replenishment in Soil:
- To enhance the soil, fertilizers and manures are employed. Nutrients including nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus are found in these
- Rhizobium is a bacteria that can transform ambient nitrogen into a useful form. Rhizobium is a nitrogen-fixing bacteria that resides in the roots of legumes like gram, peas, moong, beans, and other legumes. In exchange, the bacteria receive food and shelter from the plants. They have a symbiotic interaction as a result. This can help to reduce the amount of nitrogen fertilizer used
Conclusion
Food contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. These food components are known as nutrients, and our bodies require them. All living beings need nourishment. Creating food and receiving nutrition in plants is through the process of photosynthesis. Plants can make their food, but animals, including humans, cannot. It is obtained from plants or animals that consume plants. As a result, humans and animals are directly and indirectly dependent on nature. Nutrition is the process through which an organism consumes food and uses it. Autotrophic nutrition refers to how organisms produce their sustenance from essential ingredients. Plants prepare food for animals and most other creatures. They are known as heterotrophs. Saprophytes are organisms that get nourishment from dead and decaying substances.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out








