The intersection of the demand and supply curve sets the price for the market and goods sold in the market, this condition is termed market equilibrium.
Market Equilibrium, Excess Demand and Excess Supply
Equilibrium:
In equilibrium, firms sell the equal quantity that consumers in the market wish to buy.
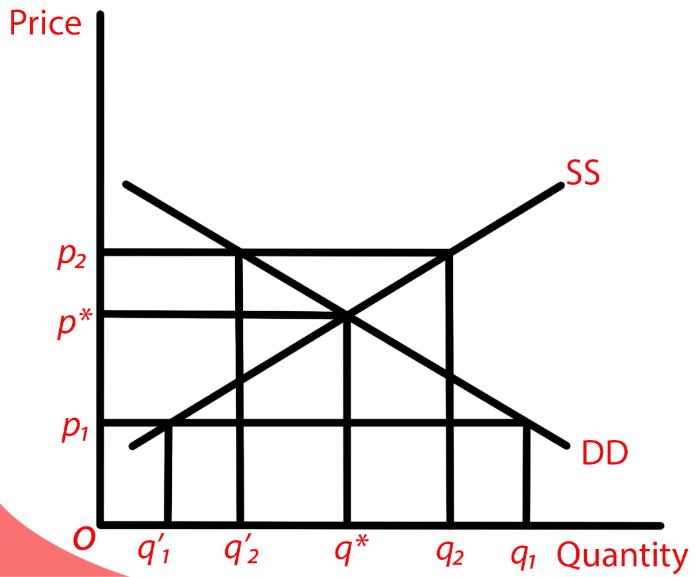
- Supply increases in the market with the increase in the demand of the market whereas on the other hand, if the demand of the market exceeds the supply price, then it is said that excess demand exists in the market
- A competitive market is a state of equilibrium having zero excess demand-supply like situation
- The price of the market is changed when there is a change in the equilibrium of market supply and market demand as of when the market is not in equilibrium
- In the given below graph, SS represents the market supply, DD represents the market demand and the equilibrium point is the point of intersection of DD and SS
The Shift in Demand and Supply:
- Any change in demand and supply curve shifts the equilibrium points
- Any change in the factors like technology, consumer Preferences etc. shifts the curve either upward or downward
- A new equilibrium point is reached when the market equilibrium is disturbed due to a change in demand or supply curve
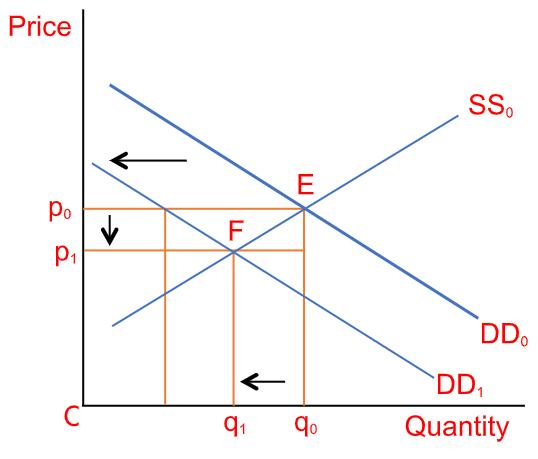
In the above graph, the original Market Demand (DD0) shifts to the new market demand (DD1). Due to which the original equilibrium point E gets disturbed, and a new equilibrium Point (Point F) is derived where the new and changed market demand now meets the market supply.
Market Equilibrium: Free Entry and Exit
Under perfect competition, an important feature being the free entry and exit firms, also has certain other implications.
- In equilibrium, no firm earns a supernormal profit or incurs loss by remaining in production (i.e., in other words, the equilibrium price will be equal to the minimum average cost of the firms)
- If, due to free entry, firms are able to earn at Supernormal Profits, then this attracts other firms too into the market
- Market supply increases with the entry of new firms while demand remains constant. As a result of this, the market price falls and hampers other profits. Similarly, when a loss occurs in the market then some firms exit from the market and this reduces the supply by driving the market price up
- Thus, free entry and exit, allows each firm to earn normal profit at the prevailing market price
Applications of Demand-Supply Analysis
Price Ceiling:
- The upper limit imposed by the Government on the price of a good or service is referred to as Price Ceiling
- Generally imposed on necessary items like wheat, rice etc. as a large section of the population cannot afford these items at the market-determined prices
- Price ceiling discourages suppliers to supply the goods at a lower price than the market determined price. Moreover, the quantity they are willing to supply is lower than the quantity that the consumers want to consume
- The government uses some policies to tackle these types of situations like rationing so that no individual can buy more than a certain amount. This stipulated amount is distributed through ration shops also called Fair Price Shops
Price Floor:
- The lower limit imposed by the Government on the price that may be charged for a particular good or service is called the price floor
- This is used for agricultural Produce
- Government sets up an agricultural price support programme, to fix prices of the produce above the market determined price
- Similarly, it is also used to set a floor wage rate which is above the market determined wage rate
- This leads to excess supply in the market, and to prevent the prices from falling, the government purchases the excess supply and produce available in the market
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have looked into what market equilibrium is. Market equilibrium or Economic equilibrium is a state in which the economic forces such as supply and demand are coordinated and the values of economic variables do not change as a result of the absence of external influences. When the supply and demand curves are merged, a point is reached where they overlap, and this is known as the point of market equilibrium. The price is the equilibrium price, and the quantity is the equilibrium quantity at this point of intersection.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out








