Marginalisation is a concept where a certain group or individual is made to feel like socially unacceptable due to their religion, caste, creed, race, and sex. There is disrespect, humiliation, and name-calling by those in power. Marginalisation can cause serious consequences, not only to the people belonging to the marginalised group, but also to the entire concept of unity of a nation. India is a secular country, thus, marginalisation is prohibited and discouraged by law.
Minorities and Marginalisation:
- The term minority is used to refer to smaller groups in comparison to the rest of the population
- This concept goes well beyond numbers and concerns issues of power, access to resources, social and cultural dimensions
- Majorities usually enjoy support due to their large number. In such a situation, the minority groups are sometimes overlooked
- Minorities are often left feeling uncertain about their lives and well-being due to the treatment they are given in society
- The Constitution of India tries to overcome these differences by providing Fundamental Rights to minority communities that protect them from being ill-treated
- Legal executive plays a critical part in maintaining the law and enforcing Fundamental Rights
Marginalised Communities in India
- Those groups that are being treated as less important, or treated like outsiders are known as marginalised communities
- This section of society faces discrimination and humiliation due to its number
- There are various kinds of marginalised communities based on color, caste, sex, and religion
- Women are considered to be marginalised due to the presence of gender equality .Often, women are excluded from certain jobs because of their gender
- Scheduled Castes are treated in a humiliating manner because of their caste. Marginalisation, in such a situation, would involve economic as well as social discrimination, and even access to certain resources
- Scheduled Tribes, or Adivasis, are robbed of their own land and its resources
- Other groups include People with Disabilities, or the elderly
Muslims and Marginalisation:
Muslims are considered a minority in India due to the fact that in contrast they have been denied the advantages of economic development throughout the years. The following three tables show the situation of the Muslim social class concerning the different spheres of issues:
- Access to Basic Amenities:
According to the India Human Development Report 2011, the following is the distribution of basic necessities among different communities:
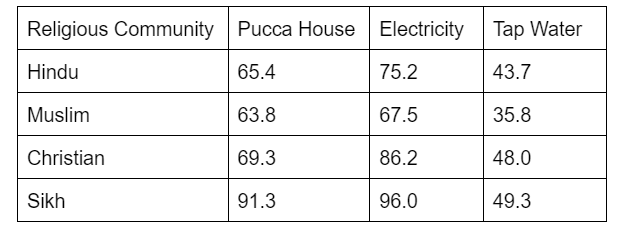
- Literacy rate by Religion: According to the Census of 2011 of India, the following is the literacy rate among different communities. The values are in percentages

- Public employment of Muslims: The Prime Minister’s High-Level Committee Report of 2006 revealed the state of employment of Muslims in the public sector. Following are the percentages:
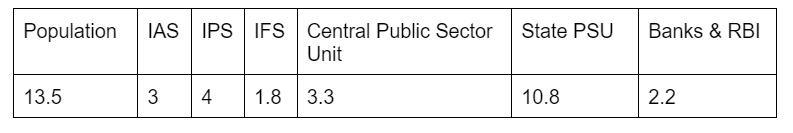
In addition to this, Muslims also face unfair treatment and discrimination because of the differences in their customs and practices from the mainstream.
Rajinder Sachar Committee for Muslims:
- The government perceived that Muslims in India were overlooked when it came to development. Hence a significant level board in 2005 was set up
- This body was known as the Sachar Committee and examined the social, economic, and educational status of the Muslim community in India
The major findings of the committee are:
- The average stretches of tutoring for Muslim kids between the ages of 7-16,is much lower than that of other socio-strict networks
- It debunked the myths about Muslims that they prefer to send their children to Madrasas. In actuality, 4 percent of Muslim children are in Madrasas, whereas 66 percent attend government schools ad 30 percent in private schools
Conclusion
Marginalisation refers to the process where individuals are made to feel like an outsider. Marginalised groups in India face humiliation, exclusion, economic deprivation, as well as ill-treatment. There are various groups that are marginalised such as women, people with disabilities, the aged, scheduled castes and scheduled tribes. Muslims and Adivasis are two groups that are highly marginalised. Due to their minority status, they are believed to be different from the normal and face discrimination on the basis of their religious practices, culture, and various other reasons. Provisions have been made by law as well as the Government to ensure equality in the nation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











