When talking about the most common type of average in statistics, the same includes mean, mode, and median. These are basically the values that represent and describe the set of observations in the entire collection. The value of mean, mode, and median used to represent the data set are referred to as measures of central tendency. In simple words, it can be said that these three types of averages are the values around which the given data is centered.
What is meant by mean in statistics?
When it comes to the Mean Types of Averages in statistics, these basically represent the average of a given set of data. It is the most common tool that is used in measures of central tendency. The value of the mean can be expressed as equal to the sum of all observations given in the set of data divided by the total number of values given in the same data set.
Calculation of mean
The mean for the ungrouped data can be calculated by dividing the sum of the values given in the data set by the total number of values. It can be represented mathematically as:
Mean = Sum of all values in a data set / Total number of values in the data set
The same formula can be represented symbolically as:
Mean = ∑x/n
where,
∑ represents the values that are to be added;
x represents all values in the given data set; and
n represents the total number of values in the given data set.
The Mean Types of Averages for the grouped data can be calculated using three methods:
- Direct method: As per this method, the following mentioned formula is used to calculate the mean:
Mean = ∑xifi / ∑fi
- Assumed Mean method: As per this method, the following mentioned formula is used to calculate the mean:
Mean = A +∑fidi / ∑fi
Step-deviation method: As per this method, the following mentioned formula is used to calculate the mean:
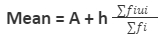
What is meant by the median in statistics?
The Median Types of Averages represent the middlemost value of the given set of observations when the same are arranged in descending or ascending order. It is imperative to know if the total numbers given in the data set are odd or even to calculate the value of the median.
Calculation of median
First, the observations in the given data set are arranged in ascending or descending order to calculate the median of the ungrouped data. In case the total number of observations (n) is odd then the following mentioned formula is used:
Median = n + 1/2th Observation
In case the total number of observations (n) is even then the following mentioned formula is used:
Median = [(n /2)th Observation + ((n/2) + 1) th Observations] / 2
When it comes to the calculation of Median Types of Averages for ungrouped data the following mentioned formula is used:
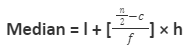
where,
l represents the lower limit of median class;
c represents the cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class;
f represents the frequency of the median class; and
h represents the class size.
What is meant by the mode in statistics?
The mode is one of the most common types of average that represents the most repetitive value in the given set of data. It is possible to have more than one mode in one particular data set. In case there are two modes for a given set of observations then it is referred to as bimodal and when there are more than two modes then it is referred to as multimodal.
Calculation of mode
When calculating the mode for ungrouped data, it can be found by visually observing the value with the highest frequency.
The following mentioned formula is used when calculating the value of mode for the grouped data:
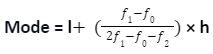
Where,
l represents the modal class’s lower limit;
h represents the class interval’s size;
f1 represents the frequency of the modal class; and
f0 represents the frequency of the class preceding the modal class
f2 represents the frequency of the class succeeceding the modal class
Conclusion
Mean, median, and mode, in statistics, are the most common type of average that is used to provide information about the center, middle part, or frequently repeated number of a given data set. These three are known as measures of central tendency that represent the values in the given data set. To learn more about the concept of types of averages it is recommended to go through the above-mentioned article.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out













