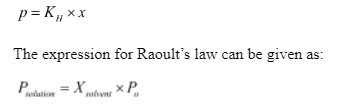The colligative properties of a solution are those that are affected by the concentration of molecules or ions in the solute, but not by the solute’s identity. Vapour pressure is reduced, the boiling point is raised, the freezing point is lowered, and the osmotic pressure is reduced.
Ideal gas laws
Boyle’s law: a law indicating that under constant temperature, the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
Charles’ law: The volume of an ideal gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to the absolute temperature, according to the law.
Avogadro’s law: a statement that equal volumes of different gases contain an equal number of molecules under the same conditions of temperature and pressure.
Ideal gas equation:
On combining all the three laws mentioned above, the ideal gas equation can be given as:
The ideal gas equation can be given in the form:
Where;
P is the pressure of the ideal gas.
V is the volume of the ideal gas.
n is the amount of ideal gas measured in terms of moles.
R is the gas constant.
T is the temperature.
What is Raoult’s law?
In 1887, Raoult’s Law was enacted. François-Marie Raoult, a French chemist, found in 1886 that when a solute is dissolved in a solvent, the vapour pressure of the resulting solution generally decreases.
His conclusion was based on the following two factors:
Vapour pressure of the pure solvent
mole fraction of the dissolved solute
The formula can be given as:
Where,
is the vapour pressure of the solution
is the mole fraction of the solvent
is the vapour pressure of the pure solvent.
What is the difference between Raoult’s and Henry’s laws?
Henry’s law can be used to explain how a gas dissolves in a liquid solvent like water. Raoult’s law describes the behaviour of a solvent in a solution that is in equilibrium with its vapour pressure.
However, there are several limitations when applying these laws to real-world circumstances.
The fundamental difference between Henry’s Law and Raoult’s Law is that Henry’s Law deals with the behaviour of the solutes in a solution, whereas Raoult’s Law deals with the behaviour of the solvent in a solution.
What is the distinction between Raoult’s and Dalton’s Law?
The partial pressures of gaseous states are explained by the Raoult’s and Dalton’s laws, which are very important rules in chemistry.
Raoult’s law is concerned with the vapour pressure of solids or liquids, whereas Dalton’s law is concerned with the partial pressure of non-reacting gases.
Raoult’s law states that the vapour pressure of a solvent above a solution is equal to the pure solvent’s vapour pressure at the same temperature scaled by the solvent mole fraction in the solution.
Meanwhile, according to Dalton’s law, the overall pressure of a mixture of non-reacting gases equals the sum of their individual pressures.
Limitations of the law
Raoult’s law is especially useful since it explains ideal solutions, which are ones in which the gas phase has thermodynamic properties that are similar to a combination of ideal gases. The only problem is that they are rare and difficult to come by.
Many solutions deviate from Raoult’s law due to the lack of chemical equivalency between distinct chemical components. As a result, do not follow it appropriately.
How Raoult’s law applies to dilute solutions:
It holds true for both a large number of highly dilute and a small number of concentrated solutions, especially those in which the affinities between the molecules of solute and solvent are the same as the affinities between the molecules of each component separately.
Conclusion:
The partial vapour pressure of a solvent in a solution (or mixture) is equal to or identical to the pure solvent’s vapour pressure multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution, according to Raoult’s law.
Raoult’s law is especially useful since it defines ideal solutions or those in which the gas phase has thermodynamic properties that are comparable to a combination of ideal gases.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out