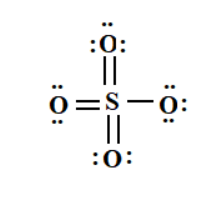As a naturally producing mineral on earth, Sulphate (SO42-) is among the most available and preferable chemical compounds known as sulphate compounds. Due to terrestrial and atmospheric processes sulphate is easily available in the environment. The main compositions of sulphate are oxygen atoms and sulphur atoms. Sulphates in Chemistry are considered polyatomic anions or inorganic ions. Sulphates are formed by the deprotonation of sulphuric acid from both the OH groups. Sulphates are also considered to be the ester or salt of sulphuric acid. Sulphate is a derivative of acid from various metals. The main function of sulphate includes cell growth in a proper way and an organism’s development.
Properties of sulphate
There are two types of properties of sulphate ions; these are physical properties and chemical properties:
The physical Properties of sulphate are –
During the reaction, sulphates form white precipitates. For example- When the reactions of sodium sulphate occur with barium chloride, then white precipitate is formed. The precipitation that is formed is of BaSO4.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
Generally, ionic sulphates are water-soluble. But there are some exceptions like calcium sulphate, lead sulphate, strontium sulphate, and barium sulphate.
The Chemical Properties of sulphate are –
Sulphate compounds have organic esters such as dimethyl sulphate falls under covalent compounds and sulphuric acid’s esters. The Sulphate ion itself is a conjugate base of two other ions like sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and bisulphate ion (HSO4-).
The easy combination of sulphates with metals is another property of sulphate. The 4 oxygen atoms that are connected in sulphate ions act as arms and have the ability for attracting metals for forming a connection.
The functions or uses of sulphate
Sulphate has various functions in our day-to-day life. The main function of sulphate is in the organism’s development and the growths of cells are also a function of sulphate in the body of living beings. Also, sulphates are easily found in nature and are commonly synthesised in industries. Sulphate is a chemical compound that has functions or uses in a large number of products. Given below are some functions of sulphates –
Cosmetics products like body sprays, soaps, make-up products, toothpaste, etc. contain sulphates within them.
Barium sulphate is used for the treatment of water and electricity domain copper sulphate is used.
In cleaning products sulphates are used, so that the cleaning products become more effective.
In constructions also sulphates are used.
In the products which are used for cleaning grease from any machinery, sulphates are contained within it as sulphates are powerful surfactants.
Generally, sulphates are used for making emulsifiers, foaming agents, detergents, etc.
In therapeutic baths, magnesium sulphates are used.
In plasters, gypsum – which is a form of hydrated calcium sulphate found naturally, is another main function of sulphate.
For making metal salts sulphate minerals are used.
The structure of sulphate
The vital part of the structure of sulphate is the molecular structure of sulphate and the chemical bonding within it. The structure of sulphate consists of a central atom which is sulphur and it contains four oxygen atoms within it which are lying on the same plane at an equal distance from the sulphur atom. The angle at which the four-oxygen atom of sulphate is placed is 109.5 degree. The oxygen atoms that surround the sulphur atoms have 2 different forms; among the four oxygen atoms – 2 of them are in the form of S-O bonds and the other 2 atoms of oxygen are in the form of S=O bonds in sulphate. The molecular structure of sulphate has a tetrahedral geometry that further relies on the theory of VSEPR. The ‘-2’ state that is present in the sulphate ions is due to the anion’s negative charge in it. The structure of sulphate can be represented as –
Conclusion
It is to be concluded that there are two groups of derivatives in sulphate – the first group contains the salts which consist of the sulphate ions themselves, and also consists of ions having positive charges of magnesium, ammonium, or sodium. The second group contains esters, where the atoms of carbon-containing groups like ethyl (C2H5) or methyl (CH3) replace the hydrogen atoms of hydrogen of sulphuric acid. There are two main functions of sulphate: the growth and development that occurs in the body of living organisms.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out