Potassium dichromate is risky to our health but beneficial to industries and labs. This dichotomy makes it an interesting compound to pursue upon. It is most commonly used as an oxidising agent in various chemical reactions. It is bright red-orangish in colour and an ionic crystalline solid. In reaction with water, it gives dichromate(Cr2O7 2–) and chromate(CrO42–) ions, and these respective ions are primarily the reason for potassium dichromate’s reactivity. When acid is used in the reaction and potassium dichromate(the mixture is acidified potassium dichromate), it provides an acidic medium used in various titrations.
Structure and Formula
It is chemically formulated as K2Cr2O7 (Molar mass: 294.185 g/mol) and is a hexavalent chromium compound wherein an ionic bond bonds two potassium ions. Each chromium atom is covalently bonded to 3 oxygen atoms forming a butterfly-like shape.
It generally exists as dichromate(Cr2O7 2–) and chromate(CrO42–) ions. The chromate ion is tetrahedral by geometry, whereas the dichromate ion consists of two tetrahedra sharing one corner with Cr–O–Cr bond angle of 126∘ and a bond length of Cr-O bond is 179pm.
The coordination geometry for chromium is tetrahedral.
The crystal structure is triclinic (unequal length and angles of a unit cell).
Chemical properties of potassium dichromate:
The various chemical properties and K2Cr2O7 reactions:
Volumetric analysis: Potassium dichromate, a very strong oxidising agent, is extensively used as a primary standard(a highly pure and stable solution) in several volumetric analyses.
Cr2O7 2– + 14H+ + 6e– → 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
Now, the above-acidified potassium dichromate will oxidise iron(II) to iron(III) or Iodides to iodine.
6I– → 3I2+ + 6e–
6Fe+2 → 6Fe+3 + 6e–
The full ionic equation in the case of iron and acidified potassium dichromate
can be written as follows:
Cr2O7 2– + 14H+ + 6Fe2+ → 2Cr3+ + 6Fe3+ + 7H2O
The full ionic equation of iodide and acidified potassium dichromate can be
written as follows:
Cr2O72-+ 14H++ 6I–→ 2Cr3+ + 7H2O+ 3I2
Chromyl chloride test: This test recognises chloride ions in solution or salt analysis experiments.The test is said to be positive for a solution when the emission of reddish and brown vapours is observed due to the formation of chromyl chloride(CrO2Cl2).
K2Cr2O7 + 4KCl + 6H2SO4 → 2CrO2Cl2 + 3H2O+ 6KHSO4
Decomposition reaction: When potassium dichromate is heated, it yields oxygen gas and potassium chromate.
4K2Cr2O7 → 4K2CrO4 + 3O2 + 2Cr2O3
Action with cold dilute and hot concentrated H2SO4: Following are the reactions of acidified potassium dichromate.With cold dilute acid:
K2Cr2O7 + 2H2SO4 → 2CrO3 + 2KHSO4 + H2O.
With hot concentrated acid:
2K2Cr2O7 + 8H2SO4 → 2K2SO4 + 2Cr2(SO4)3 + 8H2O + 3O2
With alkalies: On the reaction of potassium dichromate with alkalies, a yellow colour compound(potassium chromate) is formed
K2Cr2O7 + 2KOH → 2K2CrO4 + H2O
Orange colour Yellow colour
On the formation of acidified potassium dichromate, the orange colour can regenerate.
Sulphur dioxide test: The paper of potassium dichromate is extensively used to test sulphur dioxide. This paper is originally orange in colour, but it turns green in reaction to sulphur dioxide. The reaction for the same is as follows:
SO2 + K2Cr2O7 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 3H2O
Atomicity of Potassium
Atomicity is basically defined as the total number of atoms present in the molecule. Generally, atomicity is equal to valency. Based on this concept, molecules can be classified as
Monoatomic: Having one atom, for example, noble gases
Diatomic: Having two atoms, for example, Cl2 or O2
Triatomic: Having three atoms, for example, Ozone(O3)
Polyatomic: Having more than three atoms, for example, S8
So with that said, the atomicity of potassium is one, i.e. it’s a monatomic atom.
Miscellaneous properties
Apart from the above-listed chemical properties of potassium dichromate, there are various other properties like it is soluble in water but not in alcohol and acetone.
Following are the miscellaneous properties for the same:
Odour | Odourless |
Appearance | Orange-red crystal |
Density | 2.676 g/cm3 |
Boiling point | 500°C |
Melting point | 398°C |
Heat capacity | 219 J/mol |
Conclusion
Potassium dichromate(K2Cr2O7) is an inorganic ionic compound and is a crystalline solid of reddish-orange colour without any odour having a molar mass of about 294.185 g/mol. It has a triclinic crystal system and tetrahedral geometry for Cr. Acidified potassium dichromate is primarily insoluble in alcohol and acetone but soluble in water. A very strong oxidising agent shows various chemical properties like chromyl chloride test, decomposition reaction, etc.
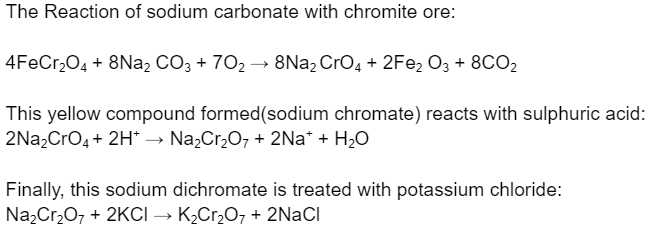
For industrial purposes, it is manufactured by a reaction of powdered manganese oxide(MnO₂) and potassium hydroxide(KOH) or by a reaction of sodium carbonate and chromite ore.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out