Newton’s law of cooling tells us that the rate of heat loss from the body or from an object is directly corresponding to the difference between the temperatures of the body or the object and the surrounding environment. The law is often qualified to incorporate the situation that the temperature difference is little and also the nature of the warmth transfer mechanism remains identical.
What Is Newton’s Law Of Cooling?
Newton’s law of cooling describes the rate at which an object cools down as compared to the difference in temperature between the thing and also the object’s surroundings. To perform this experiment just take a glass of warm water and you will observe that it cools down faster in a cool room as compared to a hot room. This simple experiment describes Newton’s law of cooling. This observation can be executed or performed by any person. This experiment is mostly met in warm conditions because the thermal conductivity of most materials is just weakly obsessed with temperature. It only determines the small temperature differences.
Newton’s Law Of Cooling Graph
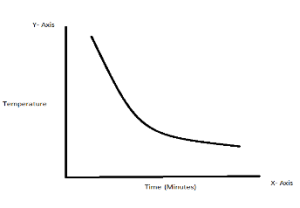
The rate at which a revealed body changes its temperature through radiation roughly corresponds to the difference between the object’s temperature and its surrounding environment.
Newton’s Law of cooling can be explained with the help figure set-up shown above. The above figure is showing a downward trend which means it is going from an upward to a downward direction. As we can see temperature is on the left side on the Y- axis and time is on the X- axis as the warm object comes in contact with the temperature of the surrounding environment it starts cooling down faster because of coming in contact with the surrounding environment.
The Formula Of Newton’s Law Of Cooling
Sir Newton, a physicist, has developed a formula through which anyone can calculate the temperature of a material or an object as it loses heat and transfers the heat from an object to the surrounding environment. As we previously see, the rate of temperature change is changing due to the difference in the temperature between the item and its surrounding environment.
According to Newton’s law of cooling, the formula of the rate of loss of heat is – dQ/dt of the body is directly corresponding to the difference in temperature is, ΔT = (T2 – T1) of the body and its surrounding environment.
. Hence, this statement can be written as:
– dQ/dt = k(T2 – T1) The above k term is a positive constant; it depends upon the environment and surroundings of the surface of the body.
Newton’s law of cooling is only for determining the small temperature differences.
Method To Apply The Newton Law Of Cooling
For the application of the Newton law of Cooling, i.e., the loss of heat is considered. Mathematically, it is expressed as the term,
dQ/dt
furthermore, the rate in the change of the temperature is considered between the body and the surrounding environment, which is expressed as,
[q-qs] (where q represents the temperature of the body and qs represent the temperature of the surrounding environment)
According to Newton’s Law of Cooling, both equations are straight corresponding to each other,
dQ/dt ∝ [q-qs]
dQ/dt=k [q-qs]
Here k is termed is donated as the constant.
However, the temperature difference between the body can be defined as the terms of the initial and final temperature of the body.
q=(qi-qf)/2
Here, qi term is the initial temperature of the body, whereas qf term is the final temperature of the body.
Applications Of Newton’s Law Of Cooling
- The Newton law of cooling is used to predict how much time will be taken for a warm object to cool down at a constant temperature of its surrounding environment.
- Through the Newton law of cooling any person can determine the temperature of the body or of any object.
Limitations Of Newton’s Law Of Cooling
- The difference between the temperatures of the surrounding environment and the object should be small.
- The loss of heat from the object should only be via radiation only.
- The temperature of the surrounding environment should remain constant during the cooling down of the object.
Conclusion
Newton’s law of cooling describes us that the rate of heat loss from a body or from an object is directly corresponding to the difference between the temperatures of the body and the environment surrounding it. The law is often qualified to incorporate the situation that the temperature difference is little and also the nature of warmth transfer. The rate at which a revealed body changes its temperature through radiation roughly corresponds to the difference between the object’s temperature and its surrounding environment, it is only for determining the small temperature. Sir Newton, a physicist, has developed a formula through which we can calculate the temperature of a material as it loses heat and transfers the heat from an object to the surrounding environment. As we previously see, the rate of temperature change is changing due to the difference in the temperature between the item and its surrounding environment.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out








