Caesium atoms when reacted with oxygen: Facts
- Caesium oxide is the main compound formed in terms of electrons as “Caesium atoms when reacted with oxygen”. It is demonstrated from “Caesium atoms when reacted with oxygen” that the reaction between any element and oxygen results in the creation of “Oxide” which is known as a binary compound
- “Caesium atoms when reacted with oxygen” are less explosive as the reaction takes some time to form a solution. It is different from “Caesium atoms when reacted with water” as it reacts quickly and produces a “colourless base of a solution” of hydrogen gas and caesium hydroxide. The reaction takes place more explosively and fast when it reacts with water (H2O)
- Apart from “Caesium atoms when reacted with oxygen” and “water”, the reaction with fluorine is enormously electronegative due to its high bonding elements attraction. The tendency of the electrons and atoms of Caesium is highly reactive as it readily makes the strongest bond with “electronegative atoms”
The general characteristics of oxides of group 2 elements: Overview
The “group 2 elements” stain in the atmosphere to form the metal oxide coating which reacts tremendously with the pure oxygen forming an oxide of white ion. “The general characteristics of oxides of group 2 elements” are:- The group 2 compounds burn with the gas of oxygen to form the metallic oxide
- Group 2 elements possess the “oxides of alkaline earth metals” which is demonstrated as less basic
- In this group, one of the important factors is that it has more bases on the “maximisation” in the character of electropositive
- Oxides in the group 2 element dissolve the water to produce “hydroxide ions” and perform as bases
- The basic oxides have the tendency to react with the substances of acid for the creation of salt and conduct electricity in the “molten state”
Group sodium and caesium: Difference and similarities
Differences
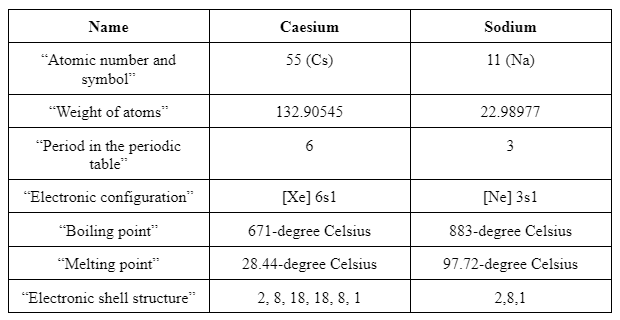
Similarities
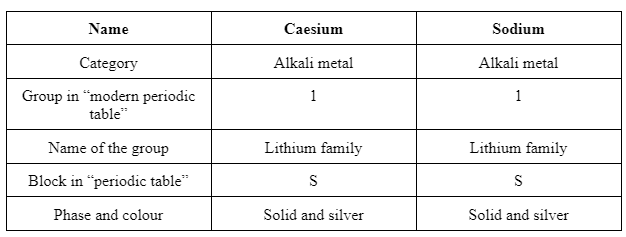
From the above tables, it is comprehended that Sodium and caesium belong to a similar group, which is collaboratively termed as “alkali metal group”. The outer electron structure of both the elements is the same, which resulted in similar chemical and physical properties. Differences shown in the table are basic in terms of atomic number, weight, structure and configuration.
Conclusion
The reaction of caesium with oxygen, water and fluorine is described which reflects that reaction with oxygen is time-consuming and is not rapid whereas fluorine is explosive. Characteristics or features of oxides of 2nd group elements are less basic as compared to the first group due to the formation of white ions. Similarities between caesium and sodium are more in comparison to the differences as they belong to the same group and same block in the periodic table. Hence, the physical and chemical properties of both the oxides are structured similarly.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











