- e-Government finds utility in harnessing ICT potential in government operations, as a measure to boost the outreach of the government services to the general public.
- e-Governance makes adequate use of ICT in bringing efficacy in the functions and structures of the system hence adding to meaningful transformation in the system of governance.
- While e-Government is a one-way communication protocol, e-Governance has a two-way channel.
Objectives of E-Governance:
- Improving service delivery to citizens: By enhancing citizens’ access to government services and by making provisions to design service delivery mechanisms that cater to all sections of society, including vulnerable groups.
- Create an informed society: By making the provisions for providing access to all, to every piece of information of public importance, an informed society is envisaged upon which is an indication of an empowered society.
- Increased interaction between Government & Citizen: In the physical world, there is rarely any interaction between the Government and Citizens. E-Governance aims to get feedback from the people and to make the Government aware of people’s problems so that necessary actions could be taken in that direction.
- Upgrading the efficiency within the Government: The introduction of technology will help in enhancing inter-governmental interactions, i.e., between centre-state and inter-states.
- Active role of a Citizen in decision-making: Working on the principles of democracy by the way of E-governance to encourage citizen participation in the Governing process and access to information by working on the feedback.
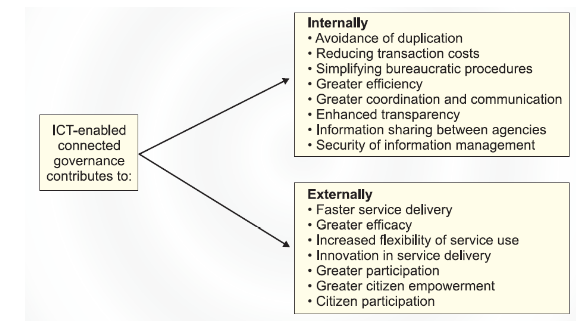
- Making the governing process more accountable and transparent: By ensuring the reach of government data to people, it results into Governing process being transparent. It is to make people aware about the policies and decisions of the Government. Government holds accountability for every decision taken by it and is answerable for the same. E-Governance plays a vital role in ensuring accountability by Government by bringing transparency and making citizens more informed.
- To cut down the cost of Governance: It also works to reduce governance costs by slashing the expenditure that is incurred because of physical delivery of services.
- To bring a significant reduction in the reaction time of the Government: Because of red-tapism, the Government takes long to respond to people’s queries and this is where E-Governance comes into play by reducing the reaction time of government to people’s issues.
Types of Interactions in E-Governance:
1. G2G (Government to Government):
- ICT finds its use in reorienting the governmental processes and to advance the reach of information and services within and between various entities.
- This kind of interaction can be horizontal (between different government agencies and different functional areas within an organisation), or vertical (between national, provincial, and local government or between different levels within an organisation).
- Primary objective is to increase performance, efficiency, and output.
2. G2C (Government to Citizens):
- With the conception of an interface between citizens and government, the accessibility and availability of public services is extended with the advancement in quality of services as well.
- It provides a choice to citizens about when, where, and how to have interaction with the government.
- The fundamental objective is to ensure citizenfriendly interface with the government.
3. G2B (Government to Business):
- E-Governance tools are utilised to help the business community to seamlessly interact with the government. The aim is to cut red tape, save time and reduce operational costs The G2B initiatives can be transactional (licensing, permits, procurement), revenue collection, promotional and facilitative, such as in trade and investment.
4. G2E (Government to Employees):
- At par with other organisations, the constant interaction of the government with the employees is needed to boost the satisfaction levels of the latter and ICT tools help in achieving this interaction in a fast and efficient manner.
Benefits of E-Governance:
- Speed: The fast-paced Internet and Cellular technologies have significantly reduced the communication time.
- Greater convenience: The benefit of accessing government services from anywhere at any time to people has been made possible with the help of e-governance.
- Cost reduction and revenue growth: The great deal of expenditure is minimised because of bringing in Internet and Phones for the purpose of communication as Paper based communication involves plentiful stationery, printers, etc. which incurs cost.
- Clarity: With the easy upload of information on the web for the citizens, the clarity quotient is ensured on the part of government.
Accountability and transparency: The Governing process automatically becomes accountable if it is made transparent.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











