Similar PYQs:
1. The ancient civilization in the Indian sub-continent differed from those of Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Greece in that its culture and traditions have been preserved without a breakdown to the present day. Comment. (2015)
भारत की प्राचीन सभ्यता, मिस्र, मीसोपोटमिया और यूनान की सभ्यताओं से इस बात में अंतर है कि उसकी संस्कृति और परंपराएं आज तक बिना किसी टूटे हुए के बनाए रखी गई हैं। टिप्पणी कीजिए।
2. What makes Indian Society Unique in sustaining its culture? (2019)
भारतीय समाज को अपनी संस्कृति को जीवित रखने में अद्वितीय बना देती हैं?
Introduction:
India’s geography has played a crucial role in shaping its civilization over millennia. Let’s explore the main features of the Indian subcontinent’s geography, which have influenced its culture and traditions:
- The Indian subcontinent comprises diverse geographical features such as the Himalayas, Peninsular India, Coastal plains, Deccan plateau, Gangetic Valley, and Vindhyachal Mountains.
Body:
Indus Valley Civilization:
- The decline of the Indus Valley Civilization was attributed to climate change, including a shift in monsoon patterns towards the east.
- Gujarat, with its protected position and lengthy coastline, has been a hub of coastal and international trade for over four thousand years. Dholavira in Gujarat had a port used for international trade.
Age of Vedas:
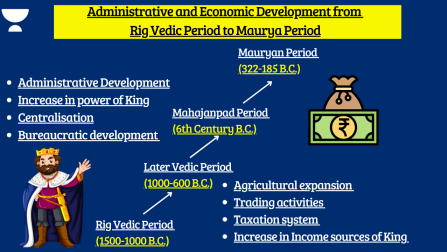
- During the Rig Veda age, Aryans didn’t shift to the Gangetic valley.
- In the Mahajanpad Period, Aryans migrated to the Gangetic valley, leading to agricultural expansion, increased trade, commerce, taxation, and the second phase of urbanization.
Geography leading to Political Development:
- India faced invasions from the northwest due to mountain passes like Khyber, Bolan, and Gomal, allowing invaders easy access. Various invaders like Persians, Indo-Greeks, Macedonians, Shakas, Kushans invaded from this region.
- There were no invasions from the northeast, and Peninsular India was geographically challenging to reach.
- The central Himalayan region facilitated trade between India and Tibet.
Influence on Art and Culture in NW India:
- Sculpture: Gandhara school influenced by Greek features, while Mathura school is indigenous.
- Script: Persians brought Kharosthi script, used in Ashoka’s inscriptions in NW India, while Brahmi script was used in central India.
- Pottery Development: Surplus agriculture led to pottery development.
- Temple Architecture: Temples were built using local materials, with thick walls and high ceilings for comfort.
- Music: Musical traditions from neighboring regions were transported through trade routes.
- Spread of Buddhism: Peninsula in south India facilitated the spread of Buddhism to Sri Lanka.
Conclusion:
Conclude giving an overall attribute of Geography which shaped ancient India.


Other important questions:
- From being a net food importer in 1960s, India has emerged as a net food exporter to the world
- Discuss the consequences of climate change on food security in tropical countries
- Why is the world today confronted with a crisis of availability of and access to freshwater resources?
- How are fjords formed? Why do they constitute some of the most picturesque areas of the world?
- Why is the South-West Monsoon called Purvaiya’ (easterly) in the Bhojpur Region?
- Comment on the resource potentials of the long coastline of India and highlight the status of natural hazard preparedness in these areas.
- Identify and discuss the factors responsible for diversity of natural vegetation in India
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out












