Introduction
- A mutual fund is an investment vehicle where many retail investors such as individual households pool their money to earn returns on their capital over a period.
- This corpus of funds is managed by an investment professional known as a fund manager, portfolio manager or an asset management company.
- The fund managers invest the corpus in different securities such as bonds, debentures, stocks, gold and other assets and seek to provide potential returns.
- The gains (or losses) on the investment are shared collectively by the investors in proportion to their contribution to the fund.
Types of Fund
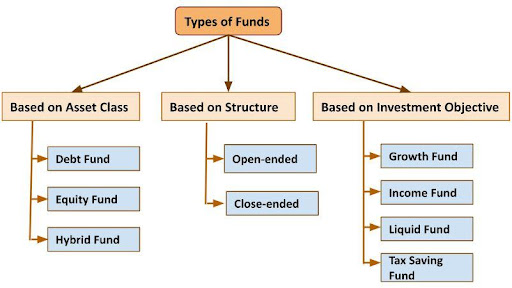
Types of Fund Based on Asset Class
- Debt Funds: They are also known as fixed income funds. Investment in this fund takes place in assets like government securities and corporate bonds.
- Equity Funds: Investment in these funds takes place in company stocks which have a higher degree of risks.
- Hybrid Funds: Hybrid funds invest in a mix of both equity and fixed income securities.
Types of Fund Based on Structure
- Open-ended Fund: These funds allow investors to trade funds at their convenience and exit when required at the prevailing NAV (Net Asset Value). These are highly liquid funds because an investor can redeem the units invested in any business day.
- Close-ended Fund: These funds come with a pre-defined maturity period. Investors can invest in the fund only when it is launched and can withdraw their money from the fund only at the time of maturity.
Types of Fund Based on Investment Objective
- Growth Fund: These funds can be relatively more risky due to high exposure to equity and hence it is good to invest in them for the long-term.
- Income Fund: These are debt funds that invest mostly in bonds, government securities and Certificate of Deposits, etc. They are suitable for different term goals and for investors with a lower-risk appetite.
- Liquid Fund:Liquid funds put money in short-term money market instruments like treasury bills, Certificate of Deposits (CDs), term deposits, commercial papers.
- Tax Saving Fund: These funds offer you tax benefits under the Income Tax Act.
Regulation of Mutual Funds |
|
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out








