Introduction
- Financial inclusion is also known as inclusive financing. It is the process of providing financial services to the unbanked and low income segments of the society.
- It must ensure financial services at an affordable cost and in a timely manner.
- Financial services include Credit facility, Savings, investments, insurance, etc. from a formal financial institution.
Need for Financial Inclusion
- Facilitates day-to-day low volume financial transactions.
- Provides safety to savings.
- Finances small business or microenterprises to grow their business.
- Facilitates channelisation of small households savings which results in capital formation.
- Promotes innovations for cost effective delivery of financial products through the use of technology.
- Helps in enhancing financial literacy.
- Promotes growth of the rural economy.
- Helps in enhancing the financial and social status of the lower income segment.
Facilities identified Under Financial Inclusion
- Credit Facility including Entrepreneurial Credit
- Loans and Insurance
- Mortgage
- Payment and Remittance Services
- Saving products and accounts
- Financial advice
Major Steps Towards Financial Inclusion
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana: Aimed at ensuring access to various financial services to the financially excluded sections. All households across the country – both rural and urban are to be covered under the scheme. Facilities provided are, basic savings bank account, access to need based credit, remittance facility, insurance and pension, etc.
- Basic Saving Bank Deposit Account (BSBDA): This facility was introduced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It is a standard account that contains basic banking services to the financially excluded population. It replaced the ‘No-Frills’ account.
- Lead Bank Scheme: Introduced by the RBI to stimulate the process of financial inclusion. It assigned lead roles to individual banks (both in public sector and private sector) for the districts allotted to them. The lead banks are responsible for ensuring flow of credit to agriculture, small-scale industries and other economic services.
- Priority Sector Lending: It is another initiative towards financial inclusion. Priority sectors are those sectors which get less credit, but contribute a lot to the national economy. Priority sector list is provided by the RBI and updated regularly.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): Cash transfer through Aadhar payment Bridge- requires Bank accounts which leads to financial inclusion.
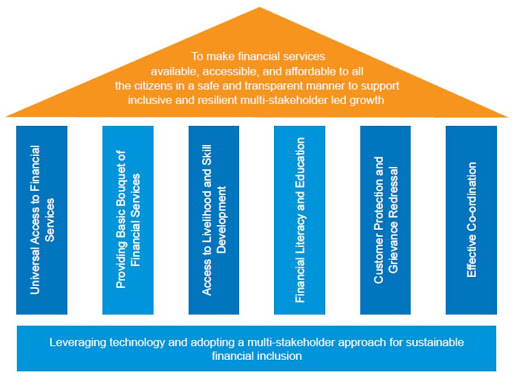
National Strategy For Financial Inclusion for India 2019-24
- It aims to provide access to formal financial services in an affordable manner, broadening & deepening financial inclusion and promoting financial literacy & consumer protection.
- Strategic Pillars
- Universal Access to Financial Services
- Providing Basic Bouquet of Financial Services
- Access to Livelihood and Skill Development
- Customer Protection and Grievance Redressal
- Effective Coordination
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out












