Demand-Side or Demand-Pull Inflation
- It is a situation when aggregate demand for goods and services in the market exceeds the aggregate supply.
- When demand for goods and services are high and supply is not adequate due to low economic output (Production), the firms increase the general price levels of goods and services.
Causes of Demand Side Inflation
- Increased liquidity in the economy.
- Increase in income levels and purchasing power of households.
- Growth in population and increase in demand for goods and services.
- Changing consumer behaviour.
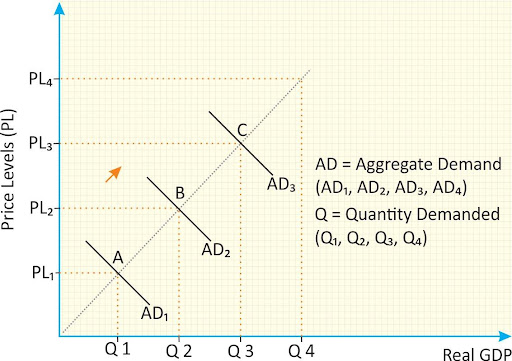
Demand Curve
- It depicts the relationship between the price of a certain commodity and the quantity demanded.
- As the quantity demanded is more (i.e. Q1 to Q2), the curve will shift upward from point A to point B with the corresponding rise in prices (i.e. from PL1 to PL2).
- It also indicates that with the increase in demand Real GDP expands.
Macroeconomic Impacts of Demand-pull Inflation
- There is full employment of resources when aggregate supply is inelastic.
- Rise in Real GDP as the economy will grow at a faster rate.
- Fall in Unemployment rate.
- Upward revision on wages as the demand for workers will increase.
- The upward pressure on wages may lead to wage-push inflation as higher wages increase the disposable income of workers leading to a rise in consumer spending.
Supply-Side (or Cost-Push) Inflation
- It develops when the factor cost or the cost of production increases with respect to the consistent demand for goods.
- It is determined by supply-side factors, such as higher wages, higher oil prices, etc.
Causes of Supply Side Inflation
- Rising nominal wages of labour
- Depreciation of exchange rates
- Rising food and energy prices
- Rising oil prices
- Higher production tax.
- Structural rigidities
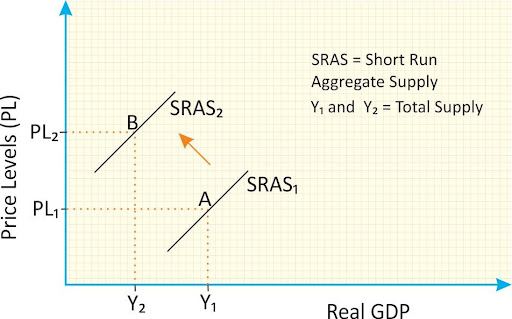
Supply Curve:
- It is the correlation between the cost of a good or service and the quantity supplied for a given period.
- When supply reduces (i.e. from Y1 to Y2), the price levels will go up (i.e. from PL1 to PL2).
- It also indicates that with the reduction in supply Real GDP shrinks for a short term.
Macroeconomic Impacts of cost-push inflation:
- Macroeconomic impact of cost push inflation is temporary in nature.
- It can lead to lower economic growth and often causes a fall in living standards.
- It will cause a higher price level.
- It lowers the Real GDP
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out










