
Achieve your IIT dreams with Unacademy
Unacademy Aarambh 2024 – Biggest Event for IIT JEE and NEET UG
“Coulomb’s law says that the force of attraction/repulsion between two electric charges is directly proportional to their magnitudes and inversely proportional to their distance”.
Coulomb’s law acts along the line connecting the two charged body’s centres. The law is also known as Coulomb’s inverse-square law because it describes an inverse square relationship between force and distance between two charged entities. Coulomb’s law is regarded as an electrical equivalent of Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation since the relation it derives is quite similar to the gravitational force acting between two large masses.
JEE Main 2024 Result Session 2
What are scalar and vector forms?
The force operating between two point charges might be accurately calculated using this law. The term “point charge” is used in physics to describe extremely small entities. This means that the charged bodies linear size is quite small, especially when compared to the distance between them. As a result, viewing these charged entities as point charges makes calculating the amount of electrostatic forces acting between them much easier.
There are two types of physical quantities: scalars and vectors. A scalar is a quantity with only magnitude, whereas a vector is a quantity with direction and magnitude. An example of a vector quantity is force which is represented by an arrow on the top.
Coulomb’s Law in its vector form
Let there be two charges, Q1 and Q2, such that r1 and r2 represent the position vectors of the two charges, respectively. The two charges will be electrically attracted to each other.
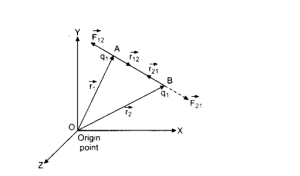



Due to the second charge, the force on the first charge is in the opposite direction and equal in magnitude to the force on the second charge. According to Coulomb’s Law, every action has its opposite reaction, which underpins Newton’s third law of motion.
The relative permittivity of the medium,

mportance of Coulomb’s law in vector form
When there is an assembly of point charges, the vector form of coulomb law is crucial. In this case, the sum of the vector forces acting on each charge is the resultant force acting on any one of the charges. That’s what’s known as the superposition principle.
Conclusion
The electric force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two charged entities. Furthermore, this law is used in deriving Gauss’s law accurately for general cases. Charges at rest exert the following properties according to Coulomb’s law- where like charges repel one another and unlike charges attract each other. The vector form of Coulomb’s law provides the direction of electric fields caused by charges. Two negative charges repel one another, while a positive charge attracts a negative charge. In physics, charges act in accordance with their lines of attraction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






