Current electricityThe formula for current electricity are as stated below |
|
| Description | Formula |
| Formula for current |
|
| Electric current in a conductor(wire) | I=nAeV_d v_d=λ/τ Here, n is the number of free electrons, A is the area of conductor, e is the charge of an electron, V_d is the drift velocity, λ is the linear charge density and τ is the relaxation time. |
| Potential difference using ohm’s law | V=IR Here, V is the potential difference, I is the current flowing through the conductor and R is the resistance offered by the conductor. |
| Resistance in terms of resistivity | R=ρl/A Here, ρ is the resistivity of the material of the conductor, l is the length of the conductor and A is the area of cross section of the conductor. |
| Change in resistance due to temperature | R=R_0 (1+αΔT) Here, R is the resistance, R_0 is the initial temperature, is the temperature coefficient of the resistivity and ΔT is the change in temperature. |
| Electric power | P=VI Here, P is the power, V is the potential difference and I is the current. Also, P=I^2 R P=V^2/R |
| Heat energy released due to current | H=VIt also H=I^2 Rt H=V^2/R t Here, H is the heat released in joules, V is the potential difference, R is the resistance, I is the current and t is the total time the current was flowing through the conductor. |
| Equivalent resistance when resistors are connected in series | Req=R_eq=R_1+R_2+R_3+⋯+R_n Here, R_eq is the equivalent resistance, R_1,R_2,R_3 are the resistance of the resistors. |
| Equivalent resistance when resistors are connected in parallel | 1/R_eq =1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3 +⋯+1/R_n |
| Potential difference when cells are connected in parallel | E_eq=((ε_1/r_1 +ε_2/r_2 +ε_3/r_3 +⋯+ε_n/r_n ))/(1/r_1 +1/r_2 +1/r_3 +⋯+1/r_n ) Here, ε_1,ε_2,ε_3 are the emf of the cells and r_1,r_2,r_3are the internal resistance of the cells. |
| Ammeter using galvanometer | To measure the maximum current I using a galvanometer, we need to connect a shunt resistance in parallel with the galvanometer. The value of the resistance is calculated as: S=(I_g R_g)/I Here, S is the value of shunt resistance, Ig is the current through galvanometer, Rg is the resistance of the galvanometer and I is the maximum current to be measured. |
| Voltmeter using galvanometer | To measure a potential difference using a galvanometer, we need to connect a series resistance with it. The value of the resistance that needs to be connected is: Rs=VIg-Rg Here, V is the maximum potential difference to be measured, I_g is the current through galvanometer andR_g is the resistance of the galvanometer. |
Electric current formulaThe formula for electric current are as stated below |
|
| Description | Formula |
| Electric current | I=q/t=ne/t Where I= strength of current; q-charge; t- time |
| Resistance | 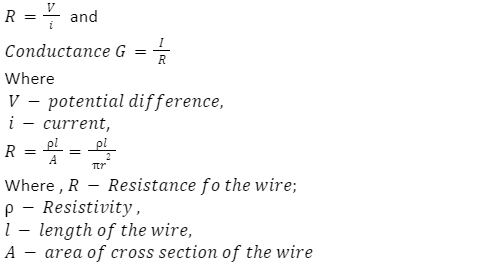 |
| Variation of resistance with the temperature | R_T=R_° [1+α(t)] →α=(R_(t-) R_(° ))/(R_° (t) ) l°∁ α=((R_1-R_2 ))/(R_1 (t_2-t_1 ) ) l °∁ Here, R = resistance at temperature t°∁ R° = resistance at temperature 0°∁= temperature coefficient of resistance |
| Conductivity | Reciprocal of resistivity. σ=1⁄ρ Where – σ -conductivity, ρ -resistivity |
| Terminal voltage | Case-1: When battery is delivering current V=E-ir or i=E/R+r Where V -terminal P.d, E – emf of the cell, r -internal resistance of the cell, R- external resistance. Case 2: when battery is charging V=E+ir |
| Kirchhoff’s laws | Kirchhoff’s First laws: ∑_ ^ i=0 at any junction. Kirchhoff’s second law: ∑_ ^ iR=0 in a closed circuit. |
| Metre Bridge | 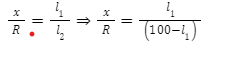 Where x – unknown resistance of given wire, R-resistance in the resistance box, l1-balancing length from left end of the bridge to Jockey.
Where x – unknown resistance of given wire, R-resistance in the resistance box, l1-balancing length from left end of the bridge to Jockey.
|
| Potentio Meter | Emf of cell in the secondary circuit
E_s=Iρl
|
Electromagnetic Induction FormulaThe formula for electromagnetic induction are as stated below |
|
| Description | Formula |
| Magnetic Flux | The magnetic flux through a plane of area dA placed in a uniform magnetic field B is given as ϕ=∫ B ⃗∙dA ⃗ When the surface is closed, then magnetic flux will be zero. This is due to magnetic lines of force are closed lines and free magnetic poles is not exist |
| Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday’s Law | First Law: Whenever magnetic flux linked with a circuit changes with time, an induced emf is generated in the circuit that lasts as long as the change in magnetic flux continues. Second Law: According to this law, the induced emf is equal to the negative rate of change of flux through the circuit. E = -dϕdt |
| Lenz’s Law | The direction of induced emf or current in the circuit is in such a way that it opposes the cause due to which it is produced. Therefore, E = -dϕ/dt |
| Induced emf | Induced emf is given as E = -N(dϕ/dt) E = -N((ϕ_1- ϕ_2)/t) |
| Induced Current | Induced Current is given as I=E/R = N/R(dϕ/dt)= N/R((ϕ_1- ϕ_2)/t) |
| Self – Induction | Change in the strength of flow of current is opposed by a characteristic of a coil is known as self-inductance. It is given as ϕ=LI Here, L = coefficient of self – inductance Magnetic flux rate of change in the coil is given as Idϕ/dt = L dl/dt=-E |
| Mutual – Induction | Mutual – Induction is given as e_2=(d(N_2 ϕ_2)/dt = M (dl_1)/dt Therefore, M=(μ_0 N_1 N_2 A)/l |
JEE Physics Important Formulas Part 3
In this article we will go through physics quick formula revision for JEE 2022. Find the important formulas of Current electricity, Electric current and Electromagnetic Induction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






