Surface area of a three-dimensional object is the sum of the area of all the sides.. Surface area is divided into two types, lateral and total surface area.
Volume is the ability of a 3 dimensional object to hold something. For example if a cube can hold 100 litres of water, 100 litres is the volume of that cube.
Surface area:
Surface area can be easily calculated through already established formulas. The objects that are mainly focused on are cube, cuboid, sphere, cone and cylinder. The object can also be a combination of two objects.
Eg: cone on top of a cylinder.
Total surface area Vs lateral or curved surface area:
The overall surface area is the region that includes the base(s) and the curving part. It refers to the space covered by an object’s surface. If the shape has a curved base and surface, the overall area will equal the sum of the two regions. “The overall area covered by an object, including its base as well as the curving part,” says the definition. “If an object contains both a base and a curved region, the total surface area will be equal to the sum of the two.”
Except for its centre, the area of a curved surface equals the area of the curved component of the shape (s). For shapes like cones, it is the lateral surface area. “The area that comprises only the curved area of an object or the lateral area of an object by removing the base area of an object,” states the explanation. The curved surface area is another name for lateral surface area.
Surface area of a cube:
It is the total area covered by all six sides of a cube. It is known that area of a square is a² and the sides of a cube are squares. Lateral surface area includes four sides and total surface area includes six sides. The surface area of a cube is determined by the length of the side of the given cube.
Therefore,
CSA of a cube = 4a²
TSA of a cube = 6a²
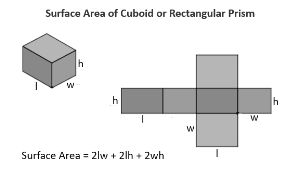
Surface area of a cuboid:
Unlike cubes, cuboids have length, height and breadth as their dimensions. Change in any dimension results in change in the value of the surface area.
A cuboid also has 6 faces and the total surface area is derived by adding the area of all sides. The 6 faces are divided into 3 rectangles repeated twice.
Area of a rectangle formula is the multiplication of its two sides.
So therefore,
Area of rectangle 1 and 3 = h x l
Area of rectangle 2 and 4 = h x w
Area of rectangle 5 and 6 = l x w
Therefore total surface area of a cuboid = 2(hl + hw+lw)
Lateral surface area is the surface area of 4 sides, i.e. 6 sides of a cuboid – the top and bottom rectangles.
The top and bottom rectangles area = 2(l x w)
Therefore, lateral surface area = 2(hl + hw+lw) – 2(lw)
= 2(hl+hw)
= 2h(l+w)
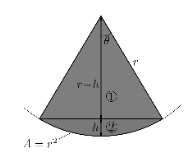
Area of a cone:
The cone is a complex object. However, finding its area is relatively easy. To find the surface area of a cone, one must be familiar with Pythagoras theory. The cone is shaped with a circle at its base and a triangular top. The height is determined by the centre point of the circle to the tip of the cone which is denoted by the letter h. Length is the length of one side of the triangular part denoted by letter l and radius is the radius of the circle at the base, denoted by letter r.
By applying pythagoras theorem, we know that h² + r² = l²
l = √h²+r²
Therefore total surface area π= r (r + l)
=π r(r+√h²+ r²)
Curved surface area = πrl
= πr(h²+r²)
Area of a cylinder:
The surface area of a cylinder can be determined by adding the curved surface of a cylinder with the flat surface of a cylinder.
There are two bases in a cylinder and it is circle in shape.
The curved surface area of a cylinder = 2πrh.
Where h is the height and r is the radius.
Total surface area of a cylinder = Area of two bases + curved surface are
= 2πr² + 2πrh
Area of a sphere:
A sphere is a three dimensional object. The 2D form of a sphere is a circle. Eg, a globe or a ball is a sphere.
A sphere is related to curved surfaces like the cylinder. The radius of a cylinder and a sphere is the same and the height is also the same.The height to a sphere is called the diameter. A sphere can perfectly fit into the cylinder,
Therefore, lateral surface area of a cylinder = total surface area of a sphere.
Lateral surface area of a cylinder = 2πrh.
h = 2r (since height = diameter, diameter = 2x radius.)
Surface area of sphere = 2πr(2r) = 4πr².
The curved surface area of the sphere = total surface of the sphere as there are no flat surfaces in a sphere.
Volume
It is defined by the capacity to hold by a three dimensional object. Volume can highly differ from object to object. It is to be remembered that empty space in an object does not solely amount to holding capacity. A solid object like an eraser also has volume in it.
Volume is identified using various formulas for different objects like, cube, cuboid, sphere, cylinder and cone.
Volume of a cube:
A cube has equal sides and volume is usually determined by multiplying the height, width and length. All sides of a cube are denoted by a.
Therefore volume = a *a*a
= a³ units.
Volume of a cuboid:
A cuboid has length, breadth and height. A cuboid can also be said as a stack of rectangles.
Therefore its volume is = l x b x h units
Volume of a cylinder:
Like a cuboid, a cylinder is the stack of circles. There are 2 bases to a cylinder and is distanced by height called h.
Volume of a cylinder = πr²h units
That is the area of a circle multiplied by the height.
Volume of a cone:
It is derived by one-third of the cone with the area of circular base and the height.
Volume of a cone = 1/3 r² h units
Volume of a cone with height and diameter = (1/12)πd²h (since r=d/2) units
Volume of a cone with slant height = (1/3)πr²h = (1/3)πr²√(L² – r²). units
h = √(L² – r²)
Volume of a sphere:
Volume of a sphere with radius r = 4/3 πr³ units.
Conclusion:
From the above mentioned formulas and concepts it is clear that surface area is the area covered by a three-dimensional object. Total surface area refers to the area covered by the entirety of an object whereas curved surface area means only the area of the curved part of an object.
Volume of an object is the ability for the object to hold something in it. The units are cubic units. Volume, too, is only identified for a three-dimensional object.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out