One of the basic chemical reactions seen in the study of organic chemistry is the oxidation and reduction reaction. Oxidation reaction represents a reaction where the loss of electrons takes place. In contrast, a reduction reaction represents a chemical reaction in which the gain of the electron is experienced. These oxidation and reduction reactions are accompanied by various agents, which are called oxidising agents and reducing agents, respectively. This chemical reaction is known for releasing a large amount of energy heat which is quite useful. Whereas the redox reaction can be seen all around in nature as it is one of the most prior aspects in nature as well as the biological energy source on the planet.
WHAT IS OXIDATION AND REDUCTION?
The oxidation and reduction definition represents the chemical reaction that is involved with the loss and gain of electrons, loss and gain of oxygen, as well as loss and gain of hydrogen. The oxidation-reduction reaction is also known as the redox reaction. The chemical reaction pertaining to oxidation and reduction always experiences a gain or loss of heat or energy to the surrounding. This redox reaction is also dependent upon the oxidation number. It is considered that oxidation and reduction reactions occur simultaneously as they cannot persist independently.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN OXIDATION AND REDUCTION REACTION:
The oxidation and reduction reaction occurs simultaneously. However, they have several differences. Some of them are:
- The oxidation reaction is considered to be a reaction in which the electrons are lost. Whereas in the reduction reaction, electrons are gained.
- In an oxidation reaction, as the name suggests, the addition of oxygen takes place, whereas, in the reduction reaction, the oxygen is removed.
- The oxidation-reduction reaction depends upon the oxidation number. In terms of oxidation reaction, the oxidation numbers increased, whereas, in the reduction reaction, the oxidation number decreased.
- Considering the loss and gain of hydrogen, in an oxidation reaction, the hydrogen is lost, whereas, in the reduction reaction, the hydrogen compound is gained.
- The oxidation-reduction reaction is known for releasing an enormous amount of energy. The oxidation reaction releases energy to the surroundings, whereas in the reduction reaction, a certain amount of energy is absorbed to carry out the reaction.
OXIDISING AND REDUCING AGENTS:
The oxidation and reduction reaction consists of several agents who take part in carrying out the reaction. As the gain and loss of electrons are considered during the reaction, the products which lose electrons are known as the reducing agent or reducers. On the other hand, the compound that receives or accepts the electrons are known as the oxidising agent or oxidiser. The oxidising agents are those substances that have the capability of oxidising other elements, i.e., they manipulate other elements to lose electrons in order to gain electrons. The oxidising agents are also called the electron receptors. However, reducing agents are substances that have the capability of losing electrons in order to complete a reaction. It is a compound that loses an electron and donates it to the other element. It is also called the electron donor. Lithium, sodium, magnesium, etc. Some good examples of reducing agents. Oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, etc., are some chemical compounds that are known as oxidising agents.
EXAMPLES:
The oxidation and reduction reaction occurs on the basis of several factors, like, electron transfer, oxygen transfer, hydrogen transfer and the oxidation number. On the basis of these factors, several examples of redox reactions are:
- Electron transfer: On the basis of electron transfer, the oxidation reaction loses electrons, whereas the reduction reaction gains an electron in order to complete a reaction.
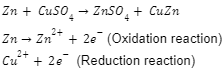
- Oxygen transfer: In an oxidation reaction, oxygen is gained, whereas, in a reduction reaction, oxygen is lost.
For example,
- Hydrogen transfer: In the oxidation reaction, loss of hydrogen is experienced, whereas, in the reduction reaction, a gain of hydrogen is observed.
For example,
CONCLUSION:
The oxidation and reduction reaction is a type of chemical reaction which occurs simultaneously and cannot exist independently, in which the oxidation state of an atom is changed. The oxidation and reduction reaction is also called redox reaction and the elements that are involved in this reaction are termed oxidising agents or reducing agents. The reaction taking place in an oxidation and reduction chemical reaction is based upon several factors, i.e., Electron transfer, hydrogen transfer, oxidation number and oxygen transfer. In order to understand this concept clearly, one is required to have the basic knowledge of the chemical reaction and types of the chemical reaction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






