Add Your Registration Details For JEE Main 2024
Travelling Microscope
A travelling microscope, a glass slab, lycopodium powder/chalk dust, and a piece of paper are all required. A vertically mounted compound microscope is known as a travelling microscope. It has a vernier scale that may be moved up and down along with the main scale. The following is an experiment utilising a travelling microscope to determine the refractive index of a glass slab.
The refractive index is a measurement of how far a light ray deviates when it pauses between two materials. It’s a one-dimensional integer that determines the speed of light. The refractive index is defined as the ratio of light velocity. The numerator is the medium that is used to determine the refractive index. The denominator is the medium for which it is defined.
Determine the Refractive Index of a Glass Slab using Travelling Microscope Practical
Apparatus
Three “glass slabs of varying thickness but made of the same material, a travelling microscope, and lycopodium powder A slab is a rectangular-shaped chunk of transparent material. All of the faces are transparent, and the faces on opposite sides are parallel. The thickness of a slab is the dimension along which light flows within it.
A Travelling Microscope’s Short Description
It’s a compound microscope with a vertical scale mounted on it. It has a Vernier scale that moves along the main scale and maybe pushed up and down. The reading is taken by combining the main scale and vernier scale readings in any position.
Theory
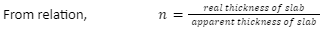
Diagram
Procedure
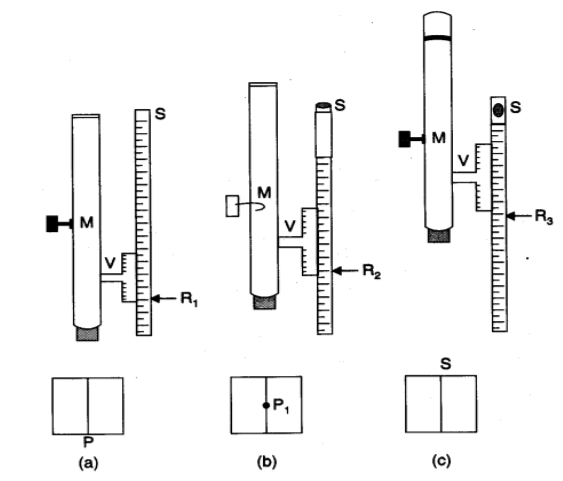
- Place the travelling microscope (M) on the table near a window to ensure that it receives enough light
- The levelling screws should be adjusted so that the microscope’s base is horizontal
- Adjust the eye piece’s position such that the cross wires are easily visible.
- Determine the vernier constant for the microscope’s vertical scale
- Make a cross-mark with black ink on the microscope’s base
- The point P will be the mark
- Make the microscope vertical and concentrate it on the cross at P so that the cross-wires and the image of the mark P do not have any parallax
- On the vertical scale, take note of the main scale and the vernier scale readings (R1)
- 8. On top of the P mark, place the thinnest glass slab
- Raise the microscope to eye level and focus it on the cross-mark image P1
- As previously, take note of the reading (R2) on the vertical scale (Step 7)
- Sprinkle a few lycopodium powder particles on the slab’s surface
- Raise the microscope even higher and concentrate it on the particle near S
- Again, take note of the reading (R3) on the vertical scale (Step 7)
- Rep the steps above with another glass slab of varying thicknesses
- Make a tabular record of your observations, as shown below
Observation and Calculation
R1 without Glass Slab
| S. No. | M. S. R (cm) (a) | V. S. R. (cm) (b) | V. S. R LC (c) | (a + c) (cm) |
| 1 | 3.7 | 4 | 4 × 0.01=0.04 | 3.74 |
| 2 | 3.6 | 5 | 5 0.01=0.05 | 3.66 |
| 3 | 3.8 | 15 | 15 × 0.01=0.15 | 3.95 |
R2 with Glass Slab
| S. No. | M. S. R (cm) (a) | V. S. R. (cm) (b) | V. S. R LC (c) | (a + c) (cm) |
| 1 | 3.6 | 32 | 0.32 | 4.0 |
| 2 | 3.9 | 20 | 0.20 | 4.10 |
| 3 | 3.5 | 40 | 0.40 | 3.9 |
R3 with Lycopodium Powder on Glass Slab
| S. No. | M. S. R (cm) (a) | V. S. R. (cm) (b) | V. S. R LC (c) | (a + c) (cm) |
| 1 | 4.1 | 35 | 0.35 | 4.45 |
| 2 | 4.2 | 37 | 0.37 | 4.57 |
| 3 | 4.3 | 38 | 0.38 | 4.68 |
Mean value of R1 = 3.78 cm
Mean value of R2 = 4.0 cm
Mean value of R3 = 4.57 cm
Result

Precautions
- The parallax in a microscope should be correctly removed.
- To minimise backlash errors, the microscope should only be adjusted upward.
Conclusion
Due to the phenomenon of refraction, when a glass slab is placed in air on a horizontal surface and its bottom side is viewed from above, it appears to be elevated. The apparent thickness of the slab is determined by the distance between the apparent bottom and the top surface of the slab. In a normal observation, the refractive index of glass with regard to the medium can be seen.
Also see:
| JEE Advanced | Standing waves |
| JEE Notification | Focal length of a convex lens |
| JEE Eligibility | pH scale |
| JEE Syllabus | Probability density |
| Equations of a parabola |
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out







