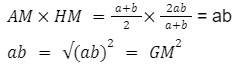When we learn about sequences in mathematics, we come across the relationship between the letters AM, GM, and HM. These three numbers represent the average or mean of the respective series. Arithmetic Mean (AM), Geometric Mean (GM), and Harmonic Mean (HM) are all abbreviations for Arithmetic Mean. The mean of Arithmetic Progression (AP), Geometric Progression (GP), and Harmonic Progression (HP) are represented by the letters AM, GM, and HM, respectively. Before understanding the link between them, it is necessary to be familiar with these three means and their respective formulas.
AM, GM, HM Formulas
Let us first gain a better understanding of the three statistical means, which are the Arithmetic Mean, the Geometric Mean, and the Harmonic Mean, before we compare them.
Arithmetic Mean
In mathematics, the arithmetic mean is a number that may be obtained by dividing the sum of the values in a set by the number of values in that set. If a1, a2, a3,…,an is a number of groups of values or the Arithmetic Progression, then the following statements are true:
AM=(a₁+a₂+a₃+….,+aₙn)/n
Geometric Mean
With respect to any given number of values and any number of observations, the Geometric Mean is defined as the nth root of the product of those values and those observations.
GM = n√(a₁+a₂+a₃+….,+aₙ)
Or
GM = (a₁+a₂+a₃+….,+aₙ)1 ⁄ n
Harmonic Mean
The Harmonic Mean (HM) of a set of data values is defined as the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the data values. It is denoted by the following symbols:
HM = n/[(1/a₁) + (1/a₂) + (1/a₃) + ….+ (1/aₙ)]
The Relation Between AM GM HM
Considering the assumption that the value of AM is greater than the values of GM and HM, the relationship between AM GM HM may be understood as follows: The arithmetic mean is greater than the geometric mean for the same set of data points, and the geometric mean is greater than the harmonic mean for the same set. Using the following phrase, we may depict the relationship between AM, GM, and HM:
AM > GM > HM
Arithmetic mean is represented in short form as AM, geometric mean is written in short form as GM, and harmonic mean is written in short form as HM in this equation.
To further comprehend this, let us first look at how to locate AM, GM, and HM in the first place. The arithmetic mean(AM), geometric mean(GM), and harmonic mean(HP) for any two numbers a and b are calculated using the following formulas: Arithmetic mean (also known as the average of the provided numbers) is the sum of two numbers divided by two, and the arithmetic mean for two numbers a and b is the sum of the two numbers divided by two in the case of two numbers a and b.
AM = a+b ⁄ 2
The geometric mean of two integers is equal to the square roots of the product of the two numbers a and b, and vice versa. Moreover, if there are n numbers of data points, then the geometric mean of those data points is equal to the nth root of the product of those n numbers, which is equal to 1.
GM =√ab
The harmonic mean of two numbers is represented by the symbol 1/a. 1/b is the reciprocal of their arithmetic mean. The arithmetic mean of these two integers, 1/a and 1/b, is equal to (a + b)/2ab, and the inverse of this is the harmonic mean of the two numbers.
HM = 2ab ⁄ a+b
Formula for Relation Between AM GM HM
The product of the arithmetic and harmonic means is equal to the square of the geometric means in the relationship between AM, GM, and HM. This can be expressed in the form of this expression in this context.
AM × HM = GM²
Let us make an effort to comprehend this formula clearly, while also deriving this formula.
Conclusion
AM, also known as Arithmetic Mean, is the mean or average of a collection of numbers that is calculated by adding all of the terms in the set of numbers and dividing the sum by the total number of terms. Geographic Mean (GM) is the mean value or the centre term in a group of integers in geometric progression, and it can be expressed as the geometric mean.
If the sequence x, a, and y represents a geometric progression, the letter ‘a’ is referred to as the geometric mean. If the numbers x, a, and y form a harmonic progression, the letter an is referred to as the harmonic mean. Let AM represent the arithmetic mean, GM represent the geometric mean, and HM represent the harmonic mean. The formula reveals the link that exists between the three variables. AM×HM=GM².
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out