When a salt that is sparingly soluble is introduced in water, only a small portion of the salt dissolves in the water, forming a solution. The equilibrium between the sparingly soluble salt and the ions dissolved in water is determined by the solubility product, Ksp.
We begin our study of solubility and complexation equilibria, which are related to the production of complex ions, by creating quantitative methods for modeling ionic compound dissolution and precipitation reactions in aqueous solution. We can use an equilibrium constant expression to represent the concentrations of ions in equilibrium with an ionic solid, much as we do with acid–base equilibria.
Solubility Product (Ksp)
The solubility product constant is the equilibrium constant for the dissolving of a solid substance into an aqueous solution. The symbol Ksp is used to represent it.
The solubility product is an equilibrium constant whose value varies with temperature. Due to increasing solubility, Ksp normally rises as the temperature rises.
The ability of a material termed a solute to dissolve in a solvent and create a solution is defined as solubility. Ionic chemicals (which dissociate to form cations and anions) have a wide range of solubility in water. Some substances are extremely soluble and can even absorb moisture from the air, whereas others are quite insoluble.
Solubility Products for Selected Ionic Substances at 25°C are as follows: –
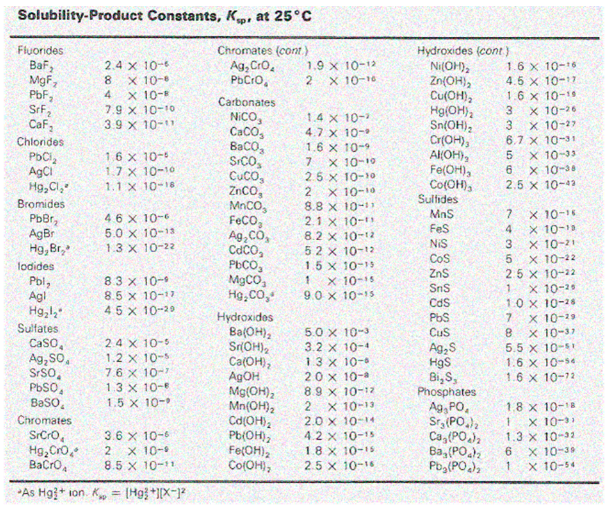
Significance of solubility product
Solubility is determined by a number of factors, the most important of which are the salt’s lattice enthalpy and the solvation enthalpy of the ions in the solution. Solubility product constant Ksp Most salts dissociate into ions when they dissolve. For example: – BaSO4(s) ⇋ Ba2+(aq)+SO42-(aq) The equilibrium system may be described by the mass- action expression- When a salt is dissolved in a solvent, the strong forces of attraction of the solute must be countered by interactions between ions and the solvent (lattice enthalpy of its ions).
- Ions’ solvation enthalpy is always negative, indicating that energy is released throughout the process.
- Solvation enthalpy, or the amount of energy released during solvation, is determined by the composition of the solvent.
- Non-polar solvents have a low solvation enthalpy, implying that this energy is inadequate to overcome the lattice enthalpy.
- As a result, non-polar solvents do not dissolve the salts. As a result, the solvation enthalpy of a salt must be greater than its lattice enthalpy in order for it to dissolve in a solvent.
- Temperature has an impact on solubility, which varies depending on the salt.
| Category I | Soluble | Solubility > 0.1M |
| Category II | Slightly soluble | 0.01M< Solubility<0.1M |
| Category III | Sparingly soluble | Solubility < 0.1M |
Solubility Product Constant
Assume you have barium sulphate and its saturated aqueous solution. The equilibrium between undissolved solids and ions is represented by the following equation: BaSO4⇌saturated solution in waterBa2+(aq)+SO4−(aq) In the example above, the equilibrium constant is: K = [Ba2+][SO4−][BaSO4] Because the concentration of pure solid substances remains constant, we can say Ksp equals K Ksp = K[BaSO4] = [Ba2+][SO4−] The solubility product constant, Ksp, is used here. This also means that when solid barium sulphate is in equilibrium with its saturated solution, the product of barium and sulphate ion concentrations equals the solubility product constant.The Ion Product (Q)
The product of the concentrations of the ions in solution raised to the same powers as in the solubility product statement is the ion product of a salt. It’s similar to the reaction quotient (Q) that was explained previously for gaseous equilibria. The ion product represents concentrations that are not necessarily equilibrium concentrations, whereas Ksp describes equilibrium concentrations. For gaseous equilibria, the ion product Q is comparable to the reaction quotient Q. An aqueous solution of an ionic substance can have three different conditions: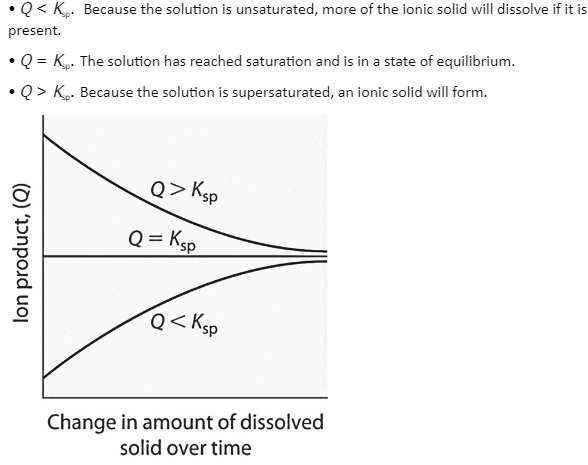
Q and Ksp Have a Relationship. The solution is unsaturated if Q is less than Ksp, and additional solid will dissolve until the system reaches equilibrium (Q = Ksp). If Q exceeds Ksp, the solution is supersaturated, and solids will form until Q equals Ksp. When Q = Ksp, the rate of dissolution equals the rate of precipitation; the solution is saturated, and there will be no net change in the amount of dissolved material.
Calculating the ion product’s value and comparing it to the magnitude of the solubility product is a simple technique to figure out whether a solution is unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated. More importantly, when two soluble salt solutions are combined, the ion product tells scientists if a precipitate will form.
The Common Ion Effect and Solubility
The equilibrium concentrations of the cation and anion are inversely linked, according to the solubility product expression. That is, as the anion concentration rises, the maximum cation concentration required for precipitation falls—and vice versa—so that Ksp remains constant. As a result, the solubility of an ionic compound is dictated by the amount of other salts having the same ions. A solubility equilibrium is shifted in the direction indicated by Le Chatelier’s principle when a common cation or anion is added.
Conclusion
The solubility product (Ksp) is used to compute equilibrium ion concentrations in solution, whereas the ion product (Q) is used to characterise concentrations that aren’t always at equilibrium. The solubility product (Ksp), the equilibrium constant for a dissolution reaction, is a measure of a compound’s solubility. Ksp is described in terms of the molar concentrations of the component ions, whereas solubility is normally represented in terms of mass of solute per 100 mL of solvent. The ion product (Q), on the other hand, describes concentrations that aren’t necessarily equilibrium. When two soluble salt solutions are mixed, we may determine if a precipitate will develop by comparing Q and Ksp. In a solution of a sparingly soluble salt, adding a common cation or common anion affects the solubility equilibrium in the direction anticipated by Le Chatelier’s principle. When a common ion is present, the salt’s solubility is almost always reduced.
Related Links:
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





