Conditional probability is the chance of occurring outcomes based on the previous occurrence and it is defined as the probability theory for multiplication. Conditional probability does not state that both events occur correspondingly. Moreover, conditional probability does not indicate that there is a casual relationship between two events in the occurrence. The concept of conditional probability is related to the Bayes theorem. Conditional probability is determined by the multiplication of the probability of the previous events with the updated probability of the succeeding events in occurrence.
What is conditional probability?
Conditional probability makes a relationship between two events in the occurrence and makes possible events. The Formula of conditional probability suggests that the events are neither independent nor mutually related to each other. The conditional probability of the two successive events can be determined by the Bayes theorem and it is denoted by the below formula:
P (A|B)= P(B|A) P(A)/ P (B)
The above equation of the Bayes theory for conditional probability determines the likelihood of event A based on the occurrence of event B.
Explain the key concept of conditional probability
The key concept of conditional probability depends on the likelihood of the previous events and it is independent of the successive events. The multiplication of the previous events with the successive events gets the result of the occurrence in the conditional probability and it can be calculated by using the below tree diagram:
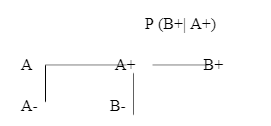
The concept of probability depends on the products of the two events if the events are not mutually exclusive.
Explain the conditional probability formula
P (A|B) = P (A∩B) / P (B)
From the above equation, it is defined as:
P (A|B) = the conditional probability of the events A based on the occurrence of event B that has previously occurred.
P (A∩B) = the likelihood of the joint probability of event A and event B, here is a chance for occurring of both events.
P (B) = is the likelihood of getting event B in the conditional probability.
Conditional probability for the mutually corresponding events can be calculated by the below formula:
P (A|B) =0 and P (B|A)=0
Here the above equation denotes that there is no chance for the occurrence of the two simultaneous events. If A occurs in the probability then the chance of occurring of B is zero.
Examples of conditional probability
In a bunch of 200 sports car buyers, 50 buyers have purchased an alarm system, 30 have purchased ventilated seats and 20 people have both alarm and ventilated seats. Therefore if people have to choose a random buy of alarm then what is the likelihood of the people also purchasing ventilated seats?
Answer: In the above question P (A) = 50% that is 0.5 and P(A∩B)= the probability of the both events occurs = 30%=0.3
Therefore from the equation of the conditional probability
P (B|A) = P (A∩B) / P (A) = 0.3/0.5=0.6
Hence from the above result, the probability that people bought ventilated seats with an alarm system is 60%.
What are the properties of conditional probability?
The properties of conditional probability depend on the properties of the single events in the occurrence. The properties of the conditional probability are described below:
- In the equation, if A and B are independent events then P(A|B)= P(A)
- If A, B, C….. are independent events then P(A ∪ B ∪ C ∪……∪ An)
- If A, B, C are three events such that A=ϕ, AB=ϕ then P (A ∩ B ∩ C) = P (A). P (B|A). P (C|AB)
What is the application of conditional probability?
The conditional probability is applied in the forecasting of the rain and determination of the outcome in the events of throwing coins in the air, and choosing cards from the deck of cards. Conditional probability has been applied by advertising agencies to determine the motivation of the consumer for a specific product or service. Conditional probability makes decisions based on the properties of the occurrence of the previous events. The conditional probability for the independent cases can be calculated by the below equation:
P (B|A) = P (B)
Conclusion
The above study indicates that the conditional probability does not change the value of the previous occurrence but only predicts the likelihood of the result based on the properties of the completed events in the equation. The article indicates that the value of the new variables depends on the multiplication of two events in the case of mutually exclusive properties. The conditional probability can be applied to finding the result of the nth variable in a series of successive events.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






