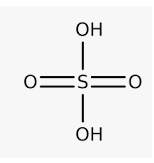
Sulphuric Acid formula
Sulphuric acid is the most often employed acid in a variety of chemical studies. It is a very potent inorganic acid. Sulphuric acid’s chemical formula is H2SO4.
Sulphuric acid contains 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms in its chemical formula. For your reference, the fundamental ideas pertaining to sulfuric acid, sulfuric acid formula, sulphuric acid molecular formula, the formula of dilute sulphuric acid, structure, chemical characteristics, and acid applications are explained here.
Attached to the sulfur atom are one Hydrogen atom, one sulfur atom, and four oxygen atoms. It has a molecular mass of 98,079 g/mol. They are structured such that there is minimal repulsion between lone pairs and bond pairs, according to the VSEPR theory. It is a sulfur oxoacid. Through the double bonds, two oxygen atoms are bonded to the sulfur. Single bonds bind two hydroxyl groups together. The structure of sulphuric acid is seen in the diagram below:
Attached to the oxygen atoms are two hydrogen atoms. Two hydrogen atoms may be mobilized. This implies they are readily removable. It is thus a diprotic acid. This is why sulfuric acid is the most powerful inorganic acid.
Concentrated sulfuric acid is exceedingly corrosive and hazardous. Therefore, water is added to dilute the concentration. This is referred to as dilute sulfuric acid. The formula for diluted sulfuric acid is identical to the formula for concentrated acid. It varies only in concentration. This potent chemical reacts strongly with water, generating a great deal of heat. Therefore, you should never combine H2SO4 with water.
Chemical Properties
- Sulfuric acid has a high molecular weight and is a dibasic acid. It is also diprotic, ionizing in an aqueous solution in two processes
- This chemical is highly reactive, corrosive, and water-soluble. It has a high oxidizing capacity, making it a potent oxidizing agent
- The amount of volatility is modest. Consequently, it facilitates the generation of more volatile acids from their dissimilar salts
- Therefore, this chemical is used to dry a range of moist gasses that do not react with acid
- It also dehydrates natural substances such as starches
- It may oxidize both nonmetals and metals due to its effectiveness as an oxidizing agent. In addition, it breaks down into sulfur dioxide
Uses of Sulphuric Acid
- It is used widely in labs, petroleum refineries, and wastewater treatment facilities
- It is used in the production of various industrially useful chemicals. It is used in paints, explosives, detergents, and dyes. In electrochemical cells and batteries, it is also employed as an electrolyte
- It is a popular chemical used in the manufacturing of explosives. TNT is one example. The existence of other essential components requires sulfuric acid. We cannot get these compounds without acids such as sulfuric, hydrochloric, phosphoric, and nitric. Additionally, it is necessary for the manufacturing of sodium carbonate
- We use it for the refining of petroleum
- It is pickling in nature
- Approximately half of the world’s supply of sulphuric acid is employed in agriculture, primarily in the fertilizer industry. Phosphate fertilizers are manufactured with sulphuric acid
Conclusion
Here, we learnt the formula, structure, and typical applications of sulfuric acid. In labs, this acid is manufactured via the contact method. As a strong acid, sulphuric acid is commonly used in labs for the synthesis of different chemicals. Consequently, it is one of the most essential subjects in Chemistry to study.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out