What is SSC?
The Staff Selection Commission or SSC is an organisation through which the Government of India hires staff for various roles. Candidates take the SSC exams to work in the government’s different ministries and other departments. Some staff are also recruited to work in several subordinate offices. The SSC exams are taken by many candidates every year and these exams are of different levels, depending on the post. The candidates can get the complete details on ssc.nic.in.
You can apply for the following SSC exams:
- SSC CGL – Combined Graduate Level
- SSC GD – Constable, General Duty
- SSC CHSL – Combined Higher Secondary Level
- SSC JE – Junior Engineer
- SSC CPO – Central Police Organisation
- SSC MTS – Multitasking Staff
- SSC Stenographer ‘C’ and ‘D’
- SSC JHT – Junior Hindi Translator
How to Apply for SSC?
To apply for the SSC exams, the candidates can refer to the following steps –
Step 1: Visit the Official Site of the Staff Selection Commission
You will need to register as a new user and add all information necessary. If you have already registered, you can log in using your username and the SSC registration password.
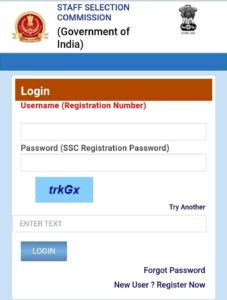
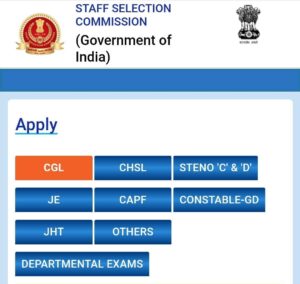
Step 2: Choose the Exam
You will need to select the exam you wish to take. If you have already started filling out the application form, you can complete it and submit it.
Step 3: Upload Images and Documents
You will need to scan and upload the necessary images. These include your image and signature. You also need to upload documents. The documents depend on the exam but you will need to upload academic documents, proof of residence and other important information.
Step 4: Review the Application Form
Before you submit, check that you have entered the right details. Review the information and the documents.
Step 5: Submit the Application Form
Click on the option to submit the form and you will be directed to the payment page.
Step 6: Pay the Examination Fee
Male, general or OBC candidates will have to pay an examination fee of Rs. 100. Female candidates, ex-servicemen, or candidates belonging to SC, ST, or PwD categories do not have to pay any fee.
You can pay online through the SBI portal or visit any SBI branch to pay offline.
Step 7: Receive Confirmation and Other Information
Once you have paid, you will receive confirmation. If you are eligible, you will get the admit card before the date of the examination.
SSC Exam Pattern
The exam pattern for SSC has been provided below. Recruitment to the post of SSC CGL, CHSL, GD Constable, JE, MTS, and CPO has been mentioned in these tables. SSC exam difficulty level of the online exam will vary from one post to another.
SSC CGL Exam Pattern
The Staff Selection Commission conducts the CGL (Combined Graduate Level) exams in four tiers. The first two-tier exams are conducted in the online mode while the SSC CGL Tier-III exam is conducted in pen-paper mode while the Tier-IV exam will be conducted as a Computer Skill Test.
| Examination | Details |
| Tier I |
|
| Tier II |
|
| Tier III |
|
| Tier IV |
|
You can check CGL notifications for information on the various posts that come under this level.
SSC GD Exam Pattern
SSC GD Constable exam pattern has been divided into the following sections which are – Computer Based Test, Physical Efficiency Test, Physical Standard Test, Medical Test
| Examination | Details |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 |
|
| Stage 3 |
|
The SSC GD examination is for recruitment for various paramilitary forces like the CRPF, BSF, CISF, SSB, ITBP, or SSF.
SSC CHSL Exam Pattern
SSC CHSL exam will be conducted through three tiers which are – Tier one for online test, Tier two for Pen-paper based test and Tier three for Computer Skill Test.
| Examination | Details |
| Tier I |
|
| Tier II |
|
| Tier III |
|
CHSL notifications will offer information on recruitment for the post of:
- Postal or Sorting Assistant
- Lower Divisional Clerk (LDC)
- Data Entry Operator (DEO)
- Court Clerk
SSC JE Exam Pattern
As per the SSC JE exam pattern, there will be two papers. SSC JE Paper-1 will only have objective type questions while Paper-2 will have written and subjective type questions.
| Examination | Details |
| Paper 1 | Computer-based examination (200 marks, negative marking of 0.25 applicable for each wrong answer) |
| Paper 2 | Written test (300 marks) |
You can check JE notifications for more information on the recruitment of junior engineers for non-gazetted Group B posts.
SSC CPO Exam Pattern
Get the complete details about the SSC CPO exam pattern from the below-provided table.
| Examination | Details |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 | Physical standard test or a physical endurance test |
| Stage 3 | Paper 2: English comprehension test |
| Stage 4 | Medical check-up |
The SSC CPO examination is for candidates who want to work in the Central Police Force. You can take a look at the CAPF notifications for more information.
SSC MTS Exam Pattern
SSC MTS exam pattern is divided into two papers such as Paper 1 and 2. Paper -1 is divided into 4 sections which are Reasoning Ability, English Language, Numerical Ability and General Awareness. Paper-2 will be the descriptive type.
| Examination | Details |
| Paper 1 | Online examination (100 multiple choice questions) |
| Paper 2 |
|
Check MTS notifications for details about recruitment for posts of
- Peon
- Daftary
- Jamadar
- Gardener
- Junior Gestetner Operator
SSC Stenographer ‘C’ and ‘D’ Exam Pattern
Check the exam pattern for SSC Stenographer from below mentioned table-
| Examination | Details |
| Stage 1 | Computer-based examination (200 questions, one mark each) |
| Stage 2 | Skills test |
These are non-gazetted posts and you can find more information on Stenographer C and D notifications.
SSC JHT Exam Pattern
SSC JHT Exam pattern is divided into two papers. Paper-1 will be the online computer-based test while Paper-2 is conducted in offline mode.
| Examination | Details |
| Paper 1 | Computer-based examination (100 objective type questions) |
| Paper 2 |
|
JHT notifications will guide you through the process and provide details about the recruitment of Hindi translators in different ministries and departments of the government.
SSC Eligibility Criteria
The most common SSC eligibility criteria for the exams are educational qualification, age limits and citizenship. The SSC exam age limit for most of the exams is a minimum of 18 years to a maximum of 32 years.
Let’s check the complete SSC Eligibility Criteria one by one for all exams –
| Exam | Eligibility Criteria |
| SSC CGL – Combined Graduate Level |
|
| SSC GD – Constable, General Duty |
|
| SSC CHSL – Combined Higher Secondary Level |
|
| SSC JE – Junior Engineer |
|
| SSC CPO – Central Police Organisation |
|
| SSC MTS – Multitasking Staff |
|
| SSC Stenographer ‘C’ and ‘D’ |
|
| SSC JHT – Junior Hindi Translator |
|
SSC Exams Dates (2021-22)
| Examination | Date of Application Form Release | Last Date for Application Form Submission | Date of Examination |
| SSC CGL – Combined Graduate Level | December 23, 2021 | January 23, 2021 | April, 2022 |
| SSC GD – Constable, General Duty | February 22, 2023 | March 31, 2023 | June, 2023 |
| SSC CHSL – Combined Higher Secondary Level | February 1, 2022 | March 7, 2022 | May, 2022 |
| SSC JE – Junior Engineer | November 28, 2022 | December 27, 2022 | March, 2023 |
| SSC CPO – Central Police Organisation | August, 2022 | September, 2022 | December, 2022 |
| SSC MTS – Multitasking Staff | March 22, 2022 | April 30, 2022 | June 2022 |
| SSC Stenographer ‘C’ and ‘D’ | December 5, 2022 | December 31, 2022 | April, 2023 |
| SSC JHT – Junior Hindi Translator | August 22, 2022 | September 21, 2022 | December, 2022 |
*Dates are tentative and can change due to unforeseen conditions.
Syllabus for SSC Exams
The staff selection commission sets the syllabus for all the SSC exams. Its goal is to provide clarity to the candidates who are appearing for the exams. In the time span of a few years, SSC keeps changing the syllabus so for that the candidates need to be prepared for it. Here on this page, we have mentioned the SSC exam syllabus for your reference –
SSC CGL Syllabus
Here the candidates can check the tier-wise syllabus for SSC CGL exam-
| Examination | Syllabus |
| Tier I |
|
| Tier II |
|
| Tier III |
|
| Tier IV |
|
SSC GD Syllabus
Here through this table, the candidates can check the SSC GD syllabus. It is important for the candidates to have a clear understanding of the SSC GD syllabus if they are appearing for the exam-
| Examination | Syllabus |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 |
For candidates from Ladakh:
|
| Stage 3 |
|
SSC CHSL Syllabus
Check the detailed syllabus for SSC CHSL below mentioned table. To ace the exam and get the job of your dream, do not miss out on anything from the SSC CHSL syllabus while doing your preparation of the exam-
| Examination | Syllabus |
| Tier I |
|
| Tier II |
|
| Tier III |
Visually handicapped candidates who are 40% disabled, are given 30 minutes to complete the test. |
SSC JE Syllabus
The candidates who are appearing for the Junior Engineer exam should refer to the following syllabus for reference. Get a clear understanding of the SSC JE syllabus and plan your preparation accordingly-
| Examination | Syllabus |
| Paper 1 |
|
| Paper 2 |
Candidates need to select any one part. |
SSC CPO Syllabus
The syllabus for SSC CPO for three stages is given below.
| Examination | Syllabus |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 | For male candidates:
For female candidates:
|
| Stage 3 |
|
| Stage 4 | Medical check-up |
SSC MTS Syllabus
SSC MTS syllabus consists of two tiers. The candidates must clear all the stages in order to get selected for the SSC MTS.
| Examination | Details |
| Paper 1 |
|
| Paper 2 |
|
SSC Stenographer ‘C’ and ‘D’ Syllabus
Get the detailed syllabus for SSC Stenographer below-
| Examination | Details |
| Stage 1 |
|
| Stage 2 |
|
SSC JHT Syllabus
Here we have mentioned the SSC JHT syllabus for both the papers.
| Examination | Details |
| Paper 1 |
|
| Paper 2 |
|
How to Prepare for SSC Exam
-
Enrol in an Online Class
Unacademy offers several classes for SSC exam preparation. You can check the syllabus of each class and then enrol in one. Learning from a top educator and interacting with your peers will help you understand different topics better and encourage you to study more. You can access questions and attend numerous online classes at Unacademy to prepare. There are classes for specific papers as well as for the whole syllabus for particular SSC exams.
-
Read the Reviews from Previous Learners at Unacademy
Previous Learners at Unacademy leave reviews of their experiences. You can read these and then decide on a class. The reviews will also give you a clear idea of how these classes can benefit you and which class you should enrol in. You can also get information on each of the educators and choose the person who will be able to guide you. This will help you kickstart your preparation and stay focused.
-
Interact with the Educators
When you are preparing for your examination, you are likely to have doubts. It is important to address these doubts and clear them. The best way to do that is by interacting with the educators. Use live learning sessions to talk to the educators and ask questions. There will be doubt clearing sessions as well. Interact with your teachers and learn through discussions. You will not only understand concepts better but also remember them longer.
-
Manage Your Time Well
Time management is one of the most important aspects of proper exam preparation. Check how much time you will have for each paper and solve questions. This will allow you to understand how long you are taking to complete a paper. If you find that you are spending too much time on certain questions, you can work on understanding those concepts better so that you can answer promptly.
Tips to Crack SSC Exams
-
Study the Entire Syllabus
You need to know the whole syllabus for the SSC exams before you start preparing. Find out the details of each paper and ensure that you have enough time to study the entire syllabus. You can focus on difficult topics before moving on to easier ones.
-
Learn the Exam Pattern
It is crucial to know the exam pattern. The exam pattern will give you a fair idea of what you need to study and which topics may not be that important. You can also judge which sections you need to do well on to pass with good marks. Knowing the exam pattern will also help you pace yourself and finish the paper on time.
-
Look at Previous Questions
To understand what questions may be given, study the previous years’ papers. You may find some common questions. Usually, these topics are the most important ones and therefore, questions are often repeated. Practice these answers as much as you can. You also need to study the other questions so that you have a fair idea of how your paper will be.
-
Study for All Papers
When you are taking a particular SSC examination, you need to prepare for all papers or stages. If there is more than one written test, prepare for it all. You cannot crack the examination unless you pass each paper. So you need to study for each paper of the exam.
-
Seek Assistance from Tutors
You might not find all topics easy. But there is no need to worry. You can always enrol in Unacademy’s online classes and train for specific subjects or papers. Seek assistance from reputed educators and experienced teachers at Unacademy, and they will guide you.
SSC Study Material
While preparing for the SSC exams, the candidates need to be well versed with the SSC Study Material. Referring to the correct books, study notes and mock banks play an important role in your preparation. So choose wisely the preparation for the SSC exams –
| World History | Indian Geography |
| Indian Polity and Constitution | General Awareness |
| Indian Economy | Mathematics |
| Indian History | Alphabet Test |
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






