There exists a global address for all locations on the planet. Individuals can converse about place regardless of what dialect they understand since the address seems to be in numbers. The coordinates of a geographical address are two digits. A place’s longitude and latitude are represented by these two digits.
Un-projected or Geographic refers to how we define the Earth using spherical coordinates. “Latitudes” and “Longitudes” are the most often used systems for finding places on Earth. Latitude and longitude are both angles that are determined using the earth’s centre as the base. Longitude is defined as an angle calculated to the east as from the prime meridian. Latitude is defined as the angle measured upwards towards the equator.
Longitude & Latitude
- The angle produced by lines running from the axis of the earth towards the equator at the position on the equator closest to the point of focus as well as another line running from the centre of the globe to the parallel lines that run across the point of interest is referred to as the latitude.
- The longitude is basically the angle produced by lines that pass from the equator and the axis of the earth, as well as another line passing across the earth’s centre, the meridian, and the equator passing over the point of interest.
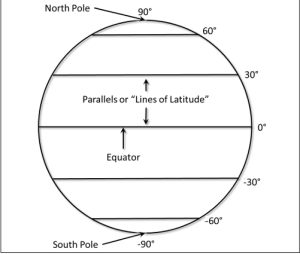
Everything About Latitudes
- The equator seems to be a fictitious or imaginary line that runs across the earth, dividing the latitude into 2 equal sections.
- The Northern Hemisphere refers to the northernmost part of the globe, whereas the Southern Hemisphere refers to the southernmost part.
- Latitude parallels are referred to as parallel circles that go across the equator toward the poles.
- They are expressed in degrees.
- The equator denotes 0 degrees latitude.
- The length between the equator to each pole is approximately one-fourth of a full circle around the planet, which equals one-fourth of 360 °, or 90°. Hence, 90 ° northern latitude corresponds to the north pole, while 90 ° southern latitude corresponds to the south pole.
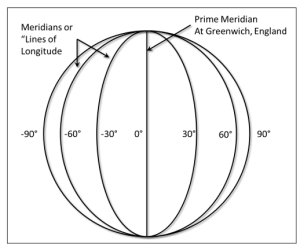
Everything About Longitudes
- The meridian that runs through Greenwich is called the prime meridian.
- It has a value of 0° longitude and thus, may be used to calculate 180° west and 180° east.
- The 180° meridian and the prime meridian split the globe into 2 components, the Western and Eastern Hemispheres.
Time Period and Longitudes –
- The motion of the planets, moon and earth is the greatest way to measure time. Daily, the sun appears as well as sets at the same time.
- Whenever the sun will be at its greatest position on the prime meridian near Greenwich, every point along this particular meridian would have noon.
- As the planet spins from west to east, areas east to Greenwich would be forward of GMT, while the ones west to Greenwich would be below it.
- It may be computed as follows: the globe rotates 360° in around 24 hours, that approximately equates to 15° each hour and otherwise 1° every four minutes.
Earth’s Heat Zones
- Torrid Zone –
- The afternoon sun lies directly above at minimum once every year on every latitude between the Tropics of Capricorn and Cancer.
- As a result, the torrid zone gets the greatest amount of heat.
- Frigid Zones –
- Frigid Zones are classified into two categories. The frigid zone throughout the north is defined as the region ranging from the Arctic circle to the north pole, whereas the frigid zone towards the south is defined as the region ranging from the Antarctic circle to the south pole.
- These zones are bordered by the polar darkness as well as the midnight sun. The Frigid Zones are considered to be the world’s coldest areas, generally covered with ice and snow. Since these regions are the furthest away in comparison to the equator, they get slanted solar beams.
- Temperate Zones –
- The afternoon sun never beams above almost any latitude other than the Tropics of Capricorn and Cancer.
- As one moves closer to both the south and north poles, the elevation of the sun’s beams decreases.
- The temperate zones, therefore, have mild temperatures.
Conclusion
Longitude and latitude are coordinate systems that may be used to identify and represent the location or position of every point on the planet. On a map or globe, latitude is a calculation of position south or north of the equator.
Longitude is a calculation of distance west or east of the prime meridian at London, Greenwich, which is a specifically defined fictitious north-south line running via both the south as well as north poles and Greenwich, London.
The intersection of latitude parallels and longitude meridians creates a framework or pattern from which exact coordinates in relation to the equator and the prime meridian may be established.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out