Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium chloride is a naturally occurring inorganic chemical with a wide range of applications in industry and medicine, as well as being an important mineral for humans.
Magnesium chloride is a salt that is extremely soluble in water and is typical of ionic halides. This chemical is available in two forms: anhydrous and numerous hydrated crystals.
Magnesium tends to give up two electrons during the interaction between magnesium and chlorine. It has a +2 charge. Chlorine, on the other hand, is willing to accept one electron, giving it a charge of -1.
To complete the octet, two chlorine atoms are required to take the two electrons from magnesium. When this occurs, the total charge is zero. As a result, MgCl2 is the chemical formula for magnesium chloride.
Formula – MgCl2
Molar Mass – 95.211 g/mol
Density – 2.32 g/cm³
Melting Point – 714 °C
Boiling Point – 1,412 °C
Occurrence
Magnesium concentrations in natural seawater range between 1250 and 1350 mg/l, accounting for around 3.7 percent of total mineral content. The magnesium chloride ratio in Dead Sea minerals is substantially higher, at 50.8 percent.
Applications of Magnesium Chloride are as follows:
- Magnesium chloride is an important chemical for preventing wind erosion, controlling dust, and stabilizing soil. In addition, magnesium chloride is applied to bare soil regions and highways.
- In the production of polyolefins, Ziegler-Natta catalysts are crucial. Magnesium chloride is used as a catalytic support in these catalysts. Magnesium chloride, above all, supports and improves the classic catalyst’s action. Additionally, it permits the fabrication of extremely stereospecific polypropylene catalysts.
- Magnesium chloride is used by experts to de-ice sidewalks, parking lots, and highways at low temperatures. Icy conditions on the highways can be quite dangerous. Magnesium chloride helps to minimize ice bonding in such situations, allowing snow ploughs to clean the roadways more quickly.
- Magnesium chloride is used to prevent pavement ice in three ways: anti-icing, pre-wetting, and pretreating. Anti-icing refers to the application of magnesium chloride to roads prior to a snowstorm to prevent snow from adhering and forming ice.
- When salt is spread onto the pavement, it is pre-wetted by spraying a liquid formulation of magnesium chloride straight onto it. Furthermore, pre-watering involves soaking the salt to ensure that it adheres to the road. Finally, salt and magnesium chloride are mixed together before being put into trucks and spread on paved roads, which is known as pre-treating.
Structural Formula
The structural formula of magnesium chloride is represented as:
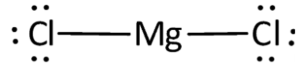
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




