Heron’s formula (also known as Hero’s formula) gives the area of a triangle when the lengths of all three sides are known in geometry. It is named after Hero of Alexandria. Unlike previous triangle area formulas, no angles or other distances in the triangle must be calculated first.
It’s used to calculate the area of various triangles, including equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles, as well as quadrilaterals. When the sides of a triangle are known, we may apply Heron’s formula to calculate the area. The area of the triangle is calculated using Heron’s formula with the triangle’s semi-perimeter and side lengths.
Definition:-
When the lengths of all of a triangle’s sides are known, Heron’s formula is used to find the area of the triangle, as well as the area of quadrilaterals. Hero’s formula is another name for it. This formula for calculating the area of a triangle is independent of the triangle’s angles. It is totally determined by the lengths of all triangle sides. It bears the letter “s,” which stands for semi-perimeter, which is obtained by halves a triangle’s perimeter. Similarly, the principle of determining the area is extended to determine the area of quadrilaterals.
History of Heron’s Formula:-
Heron of Alexandria penned Heron’s formula about 60 CE. He was a Greek engineer and mathematician who calculated the area of a triangle using only the lengths of its sides and went on to calculate the areas of quadrilaterals using the same method. This formula was used to prove trigonometric laws such as the Laws of Cosines and the Laws of Cotangents.
Mathematical Statement:-
According to Heron’s formula, the area of any triangle having lengths a, b, c, and ‘s’ as semi-perimeter of the triangle is determined using the below-given formula:
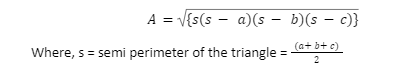
Triangle’s Area According to Heron’s Formula:-
The following are the steps to use Heron’s formula to calculate the area:
- Calculate the perimeter of the triangle.
- Halve the perimeter to find the semi-perimeter.
- Using Heron’s formula √{s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)}, calculate the triangle’s area.
- After you’ve determined the value, write the unit at the end (For example, m², cm², or in²).
Area of Equilateral Triangle by Heron Formula:-
All of the sides of an equilateral triangle are the same length. As a result, the lengths of all sides are equal in this example. Assume that the length of all sides is “a,” the semi-perimeter is “s,” and the equilateral triangle’s area is “A.” As a result, the triangle’s semi-perimeter is s=a+ a+ a ⁄ 2=3a ⁄ 2 .
So area of the equilateral triangle is determined by;
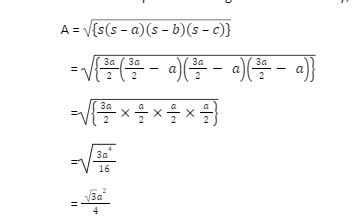
Important notes on Heron’s Formula:-
- When all of a triangle’s sides are known, Heron’s formula is used to calculate its area.
- By dividing the quadrilateral into two triangles, we can apply Heron’s formula to get the area.
- The triangle’s semi-perimeter and side lengths are used in the formula.
Application of Heron’s Formula:-
Heron’s formula can be used in a variety of situations. They are as follows:
- If the lengths of the different sides of a triangle are known, it can be used to calculate their area.
- If the lengths of all of the quadrilateral’s sides are known, it can be used to calculate its area.
- The area of any irregular quadrilateral can be calculated using Heron’s formula by turning the quadrilateral into triangles.
Conclusion:
Heron’s formula is a formula for calculating the area of a triangle in terms of the lengths of its sides that is credited to Heron of Alexandria (c. 62 CE). If the lengths of the sides are a, b, and c in symbols, then:
A = √{(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)} , where s is half the perimeter, or (a + b + c)/2.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






