Every object has an interior structure that determines the object’s shape. A building, for instance, is only constructed once the structure of the building has been established. Furthermore, the human skeleton is the body’s internal framework. The mass and muscles of a human body begin to build on this skeleton. In this post, we’ll go through the function of the skeleton system of the human body and the classification of bones in great detail.
Skeleton System of Human Body
The skeleton system of the human body, often known as the skeleton, is the total number of bones that come together (via joints). The structure enables the body’s support, protection, and shaping, allowing for more effortless movement. Multiple cells, minerals, plus protein fibres make up each bone. We wouldn’t be able to do daily activities, including standing, sitting, or walking, if we didn’t have a skeleton. It also safeguards our body’s sensitive tissues and internal organs. The skull, for example, shields and covers the brain, which is quite fragile, and the ribs protect the lungs and heart. When it comes to the number of bones in the human body, it’s important to remember that even a newborn baby has roughly 300 bones as well as an adult’s skeletal system has 206 bones as these fuse as we grow older; the skeletal system then includes various cartilage plus ligaments.
What are Main Function of Skeletal System
- The human skeletal system is responsible for six primary activities in our body: protection, movement, support, mineral storage, blood cell formation, or endocrine regulation. We’ll study more about the functions of each type of bone that makes up the skeletal system. The Skeletal System is divided into two parts: the skeleton and the skeletal system. The Axial Skeletal System: The skull, spine, and rib cage are all part of it. The Appendicular Skeletal System: The appendages or girdles, particularly the pelvic girdle bones, were connected to the axial skeleton.
- The skeletal system of the human body allows the body and individual body parts to move. The bones act as both levers and joints, allowing muscles to pull on them and move the joints.
- The function of the skeletal system does not act as a liver but works as a whole system supporting the body and serves as a structure for connecting muscles and tissues.
- The function of the appendicular skeletal system is to protect internal organs, which helps in reducing the possibility of injury following a collision.
- The axial skeletal system helps maintain the correct posture and balance of the human body.
Classification of Bones
Let’s take a closer look at the bones in the human body —
Flat Bones
Because of their flat shape, we call them flat bones. The skull, thoracic cage, and pelvis are all flat bones. They also safeguard interior organs such as the brain, pelvic organs, and heart. They also have a relatively flat surface that acts as a protective shield. They also give a vast surface area for a muscle to adhere to.
Long Bones that Help with Movement or Support Weight
They have a shape that is longer than it is wide. The femur is also included (the longest bone in the body). The femur is crucial because it accounts for a fourth of your height and is as sturdy as concrete. Furthermore, longer bones sustain the body’s weight or movement. The bones of the lower limbs and the upper limbs were primarily found in the appendicular skeleton (Hand).
Short Bones
These bones were long and broad in proportion. We can also find them in the ankle or wrist joints. In contrast, short bones give the body some strength or flexibility. In addition, short bones include the carpals of the wrist and even the tarsals of the ankle.
Irregular Bones
According to their shape and structure, these bones have a complex shape and do not fit into other bones in the human body. They are notable for having a more complex shape than just about any other bone in the body, which helps protect internal organs.
The vertebral column, for instance, is awkwardly formed but protects the spinal cord. In addition, the pelvic bone’s uneven shape shields the pelvic cavity’s organs.
Sesamoid Bones Reinforce Tendons
These are the bones that connect the tendons to the muscles. Furthermore, these tiny, spherical bones are commonly seen in the tendons of the keens, feet, or hands. Additionally, they help to protect the tendons against wearing and strain. The patella, which we typically refer to as the kneecap, is a sesamoid bone.
Suggestions For Maintaining a Healthy Skeleton System of Human Body
- In addition to other crucial roles, the skeletal system serves as the basis for all body movements.
- To keep it in efficient working order, follow these guidelines:
- Calcium should be consumed.
- Leafy green vegetables, broccoli, tofu, and salmon are all calcium-rich foods.
- Make sure you get enough vitamin D.
- Most individuals obtain enough of this by spending time outside regularly, but those who live in locations where sunlight is scarce can benefit from a vitamin D supplement.
- Weight-bearing workouts should be done.
- Walking, jogging, or climbing stairs are examples of these activities.
- Wear eye and ear protection
- To minimise bone fractures and other potentially serious injuries, always use protective gear whether riding a bike or participating in competitive sports
Conclusion
The skeletal system is a complex system of interconnected parts that help you move. Your bones, which are complex elements that form your body’s framework — the skeleton — are the most crucial aspect of your skeletal system. An adult human skeleton contains 206 bones. Now you have all the necessary information about the function of the skeleton system of the human body and classification of bones for better understanding, and you must read this information as mentioned above correctly.
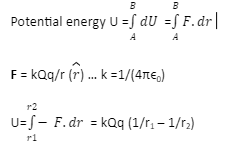
- What is the meaning of a reference point?
The point at which the electric potential can be considered as equal to zero is called the reference point. For a system of two charges when the second charge q in the electric field of Q, is displaced from point A at r1 to point B at r2; potential energy of the system of two charges is given by, U= kQq (1/r2 – 1/r1)
If we consider the initial distance r1= as the reference point then we get potential energy U = kQq (1/r2).
- What are the units of Electric Potential energy?
The SI unit of Electric potential energy is the same as that of energy, which is Joule (J).
Another unit of measurement is electron Volt (eV).
1ev = 1.6 x 10-19 joule.
- What is the meaning of Electric Potential or what is the difference between electric potential and electric potential energy?
Electric potential energy is defined as the amount of work done to displace a charge from one point to another point against the electrostatic force field.
Electric potential can be defined in terms of electric potential energy as equivalent to the work done to displace unit positive charge from one point to another point against the electrostatic field. Thus, electric potential is equal to electric potential energy per unit charge.
Therefore, Electric Potential (V) = Electric Potential energy (U) / charge (q)
This expression gives the relation between electric potential and electric potential energy.
- What is the SI unit of Electric Potential?
Electric Potential (V) = Electric Potential energy (U) / charge (q)
SI unit of Electric Potential energy (U) is joule (J), charge (q) = Coulomb (C)
Thus, the SI unit of Electric Potential is Joule/C or Volt.
- How is potential energy calculated for a system of N charges?
For a charge q brought from infinity (point of reference) to a point (at position r) in presence of another charge q1 the potential energy is given as U1 = kq1q/r. In case of a system of charge, work done or potential energy obeys the principle of superposition. Hence the total potential energy is given as the sum of potential energy between the charges present in the system.
- Why is the Electrostatic potential energy path independent?
Electrostatic field is a conservative field. That is electrostatic force law obeys inverse square law, thus the electrostatic force is a conservative force. Potential energy in consideration with the electrostatic field is defined as the work done against the electrostatic force. That is U =F.dr. Since the force field is conservative work done/ potential energy over a closed path is zero. This implies that electrostatic potential energy / work done is path independent. It depends on the initial and final position only.
- What is the expression for electrostatic potential due to a point charge?
Electric Potential (V) = Electric Potential energy (U) / charge (q)
For a unit positive charge, V = U = kQ/r. This is the expression for Electric potential due to a point charge Q at a distance r from the charge.
Conclusion
Electrostatic potential energy is considered in respect to the Electrostatic field. Word done is stored as potential energy. When this work is done to displace a charged particle in the presence of an electric field, it is stored as electrostatic potential energy.
The SI unit of electric potential energy is joule.
The electric potential is defined in terms of electrostatic potential energy. Electric potential is defined as electric potential energy per unit charge i.e. work done to displace unit charge. SI unit of electric potential is joule/C.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



